Carprofen
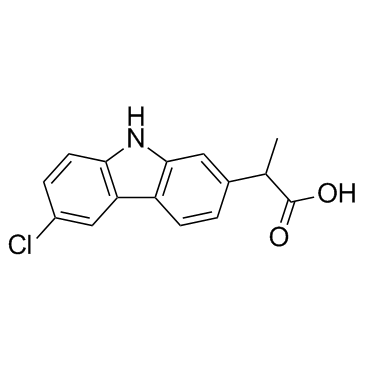
Carprofen structure
|
Common Name | Carprofen | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 53716-49-7 | Molecular Weight | 273.714 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 509.1±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12ClNO2 | Melting Point | 186-188ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 261.7±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Ultrastructural changes associated with dexamethasone-induced ocular hypertension in mice.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(8) , 4922-33, (2014) To determine whether dexamethasone (DEX)-induced ocular hypertension (OHT) in mice mimics the hallmarks of steroid-induced glaucoma (SIG) in humans, including reduced conventional outflow facility (C), increased extracellular matrix (ECM), and myofibroblasts ... |
|
|
Evaluation of amino acid ester-based ionic liquids as buffer additives in CE for the separation of 2-arylpropionic acids nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Electrophoresis 35(18) , 2573-8, (2014) The aim of the present study is the CE performance evaluation for the separation of 2-arylpropionic acid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In particular, the separation of indoprofen, carprofen, ketoprofen, ibuprofen, and flurbiprofen was obtained by supp... |
|
|
Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) and prebiotic prevent neonatal inflammation-induced visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats.
Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 26(12) , 1694-704, (2014) Increasing evidence indicates a positive effect of probiotics on the nervous system. The objective of this study was to determine if probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) and/or prebiotics polydextrose/galactooligosaccharide (PDX/GOS) can alter the colon... |
|
|
Neurokinin B signaling in the female rat: a novel link between stress and reproduction.
Endocrinology 155(7) , 2589-601, (2014) Acute systemic stress disrupts reproductive function by inhibiting pulsatile gonadotropin secretion. The underlying mechanism involves stress-induced suppression of the GnRH pulse generator, the functional unit of which is considered to be the hypothalamic ar... |
|
|
Delivery of therapeutic protein for prevention of neurodegenerative changes: comparison of different CSF-delivery methods.
Exp. Neurol. 263 , 79-90, (2014) Injection of lysosomal enzyme into cisternal or ventricular cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has been carried out in 11 lysosomal storage disorder models, with each study demonstrating reductions in primary substrate and secondary neuropathological changes, and seve... |
|
|
Generation of suppressive blood cells for control of allograft rejection.
Clin. Sci. 128(9) , 593-607, (2015) Our previous studies in rats showed that incubation of monocytic dendritic cells (DCs) with the chemotherapeutic drug mitomycin C (MMC) renders the cells immunosuppressive. Donor-derived MMC-DCs injected into the recipient prior to transplantation prolonged h... |
|
|
Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on wound healing in calvarial defects.
Acta Odontol. Scand. 73(1) , 21-7, (2014) The aim of this study is to analyze histologically the effect of CAPE on bone healing of Critical Size Defect (CSD) in rat calvaria.Thirty-two 3-month-old male rats were used. The animals were randomly divided into four groups. Group A received isotonic salin... |
|
|
Using heterogeneity of the patient-derived xenograft model to identify the chemoresistant population in ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget 5(18) , 8750-64, (2014) A cornerstone of preclinical cancer research has been the use of clonal cell lines. However, this resource has underperformed in its ability to effectively identify novel therapeutics and evaluate the heterogeneity in a patient's tumor. The patient-derived xe... |
|
|
Reduced reach-related modulation of motor thalamus neural activity in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.
J. Neurosci. 34(48) , 15836-50, (2014) Motor thalamus (Mthal) is a key node in the corticobasal ganglia (BG) loop that controls complex, cognitive aspects of movement. In Parkinson's disease (PD), profound alterations in neuronal activity occur in BG nuclei and cortex. Because Mthal is located bet... |
|
|
Increased haemodynamic adrenergic load with isoflurane anaesthesia in type 2 diabetic and obese rats in vivo.
Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 13 , 161, (2014) Increasing numbers of type 2 diabetic and obese patients with enhanced rates of cardiovascular complications require surgical interventions, however they have a higher incidence of perioperative haemodynamic complications, which has been linked to adrenergic ... |