Epicatechin
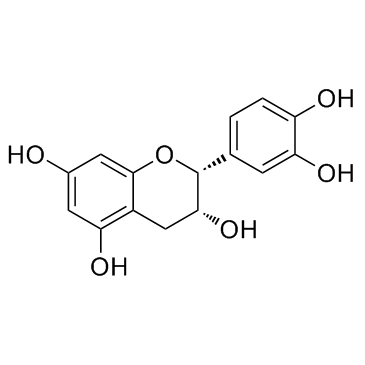
Epicatechin structure
|
Common Name | Epicatechin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 490-46-0 | Molecular Weight | 290.268 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 630.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O6 | Melting Point | 240 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 335.0±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Epicatechin(-)-Epicatechin inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) with an IC50 of 3.2 μM. (-)-Epicatechin inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of iNOS by blocking the nuclear localization of the p65 subunit of NF-κB. |
| Name | (-)-epicatechin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (-)-Epicatechin inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) with an IC50 of 3.2 μM. (-)-Epicatechin inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of iNOS by blocking the nuclear localization of the p65 subunit of NF-κB. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-1:3.2 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | (-)-Epicatechin exhibits >95% inhibitory activity at 70 μg/mL against cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) with an IC50 of 3.2 μM[1]. (-)-Epicatechin inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of iNOS by blocking the nuclear localization of the p65 subunit of NF-κB. In RINm5F cells, (-)-Epicatechin is shown to block the inhibition of insulin release after addition of IL-1β. Additionally, (-)-Epicatechin is shown to inhibit the proliferation of Hodgkin's lymphoma cells and Jurkat T cells, which is attributed to the ability of (-)-Epicatechin to inhibit the binding of NF-κB to DNA in these cells. In human colorectal cancer HCT-116 cells, combining 20 μM Panaxadiol with 150, 200, or 250 μM (-)-Epicatechin results in growth inhibition of 51%, 97%, and 95%, respectively. The combination also increases the apoptosis level by 11.9%, 16.6%, and 25.8%, as examined by annexin V/PI staining[2]. |
| In Vivo | Animals receive 1 mg/kg of (-)-Epicatechin or water (vehicle) via oral gavage (twice daily). Exercise groups undergo 15 days of treadmill exercise. Significant increases in treadmill performance (~50%) and enhanced in situ muscle fatigue resistance (~30%) are observed with (-)-Epicatechin[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] 1-year-old, male C57BL/6N mice (n=25) are randomized into four groups. Mice in the (-)-Epicatechin groups 3 and 4 are given 1.0 mg/kg twice a day (morning and evening) for 15 consecutive days, whereas animals in the control groups 1 and 2 receive the vehicle (water). Both (-)-Epicatechin and vehicle are administered via oral gavage[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 630.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 240 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 290.268 |
| Flash Point | 335.0±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 290.079041 |
| PSA | 110.38000 |
| LogP | 0.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.742 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | KB3745000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
|
Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate triggered hepatotoxicity in mice: responses of major antioxidant enzymes and the Nrf2 rescue pathway.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 283(1) , 65-74, (2015) (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a constituent of green tea, has been suggested to have numerous health-promoting effects. On the other hand, high-dose EGCG is able to evoke hepatotoxicity. In t... |
|
|
Identification of Vitis vinifera L. grape berry skin color mutants and polyphenolic profile.
Food Chem. 194 , 117-27, (2015) A germplasm set of twenty-five grapevine accessions, forming eleven groups of possible berry skin color mutants, were genotyped with twelve microsatellite loci, being eleven of them identified as true... |
|
|
Bi-layer composite dressing of gelatin nanofibrous mat and poly vinyl alcohol hydrogel for drug delivery and wound healing application: in-vitro and in-vivo studies.
J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9(9) , 1495-508, (2013) Present investigation involves the development of a bi-layer dressing of gelatin nanofibrous mat loaded with epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)/poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel and its in-vivo evaluatio... |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)chroman-3,5,7-triol |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-chromanetriol |
| (-)-3 3' 4' 5 7-Pentahydroxyflavan |
| (-)-epicatechin |
| (−)-Epicatechin,from green tea |
| (-)Epicatechin |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)chromane-3,5,7-triol |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-3,5,7-triol, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-, (2R,3R)- |
| L-Epicatechin |
| MFCD00075648 |
| (−)-cis-3,3',4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavane |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1(2H)-benzopyran-3,5,7-triol |
| epicatechin |
| EINECS 207-710-1 |
| EC |
 CAS#:87292-49-7
CAS#:87292-49-7 CAS#:29106-51-2
CAS#:29106-51-2 CAS#:989-51-5
CAS#:989-51-5 CAS#:154-23-4
CAS#:154-23-4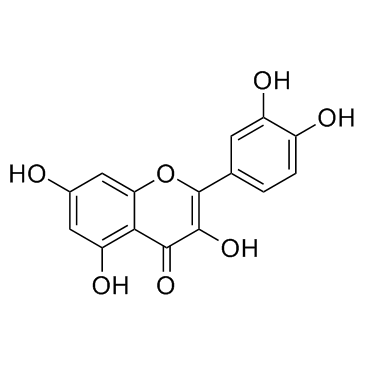 CAS#:117-39-5
CAS#:117-39-5![2-[3,4-bis(phenylmethoxy)phenyl]-3,5,7-tris(phenylmethoxy)chromen-4-on e Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/199/13157-90-9.png) CAS#:13157-90-9
CAS#:13157-90-9 CAS#:1392108-91-6
CAS#:1392108-91-6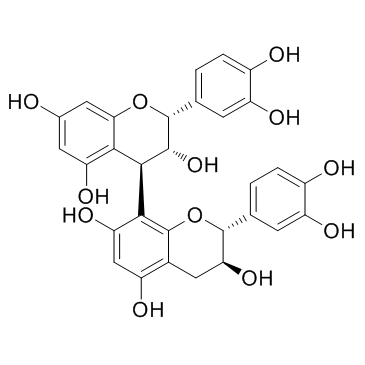 CAS#:20315-25-7
CAS#:20315-25-7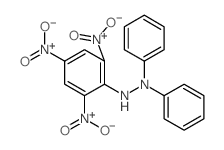 CAS#:1707-75-1
CAS#:1707-75-1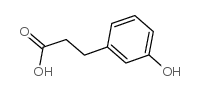 CAS#:621-54-5
CAS#:621-54-5 CAS#:31129-94-9
CAS#:31129-94-9![2-[(2S)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropyl]benzene-1,3,5-triol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/427/111397-00-3.png) CAS#:111397-00-3
CAS#:111397-00-3![2(3H)-Furanone,5-[(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methyl]dihydro-,(5R)-(9CI) structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/408/191666-22-5.png) CAS#:191666-22-5
CAS#:191666-22-5 CAS#:979-92-0
CAS#:979-92-0 CAS#:29106-49-8
CAS#:29106-49-8 CAS#:12798-57-1
CAS#:12798-57-1 CAS#:4670-05-7
CAS#:4670-05-7
