U-46619
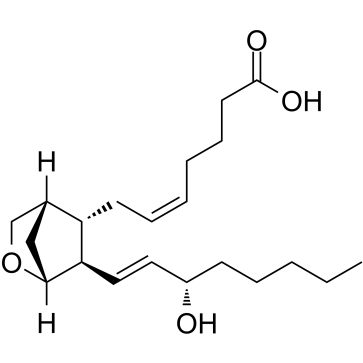
U-46619 structure
|
Common Name | U-46619 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56985-40-1 | Molecular Weight | 350.492 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 519.7±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H34O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 176.1±18.1 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of U-46619U-46619 (9,11-Methanoepoxy PGH2) is a stable analogue of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and acts as a potent TXA2 agonist[1]. |
| Name | 9,11-Dideoxy-11α,9α-epoxymethanoprostaglandin F2α |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | U-46619 (9,11-Methanoepoxy PGH2) is a stable analogue of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and acts as a potent TXA2 agonist[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TXA2[1] |
| In Vitro | U-46619 (1 nM-10 μM) causes platelets shape change and aggregation in a concentration-dependent manner, and with EC50s of 0.58 μM and 0.013 μM for aggregation and shape change, respectively[1]. U-46619 (10 nM-10 μM) increases internal Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and activates phosphoinositide (PI) hydrolysis in a concentration-dependent manner with a similar concentration-dependency[1]. U-46619 (3 nM-10 μM) also activates GTPase concentration-dependently in the membranes derived from platelets[1]. U-46619 improves the differentiation efficiency of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells by activating both p38MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways[2]. |
| In Vivo | U-46619 (5 μg/kg; i.v.) increases blood pressure in male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR)[3]. Animal Model: 12-15 weeks-old male and female SHR[2] Dosage: 5 μg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection Result: Induceed a significant increase of MABP after 1 min in male SHR. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 519.7±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H34O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 350.492 |
| Flash Point | 176.1±18.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 350.245697 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 3.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.548 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319-H336 |
| Supplemental HS | Repeated exposure may cause skin dryness or cracking. |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P304 + P340 + P312-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F;Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R36;R66;R67 |
| Safety Phrases | S16;S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 1231 3/PG 2 |
|
P2X1-initiated p38 signalling enhances thromboxane A2-induced platelet secretion and aggregation.
Thromb. Haemost. 112(1) , 142-50, (2014) ATP released by activated platelets can serve as a positive feedback machinery to amplify platelet responses by activating P2X1 receptors. It has, however, not been defined how P2X1 activities influen... |
|
|
Thromboxane A(2) receptor stimulation promotes closure of the rat ductus arteriosus through enhancing neointima formation.
PLoS ONE 9(4) , e94895, (2014) Ductus arteriosus (DA) closure follows constriction and remodeling of the entire vessel wall. Patent ductus arteriosus occurs when the DA does not close after birth, and this condition is currently tr... |
|
|
A platelet P-selectin test predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndromes treated with aspirin and clopidogrel.
Platelets 25(8) , 612-8, (2014) There is wide variation in response to antiplatelet therapy and high on-treatment platelet reactivity is associated with adverse cardiovascular events. The objective here was to determine whether the ... |
| 5-Heptenoic acid, 7-[(1R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-1-octen-1-yl]-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl]-, (5Z)- |
| (5Z)-7-{(1R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-Hydroxy-1-octen-1-yl]-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl}-5-heptenoic acid |
| MFCD00135238 |
| U 46619,(5Z)-7-[(1R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-Hydroxy-1-octenyl]-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-yl]-5-heptenoicacid |