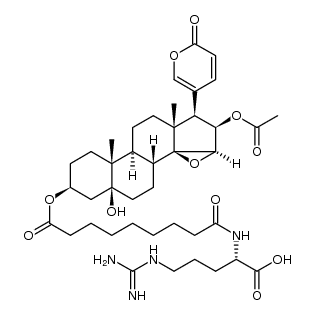
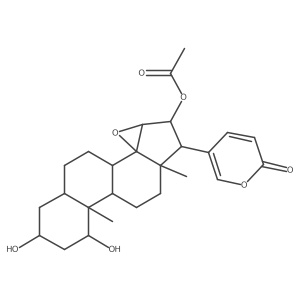
Cinobufotalin
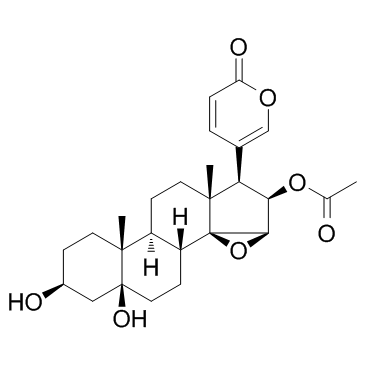
Cinobufotalin structure
|
Common Name | Cinobufotalin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1108-68-5 | Molecular Weight | 458.544 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 627.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H34O7 | Melting Point | 259 - 262ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 210.7±25.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CinobufotalinCinobufotalin is one of the bufadienolides prepared from toad venom; has anticancer activity.IC50 value:Target:in vitro: Cinobufotalin(CB) caused significant DNA fragmentation, decrease of MMP, and an increase in the intracellular Ca(2+) ion and ROS production. In addition, CB induced upregulation of Fas protein, proteolytic activation of cytochrome c, caspase-2, -3, -8 and -9 together with the activation of Bid and Bax [1]. cinobufotalin displayed considerable cytotoxicity against lung cancer cells (A549, H460 and HTB-58 lines) without inducing significant cell apoptosis. cinobufotalin mainly induces Cyp-D-dependent non-apoptotic death in cultured lung cancer cells [2]. cinobufotalin (at nmol/L) significantly inhibited HCC cell growth and survival while inducing considerable cell apoptosis. Further, cinobufotalin inhibited sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) activity and induced pro-apoptotic ceramide production. cinobufotalin inactivated Akt-S6K1 signaling in HepG2 cells, which was again inhibited by ceramide synthase-1 shRNA-depletion [3].in vivo: Using a mice xenograft model, we found that cinobufotalin inhibited A549 lung cancer cell growth in vivo [2]. |
| Name | Cinobufotalin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cinobufotalin is one of the bufadienolides prepared from toad venom; has anticancer activity.IC50 value:Target:in vitro: Cinobufotalin(CB) caused significant DNA fragmentation, decrease of MMP, and an increase in the intracellular Ca(2+) ion and ROS production. In addition, CB induced upregulation of Fas protein, proteolytic activation of cytochrome c, caspase-2, -3, -8 and -9 together with the activation of Bid and Bax [1]. cinobufotalin displayed considerable cytotoxicity against lung cancer cells (A549, H460 and HTB-58 lines) without inducing significant cell apoptosis. cinobufotalin mainly induces Cyp-D-dependent non-apoptotic death in cultured lung cancer cells [2]. cinobufotalin (at nmol/L) significantly inhibited HCC cell growth and survival while inducing considerable cell apoptosis. Further, cinobufotalin inhibited sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) activity and induced pro-apoptotic ceramide production. cinobufotalin inactivated Akt-S6K1 signaling in HepG2 cells, which was again inhibited by ceramide synthase-1 shRNA-depletion [3].in vivo: Using a mice xenograft model, we found that cinobufotalin inhibited A549 lung cancer cell growth in vivo [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 627.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 259 - 262ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C26H34O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 458.544 |
| Flash Point | 210.7±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 458.230438 |
| PSA | 109.50000 |
| LogP | 0.79 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.612 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300-H310-H330 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P284-P302 + P350-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R26/27/28 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | EI2991000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
~% 
Cinobufotalin CAS#:1108-68-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Asian Natural Products Research, , vol. 12, # 9 p. 793 - 800 |
|
~% 
Cinobufotalin CAS#:1108-68-5 |
| Literature: Drug Metabolism and Disposition, , vol. 39, # 4 p. 675 - 682 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Pre-clinical evaluation of cinobufotalin as a potential anti-lung cancer agent.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 452(3) , 768-74, (2014) Lung cancer is a major cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States and around the world. Due to the pre-existing or acquired chemo-resistance, the current standard chemotherapy regimens onl... |
|
|
Ceramide production mediates cinobufotalin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in cultured hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Tumour Biol. 36 , 5763-71, (2015) Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive and lethal neoplasm with poor prognosis. The aim of this study is to investigate the anticancer activity of cinobufotalin, a bufadienolide isolate... |
|
|
Comparative Analysis of the Bufonis Venenum by Using TLC, HPLC, and LC-MS for Different Extraction Methods.
J Pharmacopuncture 15 , 52-65, (2015) Toad venom, called Chan-Su, is a traditional Oriental medicine secreted from the auricular and the skin glands of the Bufo bufo gargarizanz Cantor or B. melanosticus Schneider and has been widely used... |
| 14,15b-Epoxy-3b,5a,16b-trihydroxy-5b,20(22)-bufadienolide 16-acetate |
| (3b,5b,15b,16b)-16-(Acetyloxy)-14,15-epoxy-3,5-dihydroxybufa-20,22-dienolide |
| MFCD00055946 |
| Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 16- (acetyloxy)-14,15-epoxy-3,5-dihydroxy-, (3β,5β,15β,16β)- |
| 5beta-Hydroxycinobufagin |
| 5β-Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 14,15β-epoxy-3β,5,16β-trihydroxy-, 16-acetate (8CI) |
| Bufa-20,22-dienolide, 16-(acetyloxy)-14,15-epoxy-3,5-dihydroxy-, (3β,5β,15β,16β)- |
| cinobufotalin venom toad |
| Cinobufotlin |
| 14,15-Epoxy-14H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene,bufa-20,22-dienolide deriv. |
| Cinobufotalin |
| CINOBUFOTALIN(RG) |
| cinobufatolin |
| (3β,5β,15β,16β)-16-Acetoxy-3,5-dihydroxy-14,15-epoxybufa-20,22-dienolide |
| 14,15b-Epoxy-3b,5,16b-trihydroxy-5b-bufa-20,22-dienolide 16-Acetate |