acetyl-dl-carnitine hydrochloride
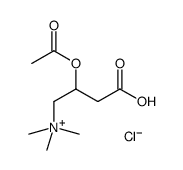
acetyl-dl-carnitine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | acetyl-dl-carnitine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2504-11-2 | Molecular Weight | 239.69700 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H18ClNO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of acetyl-dl-carnitine hydrochloride(±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride (Acetyl dl-carnitine chloride) is a weak cholinergic agonist with cholinergic properties. (±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride is an important intermediate in lipid metabolism[1][2]. |
| Name | (2-acetyloxy-3-carboxypropyl)-trimethylazanium,chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride (Acetyl dl-carnitine chloride) is a weak cholinergic agonist with cholinergic properties. (±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride is an important intermediate in lipid metabolism[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Large increases of Acetylcarnitine concentration during the flight of the blowfly and the presence of an active Acetylcarnitine transferase indicate that Acetylcarnitine is important in carbohydrate metabolism. Acetylcarnitine has been synthesized by the choline acetylase system isolated from brain tissue and is destroyed by cholinesterase[2]. |
| In Vivo | In rats, the infusion of 2 mg (±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride decreases blood flow through the hind limb vasculature 50%. (±)-Acetylcarnitine chloride also potentiates the inhibitory effect of adrenaline on the isolated rabbit duodenum[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C9H18ClNO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 239.69700 |
| Exact Mass | 239.09200 |
| PSA | 63.60000 |
| InChIKey | JATPLOXBFFRHDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC(CC(=O)O)C[N+](C)(C)C.[Cl-] |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BP2979200 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
In HepG2 cells, coexisting carnitine deficiency masks important indicators of marginal biotin deficiency.
J. Nutr. 145(1) , 32-40, (2015) A large number of birth defects are related to nutrient deficiencies; concern that biotin deficiency is teratogenic in humans is reasonable. Surprisingly, studies indicate that increased urinary 3-hyd... |
|
|
Sodium-dependent carnitine transport in human placental choriocarcinoma cells.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1284 , 109-117, (1996) The JAR human placental choriocarcinoma cells were found to transport carnitine into the intracellular space by a Na(+)-dependent process. The transport showed no requirement for anions. The Na+-depen... |
|
|
Photoaffinity labelling of carnitine acetyltransferase with S-(p-azidophenacyl)thiocarnitine.
Biochem. J. 237 , 533-540, (1986) A photolabile reagent, p-azidophenacyl-DL-thiocarnitine, was synthesized and tested as a photoaffinity label for carnitine acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.7) from pigeon breast. p-Azidophenacyl-DL-thiocar... |
| rac. Acetylcarnitinchlorid |
| Acetylcarnitin-chlorid |
| rac. Acetyl-carnithin |
| EINECS 219-709-3 |
| O-Acetylcarnitinhydrochlorid |
| Acetyl dl-carnitine chloride |
| MFCD00080826 |
| Evans Blue tetrasodium salt |
| Acetyl-DL-carnitine hydrochloride |
 CAS#:546-88-3
CAS#:546-88-3