Adipic acid
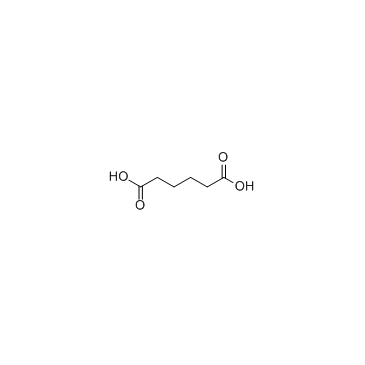
Adipic acid structure
|
Common Name | Adipic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 124-04-9 | Molecular Weight | 146.141 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 338.5±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O4 | Melting Point | 151-154 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 196 ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Adipic acidAdipic acid is found to be associated with HMG-CoA lyase deficiency, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency, and medium Chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, which are inborn errors of metabolism. |
| Name | Adipic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Adipic acid is found to be associated with HMG-CoA lyase deficiency, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency, and medium Chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, which are inborn errors of metabolism. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 338.5±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 151-154 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.141 |
| Flash Point | 196 ºC |
| Exact Mass | 146.057907 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | 0.08 |
| Vapour density | 5 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.476 |
| InChIKey | WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCCC(=O)O |
| Stability | Stable. Substances to be avoided include ammonia, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 1.44 g/100 mL (15 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 9077 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | AU8400000 |
| Hazard Class | 9.2 |
| HS Code | 2917120001 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2917120001 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2917120001 adipic acid Tax rebate rate:13.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue) , D603-10, (2009) The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB, http://www.hmdb.ca) is a richly annotated resource that is designed to address the broad needs of biochemists, clinical chemists, physicians, medical geneticists, ... |
|
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population.
Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994) Organic acid concentrations were quantified by gas chromatography and the individual acids identified by mass spectrometry in urine specimens from a healthy Turkish pediatric population of ages 2 days... |
|
|
Prediction of skeletal muscle and fat mass in patients with advanced cancer using a metabolomic approach.
J. Nutr. 142(1) , 14-21, (2012) Urine and plasma metabolites originate from endogenous metabolic pathways in different organs and exogenous sources (diet). Urine and plasma were obtained from advanced cancer patients and investigate... |
| Acifloctin |
| 1,6-Hexanedioic acid |
| Adilactetten |
| 1,4-Butanedicarboxylic acid |
| EINECS 204-673-3 |
| hexane-1,6-dicarboxylic acid |
| hexanedioic acid |
| Acinetten |
| Adipic acid |
| MFCD00004420 |
 CAS#:108-93-0
CAS#:108-93-0 CAS#:108-94-1
CAS#:108-94-1 CAS#:110-82-7
CAS#:110-82-7 CAS#:110-83-8
CAS#:110-83-8 CAS#:931-17-9
CAS#:931-17-9 CAS#:533-60-8
CAS#:533-60-8 CAS#:6338-43-8
CAS#:6338-43-8 CAS#:765-87-7
CAS#:765-87-7 CAS#:286-20-4
CAS#:286-20-4 CAS#:502-44-3
CAS#:502-44-3 CAS#:105-97-5
CAS#:105-97-5![Hexanedioic acid,1,6-bis[(tetrahydro-2-furanyl)methyl] ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/134/105-02-2.png) CAS#:105-02-2
CAS#:105-02-2 CAS#:1071-71-2
CAS#:1071-71-2 CAS#:108-63-4
CAS#:108-63-4 CAS#:4435-50-1
CAS#:4435-50-1 CAS#:3068-00-6
CAS#:3068-00-6 CAS#:107-21-1
CAS#:107-21-1 CAS#:542-32-5
CAS#:542-32-5 CAS#:3375-38-0
CAS#:3375-38-0
