Indole-3-pyrubate
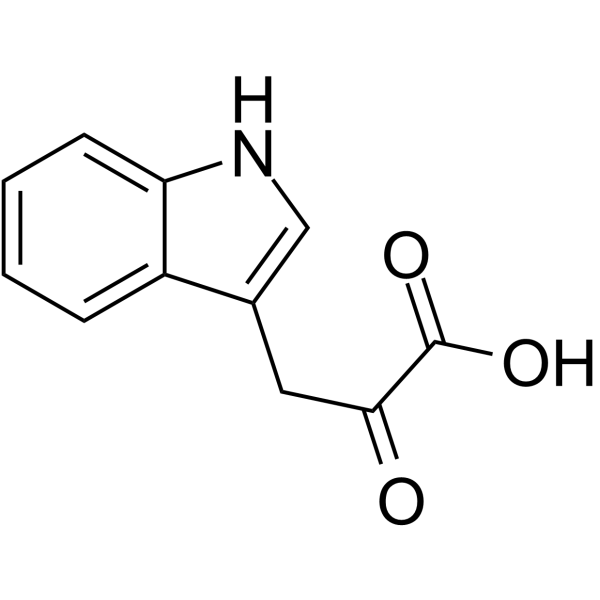
Indole-3-pyrubate structure
|
Common Name | Indole-3-pyrubate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 392-12-1 | Molecular Weight | 203.194 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 445.2±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H9NO3 | Melting Point | 215 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 223.0±24.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Indole-3-pyrubateIndole-3-pyruvic acid, a keto analogue of tryptophan, is an orally active AHR agonist. Indole-3-pyruvic acid has antioxidant properties, and can be used in the research of inflammation, anxiety[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 3-(indol-3-yl)pyruvic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Indole-3-pyruvic acid, a keto analogue of tryptophan, is an orally active AHR agonist. Indole-3-pyruvic acid has antioxidant properties, and can be used in the research of inflammation, anxiety[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microbial Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Indole-3-pyruvic acid (50 and 250 μM, 24 h) activates AHR in HepG2 cells[1]. Indole-3-pyruvic acid (50 μM, 4 days) does not inhibit Th1 cell differentiation but promotes Tr1 differentiation[1]. Indole-3-pyruvic acid (1 mM, 24 h) reduces UVB-induced cytotoxicity in HaCaT cells[1]. Indole-3-pyruvic acid (25 mM, 6 h) reduces the levels of COX-2 in HaCaT cells[2]. RT-PCR[2] Cell Line: HaCaT cells Concentration: 5-25 mM Incubation Time: 6 h Result: Inhibited UVB-stimulated mRNA expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and cyclooxygenase 2 (Cox-2). |
| In Vivo | Indole-3-pyruvic acid (oral administration, fed in MF chow (0.1%) for 5 d) activates AHR in BALB/c mice[1]. Indole-3-pyruvic acid (oral administration, fed in MF chow (0.1%) for 5 wk) abrogates chronic inflammation in a T cell-mediated colitis model[1]. Indole-3-pyruvic acid (100 μM, dose at skin) protects against UVB-induced skin damage in HR-1 hairless mice[2]. Indole-3-pyruvic acid (intraperitoneal injection, 100-200 mg/kg) increases the time spent in the open arms of the elevated plus maze in mice[3]. Animal Model: BALB/c mice[1] Dosage: Fed in MF chow.0.1% for 5 d Administration: Oral administration Result: Up-regulated the expression of Cyp1a1 (a biomarker for AHR activation) in the colon. Animal Model: T cell–mediated colitis model of SCID mice[1] Dosage: Fed in MF chow.0.1% for 5 wk Administration: Oral administration Result: Suppressed diarrhea and improved colon inflammation. Down-regulated the expression of Th1 and proinflammatory cytokines and upregulated the expression of IL-10 in the colon. Animal Model: HR-1 Hairless Mice[2] Dosage: 100 μM Administration: Dose at skin Result: Enhanced the epidermal thickness. Attenuated UVB-induced necrosis observed in upper layer of dermis. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 445.2±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 215 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C11H9NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 203.194 |
| Flash Point | 223.0±24.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 203.058243 |
| PSA | 70.16000 |
| LogP | 0.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.685 |
| InChIKey | RSTKLPZEZYGQPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)C(=O)Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NM1880000 |
| HS Code | 2918300090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918300090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918300090 other carboxylic acids with aldehyde or ketone function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Structural insight into the inhibition of human kynurenine aminotransferase I/glutamine transaminase K.
J. Med. Chem. 52 , 2786-93, (2009) Human kynurenine aminotransferase I (hKAT I) catalyzes the formation of kynurenic acid, a neuroactive compound. Here, we report three high-resolution crystal structures (1.50-1.55 A) of hKAT I that ar... |
|
|
A novel thiol-reductase activity of Arabidopsis YUC6 confers drought tolerance independently of auxin biosynthesis.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 8041, (2015) YUCCA (YUC) proteins constitute a family of flavin monooxygenases (FMOs), with an important role in auxin (IAA) biosynthesis. Here we report that Arabidopsis plants overexpressing YUC6 display enhance... |
|
|
Coordination of auxin and ethylene biosynthesis by the aminotransferase VAS1.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 9(4) , 244-6, (2013) We identify an Arabidopsis pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase, VAS1, whose loss-of-function simultaneously increases amounts of the phytohormone auxin and the ethylene precursor 1-aminocyc... |
| MFCD00005640 |
| 1H-Indole-3-propanoic acid, α-oxo- |
| 3-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-oxopropanoic acid |
| Indole pyruvic acid |
| EINECS 206-874-1 |
| Indole-3-pyrubate |
| Indole-3-pyruvic acid |
| INDOLE-3-PYRUVATE |
 CAS#:73-22-3
CAS#:73-22-3 CAS#:54753-57-0
CAS#:54753-57-0 CAS#:54-12-6
CAS#:54-12-6 CAS#:79189-76-7
CAS#:79189-76-7 CAS#:871023-09-5
CAS#:871023-09-5 CAS#:1912-33-0
CAS#:1912-33-0 CAS#:153-94-6
CAS#:153-94-6 CAS#:328-50-7
CAS#:328-50-7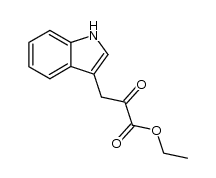 CAS#:32817-17-7
CAS#:32817-17-7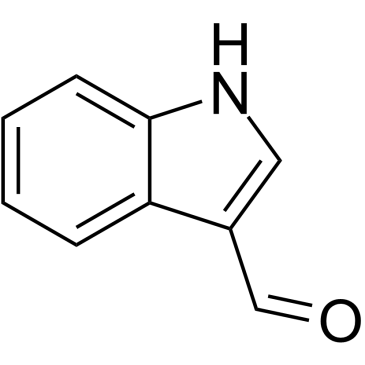 CAS#:487-89-8
CAS#:487-89-8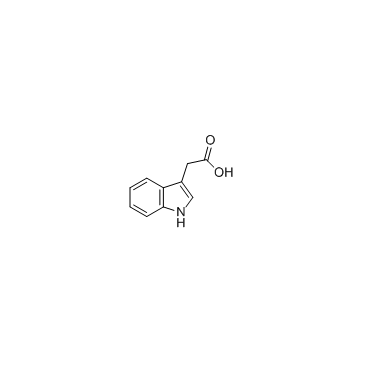 CAS#:87-51-4
CAS#:87-51-4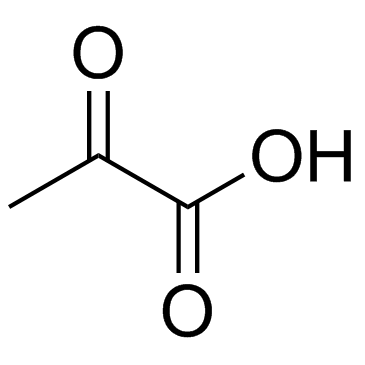 CAS#:127-17-3
CAS#:127-17-3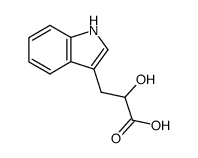 CAS#:832-97-3
CAS#:832-97-3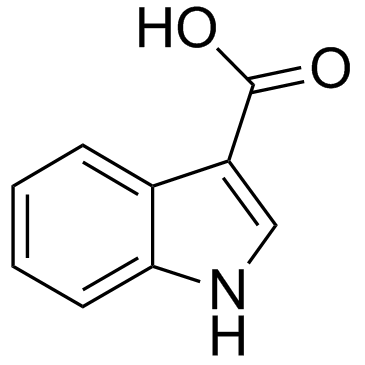 CAS#:771-50-6
CAS#:771-50-6 CAS#:879-37-8
CAS#:879-37-8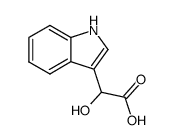 CAS#:3050-37-1
CAS#:3050-37-1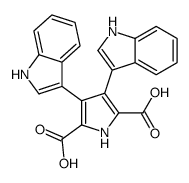 CAS#:150044-68-1
CAS#:150044-68-1