HA-100 hydrochloride
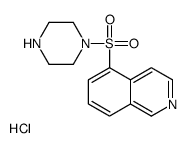
HA-100 hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | HA-100 hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 141543-63-7 | Molecular Weight | 313.80300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 497.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16ClN3O2S | Melting Point | 252-254ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 254.6ºC | |
Use of HA-100 hydrochlorideHA-100 hydrochloride is a potent protein kinase inhibitor, with IC50s of 4 μM, 8 μM, 12 μM and 240 μM for cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG), cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC) and MLC-kinase, respectively. HA-100 hydrochloride also used as a ROCK inhibitor[1][2]. |
| Name | 1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl)piperazine Hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | HA-100 hydrochloride is a potent protein kinase inhibitor, with IC50s of 4 μM, 8 μM, 12 μM and 240 μM for cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG), cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC) and MLC-kinase, respectively. HA-100 hydrochloride also used as a ROCK inhibitor[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PKG:4 μM (IC50) PKA:8 μM (IC50) PKC:12 μM (IC50) MLCK:240 μM (IC50) ROCK |
| In Vitro | HA-100 hydrochloride inhibits MLC-kinase and PKC competitively with respect to ATP, with Kis of 61 and 6.5 μM, respectively[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 497.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 252-254ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16ClN3O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 313.80300 |
| Flash Point | 254.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 313.06500 |
| PSA | 70.68000 |
| LogP | 2.97820 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~% 
HA-100 hydrochloride CAS#:141543-63-7 |
| Literature: Morikawa; Sone; Asano Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1992 , vol. 40, # 3 p. 770 - 773 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 5-piperazin-1-ylsulfonylisoquinoline,hydrochloride |