Trans-2-Hexenal
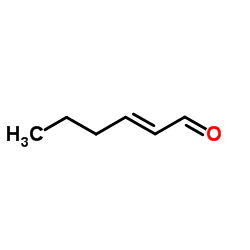
Trans-2-Hexenal structure
|
Common Name | Trans-2-Hexenal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6728-26-3 | Molecular Weight | 98.143 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 146.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 38.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Trans-2-HexenalTrans-2-Hexenal can be used for the determination of low-molecular-weight carbonyl compounds which are reactive with biological nucleophiles in biological samples[1]. |
| Name | trans-2-hexenal |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Trans-2-Hexenal can be used for the determination of low-molecular-weight carbonyl compounds which are reactive with biological nucleophiles in biological samples[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Determination of low-molecular-weight carbonyl compounds[1] |
| References |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 146.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O |
| Molecular Weight | 98.143 |
| Flash Point | 38.3±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 98.073166 |
| PSA | 17.07000 |
| LogP | 1.58 |
| Vapour density | 3.4 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 4.6±0.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.422 |
| InChIKey | MBDOYVRWFFCFHM-SNAWJCMRSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCC=CC=O |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H226-H302-H311-H317 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P312 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R10;R21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S16-S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 1988 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | MP5900000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
|
Identification of olfactory receptor neurons in Uraba lugens (Lepidoptera: Nolidae) and its implications for host range.
J. Insect Physiol. 78 , 33-46, (2015) Phytophagous insects detect volatile compounds produced by host and non-host plants, using species-specific sets of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). To investigate the relationship between the range... |
|
|
Mosquito odorant receptor for DEET and methyl jasmonate.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(46) , 16592-7, (2014) Insect repellents are important prophylactic tools for travelers and populations living in endemic areas of malaria, dengue, encephalitis, and other vector-borne diseases. DEET (N,N-diethyl-3-methylbe... |
|
|
Comparison of Aroma-Active Volatiles in Oolong Tea Infusions Using GC-Olfactometry, GC-FPD, and GC-MS.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 7499-510, (2015) The aroma profile of oolong tea infusions (Dongdingwulong, DDWL; Tieguanyin, TGY; Dahongpao, DHP) were investigated in this study. Gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O) with the method of aroma inten... |
| (e)-2-hexena |
| VH1U4 &&E Form |
| 2-Hexenal, (2E)- |
| FEMA 2560 |
| (E)-2-Hexenal |
| HEXENAL-2 |
| trans-2-Hexenal |
| Leaf aldehyde |
| EINECS 229-778-1 |
| 2-trans-Hexenal |
| Hex-2(E)-enal |
| 3-propylacrolein |
| (2E)-2-Hexenal |
| (E)-hex-2-enal |
| (E)-2-hexanal |
| (E)-Hexenal |
| T2 HEXENAL |
| 2-(E)-hexenal |
| MFCD00007008 |
| trans-hex-2-enal |
| (2E)-hexenal |
| trans-2-hexanal |
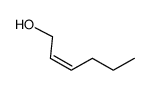 CAS#:928-94-9
CAS#:928-94-9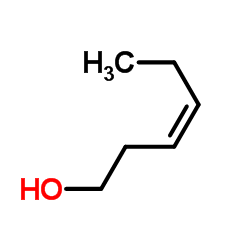 CAS#:928-96-1
CAS#:928-96-1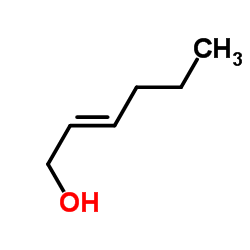 CAS#:928-95-0
CAS#:928-95-0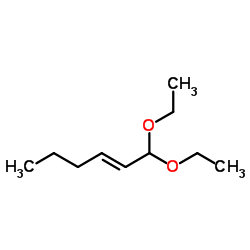 CAS#:67746-30-9
CAS#:67746-30-9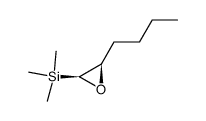 CAS#:85260-47-5
CAS#:85260-47-5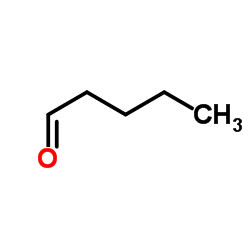 CAS#:110-62-3
CAS#:110-62-3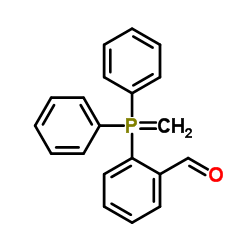 CAS#:2136-75-6
CAS#:2136-75-6 CAS#:114120-74-0
CAS#:114120-74-0 CAS#:86254-72-0
CAS#:86254-72-0 CAS#:112025-97-5
CAS#:112025-97-5 CAS#:108555-43-7
CAS#:108555-43-7 CAS#:98-01-1
CAS#:98-01-1 CAS#:496-64-0
CAS#:496-64-0 CAS#:88-14-2
CAS#:88-14-2 CAS#:13419-69-7
CAS#:13419-69-7 CAS#:1401094-48-1
CAS#:1401094-48-1 CAS#:1401094-49-2
CAS#:1401094-49-2
