Azepexole dihydrochloride
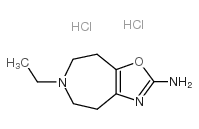
Azepexole dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Azepexole dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 36067-72-8 | Molecular Weight | 254.16 | |
| Density | 1.126g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 330.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H17Cl2N3O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 153.9ºC | |
Use of Azepexole dihydrochlorideAzepexole (B-HT 933) dihydrochloride is a potent and selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist with pKis of 8.3, 7.6, and 7.5 for α2A-, α2B- and α2C-adrenoceptor subtypes, resepctively[1]. Azepexole dihydrochloride causes concentration-dependent inhibition of peristaltic contractions (IC50= 78.72 nM)[2]. |
| Name | B-HT 933 dihydrochloride |
|---|
| Description | Azepexole (B-HT 933) dihydrochloride is a potent and selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist with pKis of 8.3, 7.6, and 7.5 for α2A-, α2B- and α2C-adrenoceptor subtypes, resepctively[1]. Azepexole dihydrochloride causes concentration-dependent inhibition of peristaltic contractions (IC50= 78.72 nM)[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | In normoglycemic rats, the sympathetically-induced vasopressor responses are dose-dependently inhibited by 1 and 3 μg/kg.min (i.v.) Azepexole dihydrochloride, with 10 and 30 μg/kg.min Azepexole dihydrochloride producing no further inhibition. In diabetic rats, the electrically-induced vasopressor responses are: (i) unchanged by 1 and 3 μg/kg.min Azepexole dihydrochloride; (ii) significantly inhibited at all frequencies of stimulation by 10 μg/kg.min B-HT 933 dihydrochloride; and (iii) similarly inhibited (i.e. supramaximal inhibition) by 30 μg/kg.min Azepexole dihydrochloride[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.126g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 330.9ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C9H17Cl2N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 254.16 |
| Flash Point | 153.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 253.07500 |
| PSA | 55.29000 |
| LogP | 2.80040 |
| InChIKey | HBLPYIOKPJVFQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCN1CCc2nc(N)oc2CC1.Cl.Cl |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | RQ5831345 |
|
The role of several alpha(1)- and alpha(2)-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating vasoconstriction in the canine external carotid circulation.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 132 , 1292-1298, (2001) 1. It has recently been shown that both alpha(1)- and alpha(2)-adrenoceptors mediate vasoconstriction in the canine external carotid circulation. The present study set out to identify the specific sub... |
|
|
Pharmacological evidence that alpha2A- and alpha2C-adrenoceptors mediate the inhibition of cardioaccelerator sympathetic outflow in pithed rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 554(2-3) , 205-11, (2007) It has been suggested that the alpha(2)-adrenoceptors mediating cardiac sympatho-inhibition in pithed rats closely resemble the pharmacological profile of the alpha(2A)-adrenoceptor subtype. However, ... |
|
|
Evidence that some imidazoline derivatives inhibit peripherally the vasopressor sympathetic outflow in pithed rats.
Auton. Neurosci. 143(1-2) , 40-5, (2008) Imidazoline derivatives (e.g. clonidine and moxonidine) and alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists (e.g. B-HT 933) have been shown to inhibit sympathetically-induced [(3)H]noradrenaline release in several iso... |