Maltose

Maltose structure
|
Common Name | Maltose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69-79-4 | Molecular Weight | 342.297 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 667.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H22O11 | Melting Point | 110ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 357.8±31.5 °C | |
Use of MaltoseMaltose is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. Maltose is a reducing sugar. |
| Name | maltose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Maltose is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. Maltose is a reducing sugar. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Maltose is the two-unit member of the amylose homologous series, the key structural motif of starch. When beta-amylase breaks down starch, it removes two glucose units at a time, producing maltose. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 667.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 110ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C12H22O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 342.297 |
| Flash Point | 357.8±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 342.116211 |
| PSA | 189.53000 |
| LogP | -3.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.652 |
| InChIKey | GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-GXGLMDGZSA-N |
| SMILES | OCC1OC(OC2C(CO)OC(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | - |
| HS Code | 1702900090 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Carbohydrate Research, , vol. 360, p. 93 - 101,9 Carbohydrate Research, , vol. 360, p. 93 - 101 |
|
~% 
Maltose CAS#:69-79-4 |
| Literature: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, , vol. 59, # 8 p. 4148 - 4155 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Soluble expression and purification of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand using Escherichia coli.
J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25(2) , 274-9, (2015) Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) is a critical factor in osteoclastogenesis. It makes osteoclasts differentiate and multinucleate in bone remodeling. In the present study, R... |
|
|
Bioengineering of bacteria to assemble custom-made polyester affinity resins.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81(1) , 282-91, (2014) Proof of concept for the in vivo bacterial production of a polyester resin displaying various customizable affinity protein binding domains is provided. This was achieved by engineering various protei... |
|
|
Direct recognition of the C-terminal polylysine residues of nonstop protein by Ltn1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 453(3) , 642-7, (2014) When mRNAs lack stop codons, errors in gene expression and coding of aberrant proteins that are harmful in cells can result. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a 180-kDa E3-ubiquitin ligase, Ltn1 has been k... |
| 4-O-a-D-glucopyranosyl-b-D-glucopyranose |
| δ-Maltose |
| Martos-10 |
| δ-(+)-maltose |
| β-D-Glucopyranose, 4-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl- |
| Maltose |
| Maltos |
| 4-O-α-δ-glucopyranosyl-δ-glucose |
| b-Maltose |
| Maltose (8CI) |
| 4-O-α-D-Glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranose |
| EINECS 200-716-5 |
| b-D-glucopyranose, 4-O-a-D-glucopyranosyl- |
| Advantose 100 |
| d-maltose |
| MFCD00135877 |

 CAS#:3767-28-0
CAS#:3767-28-0 CAS#:473-90-5
CAS#:473-90-5 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7 CAS#:3371-50-4
CAS#:3371-50-4 CAS#:35997-20-7
CAS#:35997-20-7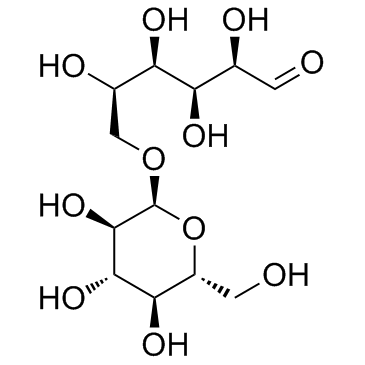 CAS#:499-40-1
CAS#:499-40-1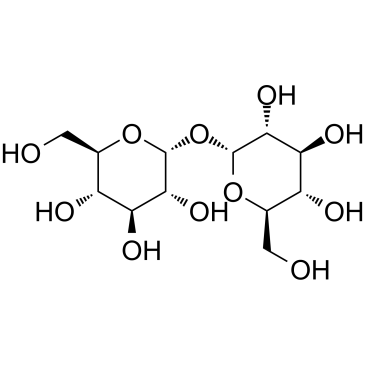 CAS#:99-20-7
CAS#:99-20-7
