1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 12:02:14

1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone structure
|
Common Name | 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3542-72-1 | Molecular Weight | 260.20 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 595.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H8O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 237.8±23.6 °C | |
Use of 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthoneNorathyriol (Mangiferitin) is a natural metabolite of Mangifera. Norathyriol inhibits α-glucosidase in a noncompetitive manner with an IC50 of 3.12 μM[1]. Norathyriol inhibits PPARα, PPARβ, and PPARγ with IC50s of 92.8 µM, 102.4 µM, and 153.5 µM, respectively[2]. Antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial activities. |
| Name | norathyriol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Norathyriol (Mangiferitin) is a natural metabolite of Mangifera. Norathyriol inhibits α-glucosidase in a noncompetitive manner with an IC50 of 3.12 μM[1]. Norathyriol inhibits PPARα, PPARβ, and PPARγ with IC50s of 92.8 µM, 102.4 µM, and 153.5 µM, respectively[2]. Antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial activities. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PPARα:92.8 μM (IC50) PPARβ:102.4 μM (IC50) PPARγ:153.5 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Norathyriol (1-25 µM) inhibits growth by inducing cell cycle arrest in JB6 P+ cells. Norathyriol inhibits JB6 cell growth by inducing G2-M arrest[3]. Norathyriol suppresses UVB-induced phosphorylation of ERKs, AP-1 and NF-κB activation in JB6 P+ cells[3]Cell Growth Assay WB Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Line: Mouse skin epidermal JB6 P+ cells Concentration: 0, 1, 10, or 25 µM Incubation Time: 24 or 72 hours Result: Inhibited cell growth in a dose- as well as time-dependent manner but does not cause cell death. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: JB6 P+ cells Concentration: 0, 1, 10, or 25 µM Incubation Time: 2 hours Result: Inhibited UVB-induced phosphorylation of ERKs and p90RSK. |
| In Vivo | Norathyriol is a natural metabolite of Mangifera in the human intestine with the oral availability and safety[1]. Norathyriol (0.92, 1.85 and 3.7 mg/kg) dose dependently decreased the serum urate levels by 27.0, 33.6 and 37.4%, respectively[4]. Animal Model: Adult Kunming mice weighing 18-22 g[4] Dosage: 0.92, 1.85 and 3.7 mg/kg Administration: Administered intragastrically; twice daily for five times Result: The serum uric acid levels were decreased by 27.0%, 33.6% and 37.4%. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 595.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H8O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 260.20 |
| Flash Point | 237.8±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 260.032074 |
| PSA | 111.13000 |
| LogP | 0.95 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.801 |
| InChIKey | ZHTQCPCDXKMMLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1c2cc(O)c(O)cc2oc2cc(O)cc(O)c12 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| Norathyriol |
| magniferitin |
| 1,3,6,7-Tetrahydroxyxanthen-9-one |
| 1,3,6,7-Tetrahydroxyxantone |
| 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone |
| 2,4,6,7-Tetrahydroxyxanthone |
| 1,3,6,7-Tetrahydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-one |
| 9H-Xanthen-9-one, 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy- |
 CAS#:3542-74-3
CAS#:3542-74-3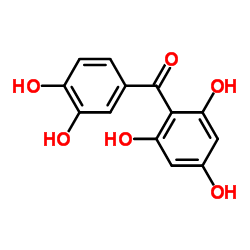 CAS#:519-34-6
CAS#:519-34-6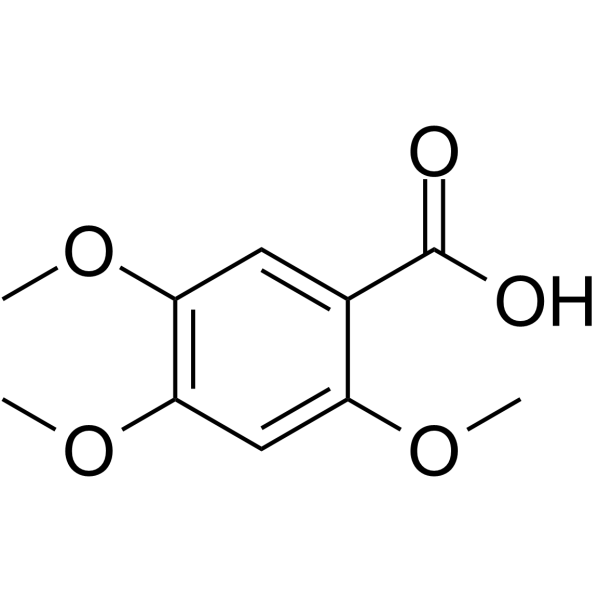 CAS#:490-64-2
CAS#:490-64-2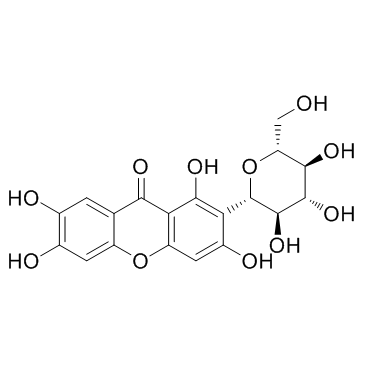 CAS#:4773-96-0
CAS#:4773-96-0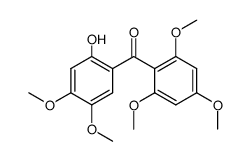 CAS#:42833-68-1
CAS#:42833-68-1 CAS#:2054-37-7
CAS#:2054-37-7 CAS#:105904-53-8
CAS#:105904-53-8 CAS#:102478-32-0
CAS#:102478-32-0 CAS#:59092-97-6
CAS#:59092-97-6![7,9-dihydroxy-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-b]xanthen-10-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/327/14103-14-1.png) CAS#:14103-14-1
CAS#:14103-14-1 CAS#:108-73-6
CAS#:108-73-6
