diethylmaleate
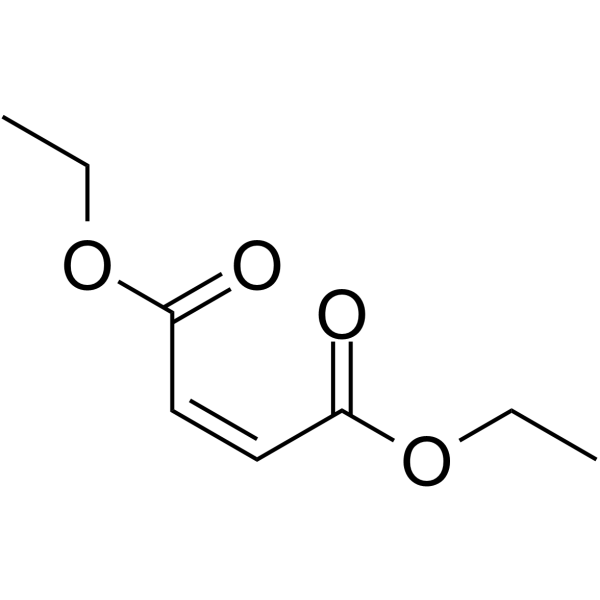
diethylmaleate structure
|
Common Name | diethylmaleate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 141-05-9 | Molecular Weight | 172.178 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 214.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12O4 | Melting Point | −10 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 93.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of diethylmaleateDiethyl maleate is a maleate ester resulting from the formal condensation of both carboxy groups of maleic acid with ethanol. Diethyl maleate (DEM), a thiol-reactive α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, depletes glutathione (GSH) in exposed cells[1]. |
| Name | diethyl maleate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diethyl maleate is a maleate ester resulting from the formal condensation of both carboxy groups of maleic acid with ethanol. Diethyl maleate (DEM), a thiol-reactive α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, depletes glutathione (GSH) in exposed cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 214.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | −10 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 172.178 |
| Flash Point | 93.3±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 172.073563 |
| PSA | 52.60000 |
| LogP | 1.68 |
| Vapour density | 5.93 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.443 |
| InChIKey | IEPRKVQEAMIZSS-WAYWQWQTSA-N |
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C=CC(=O)OCC |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, bases, acids, reducing agents. |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H319-H412 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R43 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S37-S24 |
| RIDADR | 3334 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | ON1225000 |
| HS Code | 29171990 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2917190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2917190090 acyclic polycarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Chlorantraniliprole susceptibility in Leptinotarsa decemlineata in the north Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region in China.
J. Econ. Entomol. 105(2) , 549-54, (2012) The Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say)) in the north Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region has evolved resistance to various types of insecticides. Chlorantraniliprole is a novel anthr... |
|
|
Phenobarbital induction and chemical synergism demonstrate the role of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in detoxification of naphthalophos by Haemonchus contortus larvae.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(12) , 7475-83, (2014) We used an enzyme induction approach to study the role of detoxification enzymes in the interaction of the anthelmintic compound naphthalophos with Haemonchus contortus larvae. Larvae were treated wit... |
|
|
Designing greener plasticizers: Effects of alkyl chain length and branching on the biodegradation of maleate based plasticizers.
Chemosphere 134 , 106-12, (2015) The ubiquitous presence of the plasticizer di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in the environment is of concern due to negative biological effects associated with it and its metabolites. In particular,... |
| cis-Diethyl maleate |
| MFCD00009191 |
| diethyl L-malic ester |
| Diethyl L-(-)-Malate |
| (S)-(-)-Aepfelsaeure-diethylester |
| cis-Propenoic acid diethyl ester |
| Maleic acid, diethyl ester |
| EINECS 205-451-9 |
| (S)-malic acid diethyl ester |
| diethylmaleate |
| 2-Butenedioic acid, diethyl ester, (2Z)- |
| Diethyl (2Z)-2-butenedioate |
| Diethyl (2Z)-but-2-enedioate |
| cis-EtO2CCH=CHCO2Et |
| L-(-)-Malic Acid Diethyl Ester |
| (S)-(-)-diethyl 2-hydroxybutandioate |
| diethyl (Z)-but-2-enedioate |
| diethyl (2Z)but-2-ene-1,4-dioate |
| 1,4-diethyl (2Z)-but-2-enedioate |
| 2-Butenedioic acid (2Z)-, diethyl ester |
| 2-Butenedioic acid (Z)-, diethyl ester |
| maleic acid diethyl ester |
| Ethyl Maleate |
| (2S)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid diethylester |
| Diethyl maleate |
| diethyl (S)-malate |
| (Z)-2-Butenedioic acid diethyl ester |
| Irsogladine Impurity 3 |
 CAS#:108-31-6
CAS#:108-31-6 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:762-42-5
CAS#:762-42-5 CAS#:623-73-4
CAS#:623-73-4 CAS#:292638-84-7
CAS#:292638-84-7 CAS#:98-83-9
CAS#:98-83-9![[o-((trimethylsilyl)methyl)benzyl]trimethylammonium chloride Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/260/73331-49-4.png) CAS#:73331-49-4
CAS#:73331-49-4 CAS#:608-82-2
CAS#:608-82-2 CAS#:872-05-9
CAS#:872-05-9 CAS#:710-43-0
CAS#:710-43-0 CAS#:3999-55-1
CAS#:3999-55-1 CAS#:3588-17-8
CAS#:3588-17-8 CAS#:4753-29-1
CAS#:4753-29-1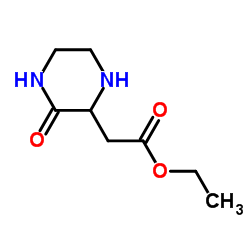 CAS#:33422-35-4
CAS#:33422-35-4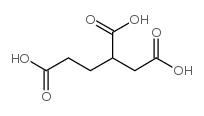 CAS#:923-42-2
CAS#:923-42-2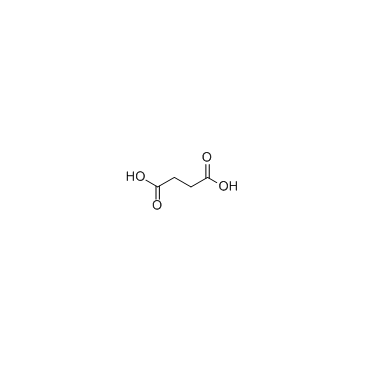 CAS#:110-15-6
CAS#:110-15-6 CAS#:924-44-7
CAS#:924-44-7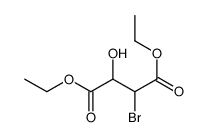 CAS#:188944-76-5
CAS#:188944-76-5 CAS#:192389-48-3
CAS#:192389-48-3
