Lodoxamide tromethamine
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 08:51:35
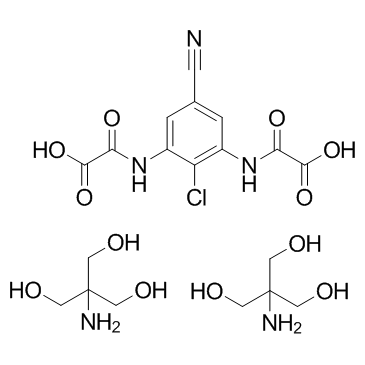
Lodoxamide tromethamine structure
|
Common Name | Lodoxamide tromethamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 63610-09-3 | Molecular Weight | 553.90500 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 827.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H28ClN5O12 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 454.3ºC | |
Use of Lodoxamide tromethamineLodoxamide tromethamine (U 42585 E) is a medication for the treatment of prophylaxis of mast cell-mediated allergic disease. |
| Name | Lodoxamidetromethamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Lodoxamide tromethamine (U 42585 E) is a medication for the treatment of prophylaxis of mast cell-mediated allergic disease. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | lodoxamide inhibits compound 48/80-induced histamine release and ionophore-induced 45Ca influx with associated histamine release in purified rat peritoneal mast cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | Lodoxamide has been demonstrated to have cromolyn-like activity when studied in the rat peritoneal mast cell assay (PCA) model3 and in Ascaris antigen-sensitized rhesus monkeys. When given intravenously, orally, or intrabronchially by aerosol, lodoxamide significantly inhibits the increased respiratory frequency and decreased tidal volume induced by antigen challenge in Ascaris-sensitized. anesthetized rhesus monkeys[1]. Addition of lodoxamide tromethamine to Euro-Collins or University of Wisconsin solution results in a marked decrease in lung reperfusion injury as demonstrated by increased oxygenation, decreased microvascular permeability, and increased compliance[2]. Patients treated with lodoxamide tromethamine demonstrate an improvement in daytime breathing difficulty, cough, sputum production, and sleep[3]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 827.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H28ClN5O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 553.90500 |
| Flash Point | 454.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 553.14200 |
| PSA | 330.01000 |
| InChIKey | JJOFNSLZHKIJEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N#Cc1cc(NC(=O)C(=O)O)c(Cl)c(NC(=O)C(=O)O)c1.NC(CO)(CO)CO.NC(CO)(CO)CO |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Hazard Codes | N |
|---|
| LodoxaMide troMethaMineon |
| Lodoxamide (tromethamine) |

