Carprofen
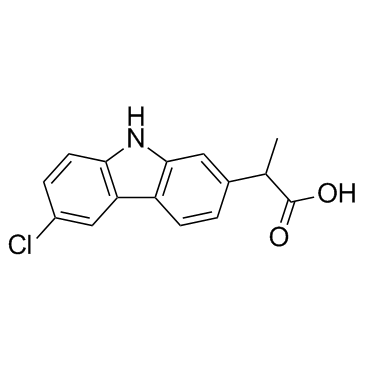
Carprofen structure
|
Common Name | Carprofen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 53716-49-7 | Molecular Weight | 273.714 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 509.1±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12ClNO2 | Melting Point | 186-188ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 261.7±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CarprofenCarprofen is a nonsteroid anti-inflammatory agent, acts as a multi-target FAAH/COX inhibitor, with IC50s of 3.9 μM, 22.3 μM and 78.6 μM for COX-2, COX-1 and FAAH, respectively. |
| Name | carprofen |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carprofen is a nonsteroid anti-inflammatory agent, acts as a multi-target FAAH/COX inhibitor, with IC50s of 3.9 μM, 22.3 μM and 78.6 μM for COX-2, COX-1 and FAAH, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-2:3.9 μM (IC50) COX-1:22.3 μM (IC50) FAAH:78.6 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Carprofen (Compound 1) is a nonsteroid anti-inflammatory agent, acts as a multi-target FAAH/COX inhibitor, with IC50s of 3.9 μM, 22.3 μM and 78.6 μM for COX-2, COX-1 and FAAH, respectively[1]. Carprofen (10 µg/mL) shows cytoprotective effects in CCL and CaCL cells and decreases apoptosis of both cells. Carprofen (10 µg/mL) exhibits nonsignificant increase in PGE2 concentration, compared with that of the respective CCL or CaCL controls[2]. |
| In Vivo | Carprofen (2.2 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly decreases PGE2 concentration in blood of dogs on days 3 and 10. Carprofen also decreases amounts of gastric PGE2 synthesis on day 3, but the inhibition is not obvious on day 10. In addition, Carprofen shows no activity against gastric PGE1 synthesis in dogs on day 3 and 10[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Cruciate ligament cells are used and incubated with DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS for 24 hours to synchronize cell cycles. The cell cultures are then preincubated without (control) or with a nonselective COX inhibitor (acetylsalicylic acid) or a preferential COX-2 inhibitor (Carprofen, meloxicam, or robenacoxib) to ssess whether NSAIDs prevented apoptosis when the cells are subsequently incubated with SNP. For all cell cultures except those designated as controls, 1 of 3 concentrations of 1 of the 4 NSAIDs (10, 100, or 200 µg of acetylsalicylic acid/mL; 0.1, 1, or 10 µg of Carprofend/mL; 0.1, 1, or 10 µg of meloxicame/mL; or 0.1, 1, or 10 µg of robenacoxibf/mL) is added to the culture media of each cell culture, and the cells are incubated for 2 hours[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Dogs[3] Each dog receives Carprofen (2.2 mg/kg, PO, q 12 h), deracoxib (2 mg/kg, PO, q 24 h), or etodolac (10 to 15 mg/kg, PO, q 24 h) for 10 days in a crossover design with a 30- to 60-day washout period between treatments. On days 0, 3, and 10 of each treatment period, blood is collected for evaluation of TXB2 and PGE2 concentrations. In addition, anesthesia is induced with propofol (4 mg/kg) and maintained with isoflurane. Synovial fluid is collected from both stifle joints by use of a standard arthrocentesis technique for evaluation of PGE2 concentrations. Gastroscopy is performed during each anesthetic episode, and 3 to 6 endoscopic biopsy specimens are collected from the gastric antrum for evaluation of PGE1 and PGE2 synthesis. On day 0 for each dog, a gastric biopsy specimen is placed into a Campylobacter-like organism test kit and evaluated for up to 24 hours for Helicobacter spp. Stained slides (H&E) of gastric biopsy specimens are also evaluated for the presence of underlying inflammation[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 509.1±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 186-188ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 273.714 |
| Flash Point | 261.7±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 273.055664 |
| PSA | 53.09000 |
| LogP | 4.03 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.732 |
| InChIKey | PUXBGTOOZJQSKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)O)c1ccc2c(c1)[nH]c1ccc(Cl)cc12 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Ultrastructural changes associated with dexamethasone-induced ocular hypertension in mice.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(8) , 4922-33, (2014) To determine whether dexamethasone (DEX)-induced ocular hypertension (OHT) in mice mimics the hallmarks of steroid-induced glaucoma (SIG) in humans, including reduced conventional outflow facility (C)... |
|
|
Evaluation of amino acid ester-based ionic liquids as buffer additives in CE for the separation of 2-arylpropionic acids nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Electrophoresis 35(18) , 2573-8, (2014) The aim of the present study is the CE performance evaluation for the separation of 2-arylpropionic acid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In particular, the separation of indoprofen, carprofen, k... |
|
|
Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) and prebiotic prevent neonatal inflammation-induced visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats.
Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 26(12) , 1694-704, (2014) Increasing evidence indicates a positive effect of probiotics on the nervous system. The objective of this study was to determine if probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) and/or prebiotics polyde... |
| UNII:FFL0D546HO |
| Imadyl |
| Rimadyl |
| MFCD00079028 |
| 9H-Carbazole-2-acetic acid, 6-chloro-α-methyl- |
| 2-(6-Chloro-9H-carbazol-2-yl)propanoic acid |
| EINECS 258-712-4 |
| Carprofen |
| Ro-20-5720/000 |
| 6-Chloro-α-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-acetic Acid |
| c5720 |
 CAS#:70929-08-7
CAS#:70929-08-7 CAS#:23592-73-6
CAS#:23592-73-6 CAS#:86-74-8
CAS#:86-74-8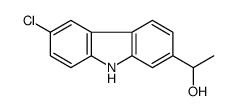 CAS#:92841-21-9
CAS#:92841-21-9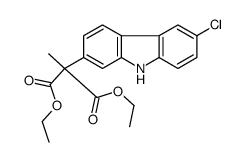 CAS#:71208-55-4
CAS#:71208-55-4 CAS#:71208-54-3
CAS#:71208-54-3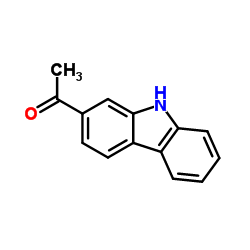 CAS#:23592-74-7
CAS#:23592-74-7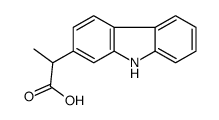 CAS#:52263-68-0
CAS#:52263-68-0
