Mangiferin
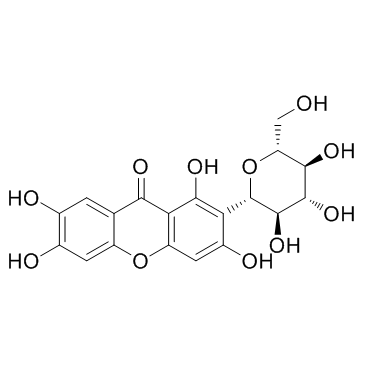
Mangiferin structure
|
Common Name | Mangiferin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4773-96-0 | Molecular Weight | 422.340 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 842.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18O11 | Melting Point | 269-270ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 303.6±27.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of MangiferinMangiferin is a Nrf2 activator. Mangiferin suppresses nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunits p65 and p50. |
| Name | mangiferin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Mangiferin is a Nrf2 activator. Mangiferin suppresses nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunits p65 and p50. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
p65 p50 Nrf2 |
| In Vitro | Mangiferin is glucosylxanthone extracted from plants of the Anacardiaceae and Gentianaceae families. Mangiferin (50 μM) significantly increases Nrf2 protein accumulation in HL-60 cells, particularly in the nucleus. Mangiferin also enhances the binding of Nrf2 to an antioxidant response element (ARE), significantly up-regulates NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) expression and reduces intracellular ROS in HL60 cells. Mangiferin alone dose-dependently inhibits the proliferation of HL-60 cells. In mononuclear cells (MNCs), Mangiferin significantly relieves oxidative stress, but attenuates etoposide-induced cytotoxicity[1]. Mangiferin is a natural phytopolyphenol that exhibits various pharmacological properties. Mangiferin is present in several plant species such as Mangifera indica, Iris unguicularis, and Anemarrhena asphodeloides. Mangiferin downregulates TNF-α-induced MMP-9 mRNA and protein expression by suppressing NF-κB activity, consequently suppressing the invasion of LNCaP cells.To assess whether Mangiferin influences the viability of LNCaP cells, MTT assay is performed 24 h after treatment with different concentrations of Mangiferin in the presence or absence of TNF-α in serum and serum-free conditions. There are no cytotoxic evident in LNCaP cells treated with up to 400 μM of Mangiferin alone under both serum and serum-free conditions. Additionally, in the presence of TNF-α (20 ng/mL), Mangiferin does not affect cell viability. Mangiferin (400 μM) treatment significantly decreases the NF-κB luciferase activity in TNF-α-stimulated LNCaP cells. Pretreatment with Mangiferin (400 μM) for 1 h significantly decreases TNF-α-induced NF-κB activity. The RT-PCR shows that Mangiferin (400 μM) significantly suppresses the TNF-α-induced MMP-9 expression in LNCaP cells[2]. |
| Cell Assay | LNCaP cells are cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS and antibiotics. Cell viability is determined by an MTT assay. Briefly, LNCaP cells (1×105 cells/mL) are plated onto 24 well plates and incubated overnight in serum and serum-free RPMI media. The cells are treated with the indicated concentrations of Mangiferin (100, 200, and 400 μM) for 1 h and then stimulated with TNF-α (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. Then, the cells are incubated with a solution of 0.5 mg/mL MTT and incubation for 45 min at 37°C and 5% CO2. Supernatant is removed and the formation of formazan is observed by monitoring the signal at 540 nm using a microplate reader[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 842.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 269-270ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 422.340 |
| Flash Point | 303.6±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 422.084900 |
| PSA | 201.28000 |
| LogP | 0.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.789 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+:Verytoxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R28 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S28-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3462 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OP1927800 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
|
Thermal Degradation Kinetics Modeling of Benzophenones and Xanthones during High-Temperature Oxidation of Cyclopia genistoides (L.) Vent. Plant Material.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 5518-27, (2015) Degradation of the major benzophenones, iriflophenone-3-C-glucoside-4-O-glucoside and iriflophenone-3-C-glucoside, and the major xanthones, mangiferin and isomangiferin, of Cyclopia genistoides follow... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents of Gentiana rhodantha].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(3) , 362-5, (2013) To determine the chemical constituents of Gentiana rhodantha.To isolate the constituents, column chromatography over silica gel, MCI, Sephadex LH-20 and C18 reverse-phased silica gel were used. Spectr... |
|
|
Mangiferin activates the Nrf2-ARE pathway and reduces etoposide-induced DNA damage in human umbilical cord mononuclear blood cells.
Pharm. Biol. 53(4) , 503-11, (2015) Mangiferin (2-C-β-d-gluco-pyranosyl-1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone) is a well-known natural antioxidant distributed in various plants of the Anacardiaceae and Gentianaceae families. Mangiferin can inhib... |
| Hedysaride |
| (1S)-1,5-Anhydro-1-(1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-9-oxo-9H-xanthen-2-yl)-D-glucitol |
| D-Glucitol, 1,5-anhydro-1-C-(1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-9-oxo-9H-xanthen-2-yl)-, (1S)- |
| hedysarid |
| MANGIFERN |
| 1,3,6,7-Tétrahydroxy-2-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-9H-xanthén-9-one |
| aphloiol |
| chinonin |
| 9H-Xanthen-9-one, 2-β-D-glucopyranosyl-1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy- |
| chinomin |
| MFCD00075656 |
| Alpizarine |
| alpizarin |
| 1,3,6,7-Tetrahydroxy-2-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-9H-xanthen-9-on |
| 1,3,6,7-Tetrahydroxy-2-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-9H-xanthen-9-one |
| Mangiferin |
| ChinoMine |
 CAS#:1239694-50-8
CAS#:1239694-50-8 CAS#:2054-37-7
CAS#:2054-37-7 CAS#:3542-72-1
CAS#:3542-72-1
