Adenine
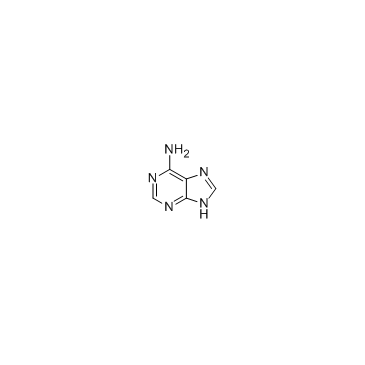
Adenine structure
|
Common Name | Adenine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73-24-5 | Molecular Weight | 135.127 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 243.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N5 | Melting Point | 360-365ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100.9±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of AdenineAdenine is a purine derivative and a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry. Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analogAdenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), andprotein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. The shape of adenine is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.In older literature, adenine was sometimes called Vitamin B4. It is no longer considered a true vitamin or part of the Vitamin B complex. However, two B vitamins, niacin and riboflavin, bind with adenine to form the essential cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), respectively. Hermann Emil Fischer was one of the early scientists to study adenine. Experiments performed in 1961 by Joan Oró have shown that a large quantity of adenine can be synthesized from the polymerization of ammonia with fivehydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecules in aqueous solution, whether this has implications for the origin of life on Earth is under debate. |
| Name | adenine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Adenine is a purine derivative and a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry. Target: Nucleoside antimetabolite/analogAdenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), andprotein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA and RNA. The shape of adenine is complementary to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA.In older literature, adenine was sometimes called Vitamin B4. It is no longer considered a true vitamin or part of the Vitamin B complex. However, two B vitamins, niacin and riboflavin, bind with adenine to form the essential cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), respectively. Hermann Emil Fischer was one of the early scientists to study adenine. Experiments performed in 1961 by Joan Oró have shown that a large quantity of adenine can be synthesized from the polymerization of ammonia with fivehydrogen cyanide (HCN) molecules in aqueous solution, whether this has implications for the origin of life on Earth is under debate. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[1]. Reader V. The assay of vitamin B(4). Biochem J. 1930;24(6):1827-31. |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 243.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 360-365ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N5 |
| Molecular Weight | 135.127 |
| Flash Point | 100.9±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 135.054489 |
| PSA | 80.48000 |
| LogP | -2.12 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.954 |
| Water Solubility | 0.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AU6125000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2936290090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Multifactorial analysis of conditional reprogramming of human keratinocytes.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0116755, (2015) Co-culture of human primary epithelial cells with irradiated 3T3 fibroblast feeder cells (J2 cells) and the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (Y) allows for the unrestricted growth of cells of epithelial o... |
|
|
Vegetables' juice influences polyol pathway by multiple mechanisms in favour of reducing development of oxidative stress and resultant diabetic complications.
Pharmacogn. Mag. 10(Suppl 2) , S383-91, (2014) Hyperglycemia induced generation of free radicals and consequent development of oxidative stress by polyol pathway is one of the crucial mechanisms stirring up development of diabetic complications. W... |
|
|
Dynamic switching of active promoter and enhancer domains regulates Tet1 and Tet2 expression during cell state transitions between pluripotency and differentiation.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 35(6) , 1026-42, (2015) The Tet 5-methylcytosine dioxygenases catalyze DNA demethylation by producing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and further oxidized products. Tet1 and Tet2 are highly expressed in mouse pluripotent cells and d... |
| 7(9)H-purin-6-ylamine |
| Ade |
| 1H-Purine-6-amine |
| 1H-Purine, 6-amino- |
| Vitamin- B4 |
| Adenin |
| 1,9-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-imine |
| 9H-Purine-6-amine |
| EINECS 200-796-1 |
| adensoine |
| Crytidine |
| 6H-Purin-6-imine, 1,9-dihydro- |
| 1H-Purin-6-amine |
| 9H-Purin-6-yl-amin |
| 9H-Purin-6-amin |
| 9H-Adenine |
| T56 BM DN FN HNJ IZ |
| Leuco-4 |
| 9H-Purin-6-amine |
| MFCD00041790 |
| Adenine |
| ADENINE(P) |
| usafcb-18 |
| 6-aminopurine |
| 6-amino-Purine |
| Vitamin B4 |
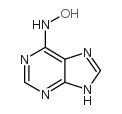 CAS#:5667-20-9
CAS#:5667-20-9 CAS#:65758-94-3
CAS#:65758-94-3 CAS#:122-51-0
CAS#:122-51-0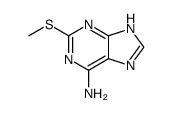 CAS#:1198-83-0
CAS#:1198-83-0 CAS#:3647-48-1
CAS#:3647-48-1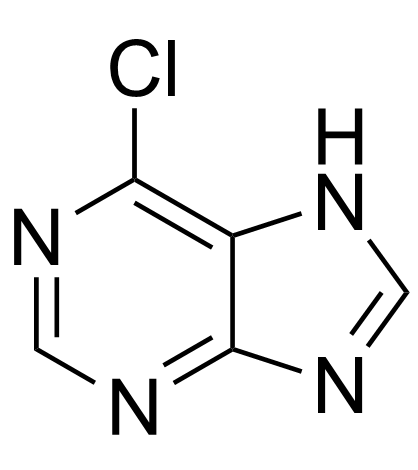 CAS#:87-42-3
CAS#:87-42-3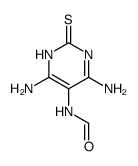 CAS#:753502-74-8
CAS#:753502-74-8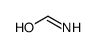 CAS#:77287-34-4
CAS#:77287-34-4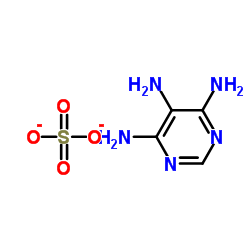 CAS#:49721-45-1
CAS#:49721-45-1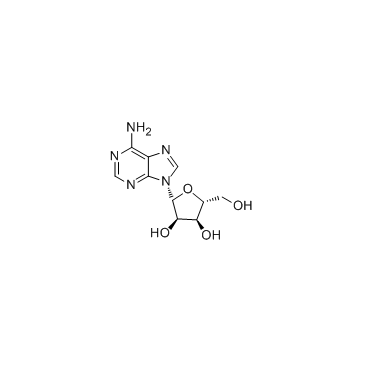 CAS#:58-61-7
CAS#:58-61-7 CAS#:4261-14-7
CAS#:4261-14-7 CAS#:3691-50-7
CAS#:3691-50-7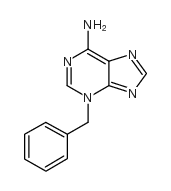 CAS#:7280-81-1
CAS#:7280-81-1 CAS#:22917-81-3
CAS#:22917-81-3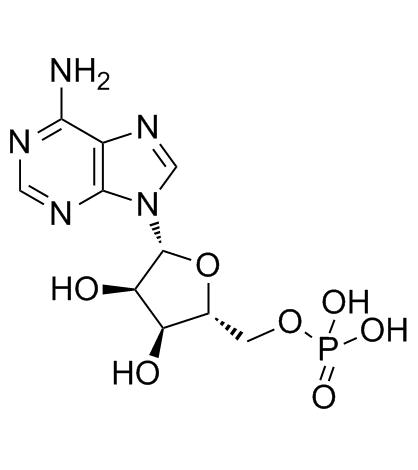 CAS#:61-19-8
CAS#:61-19-8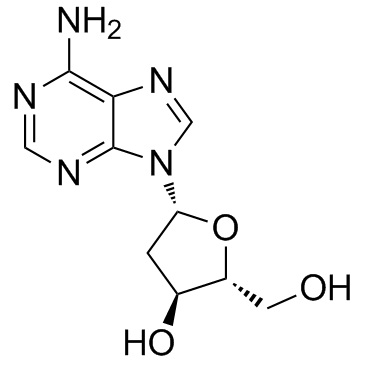 CAS#:958-09-8
CAS#:958-09-8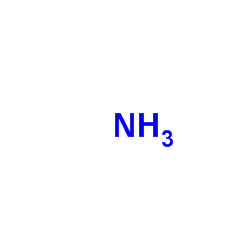 CAS#:7664-41-7
CAS#:7664-41-7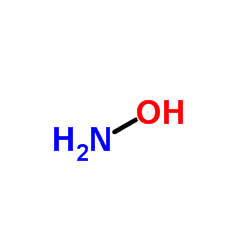 CAS#:7803-49-8
CAS#:7803-49-8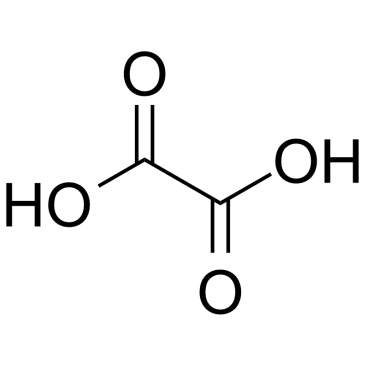 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7
