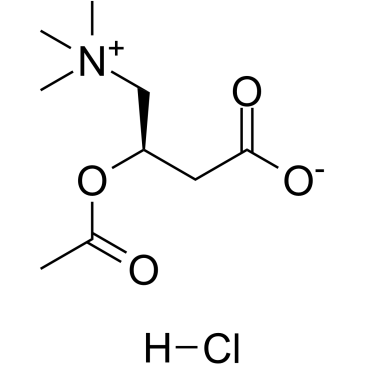
DL-Carnitine hydrochloride

DL-Carnitine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | DL-Carnitine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 461-05-2 | Molecular Weight | 197.660 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H16ClNO3 | Melting Point | 190-205ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DL-Carnitine hydrochloride(±)-Carnitine chloride exists in two isomers, known as D and L. L-carnitine plays an essential role in the β-oxidation of fatty acids and also shows antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. |
| Name | carnitinamide chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (±)-Carnitine chloride exists in two isomers, known as D and L. L-carnitine plays an essential role in the β-oxidation of fatty acids and also shows antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | The main role of L-carnitine is to shuttle long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane. After L-carnitine and acyl-CoA become acyl-carnitine by activation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase (CPT)-I, the transported acyl-carnitine is changed into acyl-CoA by CPT-II in the mitochondria matrix. Palmitoyl-CoA-induced mitochondrial respiration is increased by L-carnitine treatment, and then is accelerated by the presence of ADP. This acceleration is induced by treatment with L-carnitine in a concentration-dependent manner, and is saturated at 5 mM L-carnitine[1]. Pretreatment with L-carnitine augments Nrf2 nuclear translocation, DNA binding activity and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression in H2O2-treated HL7702 cells. L-carnitine protects HL7702 cells against H2O2-induced cell damage through Akt-mediated activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway[2]. |
| In Vivo | L-carnitine is found to down-regulate the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and increase IGF-1 concentrations in animal models. L-carnitine administration for 2 weeks of hindlimb suspension alleviates the decrease in weight and fiber size in the soleus muscle. In addition, L-carnitine suppresses atrogin-1 mRNA expression, which has been reported to play a pivotal role in muscle atrophy[3]. Simultaneous treatment with L-carnitine attenuates the renal fibrosis (which correlated with a reduction of plasma TGF-β1 levels) and the pro-oxidative and proinflammatory status reported in L-NAME groups, with a concomitant increase in the expression of PPAR-γ[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Mitochondria (0.6 mg protein/mL) are incubated in 2.5 mM Hepes (pH7.4) containing 225 mM mannitol, 75 mM sucrose and 100 μM ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA) with or without 5 mM L-carnitine at 25°C. To measure oxygen uptake, 10 min after inorganic phosphate (Pi) 4 mM are added, the mitochondria are treated with palmitoyl-CoA (50 μM) and then ADP is added (200 μM). Oligomycin (5 μM) and rotenone (10 μM) are added 3-4 min after the ADP treatment. HPG (0-10 mM), which can specifically inhibit carnitine palmitoyl transferase (CPT)-I activity in the mitochondria, is added in the Hepes medium before incubation of the mitochondria[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: After 1 week of acclimatization, rats are randomly assigned to a hindlimb suspension group, hindlimb suspension with L-carnitine administration group, and a pair-fed group. The L-carnitine group are administered a 1250 mg L-carnitine/kg dissolved in distilled water orally using a sonde. The body weight is measured every morning at 09:00 and L-carnitine solution is ingested every morning at 10:00. The experiment is conducted for 14 days[3]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 190-205ºC |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H16ClNO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 197.660 |
| Exact Mass | 197.081863 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| InChIKey | JXXCENBLGFBQJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)CC(=O)O.[Cl-] |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BP2979140 |
| HS Code | 2923900090 |
|
~% 
DL-Carnitine hy... CAS#:461-05-2 |
| Literature: Lonza Ltd. Patent: US3969406 A1, 1976 ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2923900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2923900090 other quaternary ammonium salts and hydroxides。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Fenofibrate causes elevation of betaine excretion but not excretion of other osmolytes by healthy adults.
J. Clin. Lipidol. 8(4) , 433-40, (2014) Cross-sectional data suggest that bezafibrate increases betaine excretion in dyslipidemic patients.We aimed to demonstrate that fenofibrate induces increased betaine excretion in normal subjects and e... |
|
|
Extreme urinary betaine losses in type 2 diabetes combined with bezafibrate treatment are associated with losses of dimethylglycine and choline but not with increased losses of other osmolytes.
Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 28(5) , 459-68, (2014) Betaine deficiency is a probable cardiovascular risk factor and a cause of elevated homocysteine. Urinary betaine excretion is increased by fibrate treatment, and is also often elevated in diabetes. D... |
|
|
Carnitine transporter CT2 (SLC22A16) is over-expressed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and target knockdown reduces growth and viability of AML cells.
Apoptosis 20 , 1099-108, (2015) AML (acute myeloid leukemia) cells have a unique reliance on mitochondrial metabolism and fatty acid oxidation (FAO). Thus, blocking FAO is a potential therapeutic strategy to target these malignant c... |
| DL-Carnitine Hydrochloride |
| 3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium chloride |
| 3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylammonio)butanoate hydrochloride |
| EINECS 207-309-1 |
| UNII:F64264D63N |
| Vitamin BT Hydrochloride |
| Carnitine chloride |
| 3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylammonio)butyrate Hydrochloride |
| carnitine hydrochloride |
| MFCD00011904 |
| 3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium, inner salt, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 1-Propanaminium, 3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| 3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylpropan-1-aminium chloride |
| QV1YQ1K1&1&1 &&Anhydro HCl |
| (±)-Carnitine (chloride) |
 CAS#:5080-50-2
CAS#:5080-50-2 CAS#:142674-34-8
CAS#:142674-34-8 CAS#:142674-38-2
CAS#:142674-38-2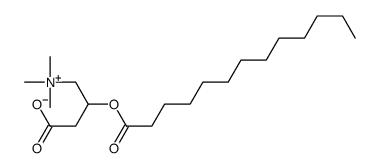 CAS#:142674-35-9
CAS#:142674-35-9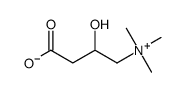 CAS#:461-06-3
CAS#:461-06-3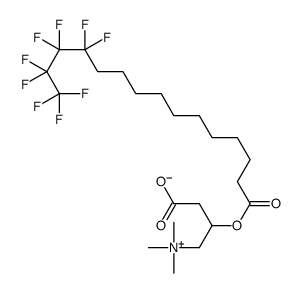 CAS#:142674-37-1
CAS#:142674-37-1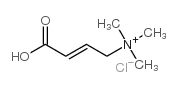 CAS#:6538-82-5
CAS#:6538-82-5
