(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen
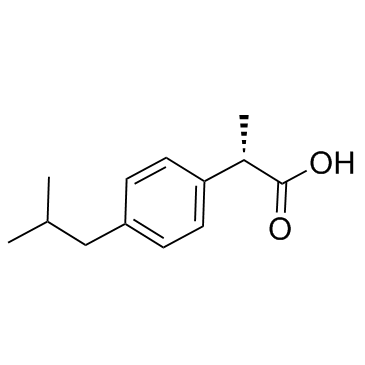
(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen structure
|
Common Name | (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51146-56-6 | Molecular Weight | 206.281 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 319.6±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18O2 | Melting Point | 49-53ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.7±14.4 °C | |
Use of (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen(S)-(+)-Ibuprofen is the S-enantiomer of Ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is an anti-inflammatory inhibitor targeting COX-1 and COX-2 with IC50 of 13 μM and 370 μM, respectively. |
| Name | dexibuprofen |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen is the S-enantiomer of Ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is an anti-inflammatory inhibitor targeting COX-1 and COX-2 with IC50 of 13 μM and 370 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 319.6±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 49-53ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 206.281 |
| Flash Point | 216.7±14.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 206.130676 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 3.72 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.519 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R63 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | 2811.0 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
|
|
The advantages and limitations of the analgesics available for control of postoperative pain after a dental procedure.
SAAD Dig. 29 , 70-81, (2013)
|
|
|
Pegylation improves the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of small-molecule drugs hydrolyzable by esterases: a study of phospho-Ibuprofen.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 351(1) , 61-6, (2014) Esterase hydrolysis of drugs can accelerate their elimination, thereby limiting their efficacy. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) covalently attached to drugs (pegylation) is known to improve the efficiency o... |
| (2S)-2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propanoic acid |
| (S)-(+)-4-Isobutyl-α-methylphenylacetic Acid |
| (S)-2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propanoic acid |
| Benzeneacetic acid, α-methyl-4-(2-methylpropyl)-, (αS)- |
| (+)-(S)-Ibuprofen |
| (+)-ibuprofen |
| MFCD00069289 |
| Dexibuprofen |
| (S)-4-Isobutyl-α-methylphenylacetic acid |
| (2S)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid |
| (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen |
| (S)-(+)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoic acid |
| d-Ibuprofen |
| (S)-(+)-4-Isobutyl-Alpha-Methylphenylacetic Acid |
| Ibuprofen |
| (S)-(+)-2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propionic Acid |
| (S)-a-Methyl-4-(2-methylpropyl)benzeneacetic acid |
| (S)-ibuprofen |
| (2S)-2-[4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl]propionic acid |
![N-[3-[(3-propoxybenzoyl)carbamothioylamino]phenyl]furan-2-carboxamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/447/6448-14-2.png) CAS#:6448-14-2
CAS#:6448-14-2 CAS#:15687-27-1
CAS#:15687-27-1 CAS#:62784-66-1
CAS#:62784-66-1 CAS#:61566-34-5
CAS#:61566-34-5 CAS#:110282-71-8
CAS#:110282-71-8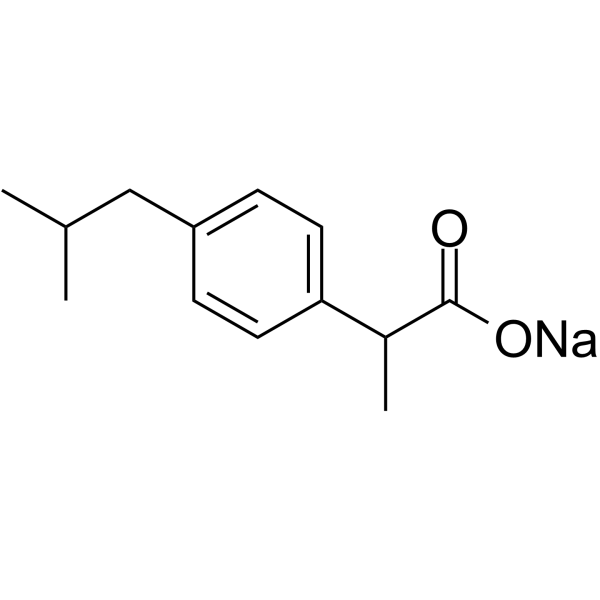 CAS#:31121-93-4
CAS#:31121-93-4![1-isobutyl-4-[(1R,2E)-1-methyl-2-heptenyl]benzene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/378/570368-33-1.png) CAS#:570368-33-1
CAS#:570368-33-1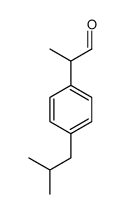 CAS#:51407-46-6
CAS#:51407-46-6 CAS#:1224446-49-4
CAS#:1224446-49-4 CAS#:51146-57-7
CAS#:51146-57-7
