Afzelin
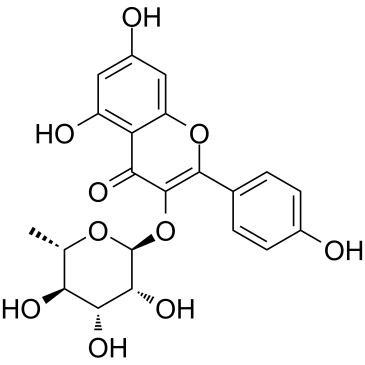
Afzelin structure
|
Common Name | Afzelin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 482-39-3 | Molecular Weight | 432.378 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 765.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H20O10 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 272.4±26.4 °C | |
Use of AfzelinAfzelin (Kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside) is is a flavonol glycoside found in Houttuynia cordata Thunberg and is widely used in the preparation of antibacterial and antipyretic agents, detoxicants and for the treatment of inflammation. Afzelin attenuates the mitochondrial damage, enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and decreases the level of mitophagy-related proteins, parkin and PTEN-induced putative kinase 1. Afzelin improves the survival rate and reduces the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and pro-inflammatory cytokines in D-galactosamine (GalN)/LPS -treated mice[1]. |
| Name | afzelin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Afzelin (Kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside) is is a flavonol glycoside found in Houttuynia cordata Thunberg and is widely used in the preparation of antibacterial and antipyretic agents, detoxicants and for the treatment of inflammation. Afzelin attenuates the mitochondrial damage, enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and decreases the level of mitophagy-related proteins, parkin and PTEN-induced putative kinase 1. Afzelin improves the survival rate and reduces the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and pro-inflammatory cytokines in D-galactosamine (GalN)/LPS -treated mice[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 765.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H20O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 432.378 |
| Flash Point | 272.4±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 432.105652 |
| PSA | 170.05000 |
| LogP | 2.37 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.748 |
| InChIKey | SOSLMHZOJATCCP-AEIZVZFYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC1OC(Oc2c(-c3ccc(O)cc3)oc3cc(O)cc(O)c3c2=O)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Antibacterial effects of afzelin isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals.
Molecules 19(3) , 3173-80, (2014) The crude ethyl acetate extract of the leaves of Cornus macrophylla showed antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals. Bioactivi... |
|
|
Antagonizing effects and mechanisms of afzelin against UVB-induced cell damage.
PLoS ONE 8(4) , e61971, (2013) Ultraviolet (UV) radiation induces DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inflammatory processes in human keratinocytes, resulting in skin inflammation, photoaging, and photocarcinogenesis. Adequate protec... |
| kaempferol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside |
| kaempferol-3-rhamnoside |
| 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranoside |
| 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3-[(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- |
| Kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside |
| Kaempferol 3-O-Alpha-L-Rhamnoside |
| Afzelin |
| Trihydroxy-SL0101 |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3-((6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- |
| Kaempferol 3-rhamnoside |
| 3-O-α-rhamnosylkaempferol |
| Kaempferin |
 CAS#:865484-73-7
CAS#:865484-73-7 CAS#:23405-70-1
CAS#:23405-70-1 CAS#:1192-62-7
CAS#:1192-62-7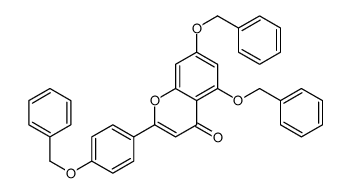 CAS#:96333-59-4
CAS#:96333-59-4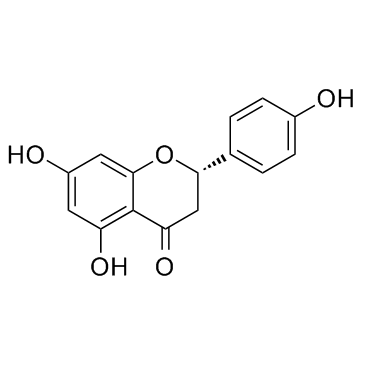 CAS#:480-41-1
CAS#:480-41-1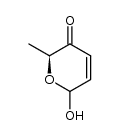 CAS#:247244-65-1
CAS#:247244-65-1 CAS#:520-18-3
CAS#:520-18-3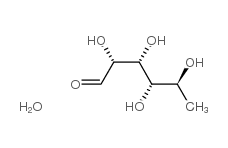 CAS#:6014-42-2
CAS#:6014-42-2
