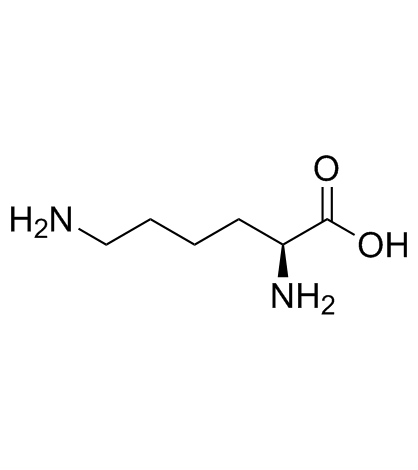
N6-Cbz-L-Lysine

N6-Cbz-L-Lysine structure
|
Common Name | N6-Cbz-L-Lysine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1155-64-2 | Molecular Weight | 280.320 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 499.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20N2O4 | Melting Point | 259ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 255.9±28.7 °C | |
Use of N6-Cbz-L-LysineH-Lys(Z)-OH is a lysine derivative[1]. |
| Name | N~6~-[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]-L-lysine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-Lys(Z)-OH is a lysine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 499.6±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 259ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 280.320 |
| Flash Point | 255.9±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 280.142303 |
| PSA | 101.65000 |
| LogP | 1.36 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.550 |
| InChIKey | CKGCFBNYQJDIGS-LBPRGKRZSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(CCCCNC(=O)OCc1ccccc1)C(=O)O |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Transfection of cells mediated by biodegradable polymer materials with surface-bound polyethyleneimine.
Biotechnol. Prog. 16 , 254-257, (2000) Poly(epsilon-CBZ-L-lysine) can be mixed with biodegradable polymers such as poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) or poly(L-lactic acid) and formed into films, foams, or microspheres. Surface amino groups... |
|
|
Production of microspheres with surface amino groups from blends of Poly(Lactide-co-glycolide) and Poly(epsilon-CBZ-L-lysine) and use for encapsulation.
Biotechnol. Prog. 15 , 763-767, (1999) Microspheres were formed from blends of the biodegradable polymer poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) together with poly(epsilon-CBZ-L-lysine) (PCBZL) by a double-emulsification/solvent evaporatio... |
|
|
Transformation of N epsilon-CBZ-L-lysine to CBZ-L-oxylysine using L-amino acid oxidase from Providencia alcalifaciens and L-2-hydroxy-isocaproate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus confusus.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37(5) , 599-603, (1992) Biotransformations were developed to oxidize N epsilon-carbobenzoxy(CBZ)-L-lysine and to reduce the product keto acid to L-CBZ-oxylysine. Lysyl oxidase (L-lysine: O2 oxidoreductase, EC 1.4.3.14) from ... |
| N(ε)-Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine |
| L-lysine, N-[hydroxy(phenylmethoxy)methylene]-, (E)- |
| 6-N-Cbz-L-lysine |
| N6-[(phenylmethoxy)carbonyl]-L-lysine |
| L-Lysine, N-[(phenylmethoxy)carbonyl]- |
| N-[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]-L-lysine |
| N6-(Benzyloxycarbonyl)-L-lysine |
| MFCD00002638 |
| N6-Carbobenzyloxy-L-lysine |
| Nepsilon-Carbobenzyloxy-L-lysine |
| LYSINE(Z)-OH |
| N6-Cbz-L-Lysine |
| EINECS 214-585-7 |
| LYS(Z) |
| Nε-Carbobenzoxy-L-lysine |
| Nε-Cbz-L-lysine |
| L-LYSINE(CBZ) |
| H-LYS(Z)-OH |
| H-LYS(CBZ)-OH |
| H-L-Lys(Z)-OH |
| (S)-N6-Benzyloxycarbonyllysine |
| L-Lys(Cbz)-OH |
| L-LYS(Z) |
 CAS#:56-87-1
CAS#:56-87-1 CAS#:501-53-1
CAS#:501-53-1 CAS#:657-27-2
CAS#:657-27-2 CAS#:42533-12-0
CAS#:42533-12-0 CAS#:57710-80-2
CAS#:57710-80-2 CAS#:405-39-0
CAS#:405-39-0 CAS#:62210-73-5
CAS#:62210-73-5 CAS#:6366-70-7
CAS#:6366-70-7 CAS#:19506-72-0
CAS#:19506-72-0 CAS#:39608-52-1
CAS#:39608-52-1![5-{[(Benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}pentanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/157/23135-50-4.png) CAS#:23135-50-4
CAS#:23135-50-4 CAS#:106412-35-5
CAS#:106412-35-5 CAS#:34235-82-0
CAS#:34235-82-0 CAS#:576-19-2
CAS#:576-19-2 CAS#:34622-39-4
CAS#:34622-39-4 CAS#:14609-04-2
CAS#:14609-04-2 CAS#:1946-80-1
CAS#:1946-80-1 CAS#:2756-89-0
CAS#:2756-89-0 CAS#:86060-82-4
CAS#:86060-82-4
