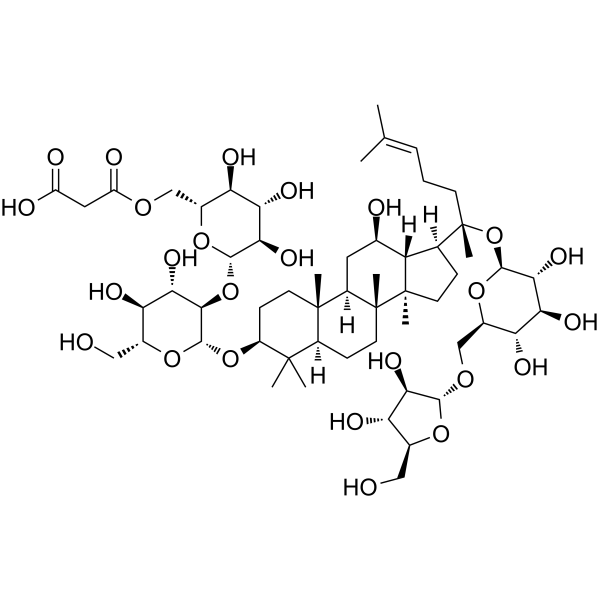
Ginsenoside Rc
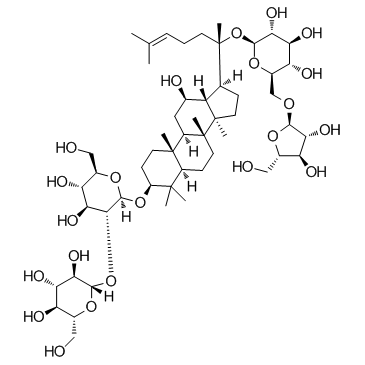
Ginsenoside Rc structure
|
Common Name | Ginsenoside Rc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 11021-14-0 | Molecular Weight | 1079.269 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1128.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C53H90O22 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 636.2±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Ginsenoside RcGinsenoside Rc, one of major Ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, enhances GABA receptorA (GABAA)-mediated ion channel currents (IGABA). Ginsenoside Rc inhibits the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β. |
| Name | ginsenoside Rc |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ginsenoside Rc, one of major Ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, enhances GABA receptorA (GABAA)-mediated ion channel currents (IGABA). Ginsenoside Rc inhibits the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
GABA Receptor TNF-α IL-1β |
| In Vitro | Ginsenoside Rc, one of major Ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, enhances γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptorA (GABAA)-mediated ion channel currents. Ginsenoside Rc enhances GABA-mediated ion currents in oocytes expressing the GABAA receptor[1]. Ginsenoside Rc significantly inhibits the expression of macrophage-derived cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β. Ginsenoside Rc also markedly suppresses the activation of TANK-binding kinase 1/IκB kinase ε/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2 signaling in activated RAW264.7 macrophages, human synovial cells, and HEK293 cells. Ginsenoside Rc exerts its anti-inflammatory actions by suppressing TANK-binding kinase 1/IκB kinase ε/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2 signaling. Ginsenoside Rc suppresses the nuclear translocation of phospho-ATF-2 and phospho-FRA-1, whereas the translocation of p65 at its peak time points (30 and 60 min) is not decreased by Ginsenoside Rc treatment. Ginsenoside Rc regulates the expression of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α, which is produced by macrophages, by suppressing AP-1 activation[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | To evaluate the effects of Ginsenoside Rc on kinase activity, immunoprecipitated TBK1, IKKε, and p38 are incubated in reaction buffer in the presence or absence of Ginsenoside Rc. The reactions are initiated by the addition of Mg-ATP. After a 30 min incubation at 30°C, the reactions are stopped by the addition of sample buffer and the samples are boiled. Kinase activity is assessed by immunoblotting with antibodies against the phospho-forms of IKKε, IRF-3, and ATF-2[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1128.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C53H90O22 |
| Molecular Weight | 1079.269 |
| Flash Point | 636.2±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 1078.592407 |
| PSA | 357.06000 |
| LogP | 5.10 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.622 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LY9536300 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rc CAS#:11021-14-0 |
| Literature: Kitagawa; Taniyama; Yoshikawa; Ikenishi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1989 , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
Ginsenoside Rc CAS#:11021-14-0 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
[A quantitative method using one marker for simultaneous assay of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng and P. notoginseng].
Yao Xue Xue Bao 43(12) , 1211-6, (2008) Current quality control patterns are limited to industrial application, for most of the natural chemical reference substances are expensive and unavailable. Herein, a method, quantitative analysis of ... |
|
|
Microbial transformation of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb3 and Rc by Fusarium sacchari.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 109(3) , 792-8, (2010) This study examined the transformation pathways of ginsenosides G-Rb(1) , G-Rb(3) , and G-Rc by the fungus Fusarium sacchari.Ginsenosides G-Rb(1) , G-Rb(3) and G-Rc were isolated from leaves of Radix ... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents of flower-buds of Panax ginseng--isolation and identification of ginsenoside-Rb3 and ginsenoside-Rc].
Zhong Yao Tong Bao 9(4) , 172-3, (1984)
|
| EINECS 234-253-5 |
| Ginsenoside Rc |
| (3β,12β)-20-{[6-O-(α-L-Arabinofuranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy}-12-hydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,12β)-20-[(6-O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-12-hydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl- |
| 20-((6-O-α-L-Arabinofuranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-12β-hydroxydammar-24-en-3β-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| MFCD00133368 |
| Ginsenoside-Rc from Panax ginseng (Korean ginseng) root |