Moclobemide

Moclobemide structure
|
Common Name | Moclobemide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 71320-77-9 | Molecular Weight | 268.739 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 447.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H17ClN2O2 | Melting Point | 137°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 224.6±27.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of MoclobemideMoclobemide(Ro111163) is a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) selective for isoform A (RIMA) used to treat major depressive disorder.Target: Monoamine OxidaseMoclobemide orally administered 2 hours before decapitation preferentially inhibits MAO-A and PEA in rat brain with ED50 of 7.6 μmol/kg and 78 μmol/kg, respectively. Moclobemide orally administered 2 hours before decapitation preferentially inhibits MAO-A and PEA in rat liver with ED50 of 8.4 μmol/kg and 6.6 μmol/kg, respectively. Moclobemide (0.1 mM), which inhibits brain MAO-A activity by over 80%, does not affect benzylamine oxidase (rat heart) and diamine oxidase (rat small intestine) activity in vitro [1]. Moclobemide (10 mM-100 mM) includes in the culture medium during anoxia or with glutamate significantly increases in a concentration-dependent manner the amount of surviving neurons compared to controls in neuronal-astroglial cultures from rat cerebral cortex [2].Moclobemide (10 mg/kg p.o.) induces a significant decrease of all monoamine metabolites measured in rat brain [1]. Moclobemide, given via the drinking water (4.5 mg/kg/day), produces significant decreases in adrenal weight of rats after 5 (-23%) and 7 weeks (-16%) of treatment. Moclobemide upregulates hippocampal mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) levels in rats by 65%, 76% and 19% at 2 weeks, 5 weeks and 7 weeks of treatment, and upregulates Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) levels in this limbic brain structure by 10% at 5 weeks. Moclobemide treatment (5 weeks, 4.5 mg/kg/day) significantly attenuates stress (30 min novel environment)-induced plasma ACTH (-35%) and corticosterone (-29%) levels [3]. |
| Name | moclobemide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Moclobemide(Ro111163) is a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) selective for isoform A (RIMA) used to treat major depressive disorder.Target: Monoamine OxidaseMoclobemide orally administered 2 hours before decapitation preferentially inhibits MAO-A and PEA in rat brain with ED50 of 7.6 μmol/kg and 78 μmol/kg, respectively. Moclobemide orally administered 2 hours before decapitation preferentially inhibits MAO-A and PEA in rat liver with ED50 of 8.4 μmol/kg and 6.6 μmol/kg, respectively. Moclobemide (0.1 mM), which inhibits brain MAO-A activity by over 80%, does not affect benzylamine oxidase (rat heart) and diamine oxidase (rat small intestine) activity in vitro [1]. Moclobemide (10 mM-100 mM) includes in the culture medium during anoxia or with glutamate significantly increases in a concentration-dependent manner the amount of surviving neurons compared to controls in neuronal-astroglial cultures from rat cerebral cortex [2].Moclobemide (10 mg/kg p.o.) induces a significant decrease of all monoamine metabolites measured in rat brain [1]. Moclobemide, given via the drinking water (4.5 mg/kg/day), produces significant decreases in adrenal weight of rats after 5 (-23%) and 7 weeks (-16%) of treatment. Moclobemide upregulates hippocampal mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) levels in rats by 65%, 76% and 19% at 2 weeks, 5 weeks and 7 weeks of treatment, and upregulates Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) levels in this limbic brain structure by 10% at 5 weeks. Moclobemide treatment (5 weeks, 4.5 mg/kg/day) significantly attenuates stress (30 min novel environment)-induced plasma ACTH (-35%) and corticosterone (-29%) levels [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 447.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 137°C |
| Molecular Formula | C13H17ClN2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 268.739 |
| Flash Point | 224.6±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 268.097870 |
| PSA | 41.57000 |
| LogP | 0.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.550 |
| InChIKey | YHXISWVBGDMDLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(NCCN1CCOCC1)c1ccc(Cl)cc1 |
| Storage condition | Room temp |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39 |
| RIDADR | 3249 |
| RTECS | CV2462000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Antidepressant-like effect of the novel MAO inhibitor 2-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole (2-DMPI) in mice.
Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 39(1) , 31-9, (2012) Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors were the first antidepressant drugs to be prescribed and are still used today with great success, especially in patients resistant to other antidepressants. In this ... |
|
|
[Serotonin syndrome in the course of drug-poisoning--case presentation].
Prz. Lek. 68(8) , 523-6, (2011) Serotonin syndrome is caused by excess serotonin in the central nervous system. It usually occurs as adverse drug-therapy (neuroleptic agents, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, serotonin reuptake inhibito... |
|
|
[Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome as the cause of atypical depression].
Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 79(9) , 531-4, (2011) Sleep apnoea is a common disorder presenting with somatic comorbidities and psychiatric symptoms. This case report describes a 43-year-old man with an organic depressive disorder due to obstructive sl... |
| 4-chloro-N-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]benzamide |
| Moclamide |
| moclbemide |
| Manefix |
| Moclobemide |
| aurorix |
| 4-Chloro-N-(2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl)benzamide |
| 4-Chloro-N-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl]benzamide |
| MFCD00865388 |
| Moclobemidum |
| MODOBEMDE |
| ro11-1163 |
| Moclaime |
| Benzamide, 4-Chloro-N-(2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl)- |
| p-Chloro-N-(2-morpholinoethyl)benzamide |
| UNII-PJ0Y7AZB63 |
| manerix |
| Benzamide, 4-chloro-N-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl]- |
| Moclamine |
 CAS#:2038-03-1
CAS#:2038-03-1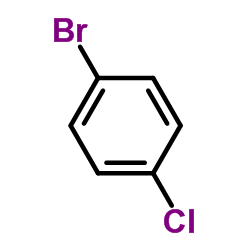 CAS#:106-39-8
CAS#:106-39-8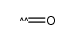 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2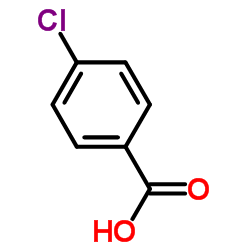 CAS#:74-11-3
CAS#:74-11-3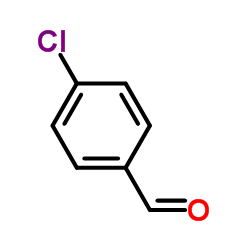 CAS#:104-88-1
CAS#:104-88-1 CAS#:637-87-6
CAS#:637-87-6 CAS#:32417-60-0
CAS#:32417-60-0 CAS#:110-91-8
CAS#:110-91-8 CAS#:51847-02-0
CAS#:51847-02-0