SCH 28080
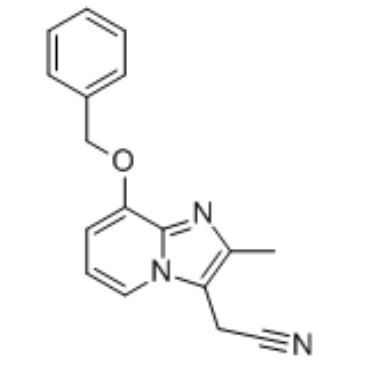
SCH 28080 structure
|
Common Name | SCH 28080 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 76081-98-6 | Molecular Weight | 277.32 | |
| Density | 1.16g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H15N3O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of SCH 28080SCH28080 inhibits gastric H+/K+-ATPase by K+-competitive binding, with an IC50 value of 20 nM in rabbit microsomal membranes[1]. Antisecretory and cytoprotective activities[2]. |
| Name | 2-(2-methyl-8-phenylmethoxyimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)acetonitrile |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | SCH28080 inhibits gastric H+/K+-ATPase by K+-competitive binding, with an IC50 value of 20 nM in rabbit microsomal membranes[1]. Antisecretory and cytoprotective activities[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 20 nM (H+/K+-ATPase, rabbit microsomal membranes)[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.16g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H15N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 277.32 |
| Exact Mass | 277.12200 |
| PSA | 50.32000 |
| LogP | 3.28778 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.615 |
| InChIKey | PYKJFEPAUKAXNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1nc2c(OCc3ccccc3)cccn2c1CC#N |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~% 
SCH 28080 CAS#:76081-98-6 |
| Literature: Kaminski, James J.; Bristol, James A.; Puchalski, Chester; Lovey, Raymond G.; Elliott, Arthur J.; et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1985 , vol. 28, # 7 p. 876 - 892 |
|
~% 
SCH 28080 CAS#:76081-98-6 |
| Literature: Schering Corporation Patent: US4450164 A1, 1984 ; |
|
~% 
SCH 28080 CAS#:76081-98-6 |
| Literature: Schering Corporation Patent: US4450164 A1, 1984 ; |
|
~67% 
SCH 28080 CAS#:76081-98-6 |
| Literature: Kaminski, James J.; Bristol, James A.; Puchalski, Chester; Lovey, Raymond G.; Elliott, Arthur J.; et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1985 , vol. 28, # 7 p. 876 - 892 |
|
~% 
SCH 28080 CAS#:76081-98-6 |
| Literature: Kaminski, James J.; Bristol, James A.; Puchalski, Chester; Lovey, Raymond G.; Elliott, Arthur J.; et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1985 , vol. 28, # 7 p. 876 - 892 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Inorganic phosphate uptake in Trypanosoma cruzi is coupled to K(+) cycling and to active Na(+) extrusion.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1830(8) , 4265-73, (2013) Orthophosphate (Pi) is a central compound in the metabolism of all organisms, including parasites. There are no reports regarding the mechanisms of Pi acquisition by Trypanosoma cruzi.(32)Pi influx wa... |
|
|
Potential role of sodium-proton exchangers in the low concentration arsenic trioxide-increased intracellular pH and cell proliferation.
PLoS ONE 7(12) , e51451, (2012) Arsenic main inorganic compound is arsenic trioxide (ATO) presented in solution mainly as arsenite. ATO increases intracellular pH (pHi), cell proliferation and tumor growth. Sodium-proton exchangers ... |
|
|
Mechanisms of secretion-associated shrinkage and volume recovery in cultured rabbit parietal cells.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292(3) , G711-7, (2007) We have previously shown that stimulation of acid secretion in parietal cells causes rapid initial cell shrinkage, followed by Na(+)/H(+) exchange-mediated regulatory volume increase (RVI). The factor... |
| MFCD00834620 |

![2-(8-(benzyloxy)-2-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)acetamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/424/79707-50-9.png)
![2-(8-hydroxy-2-methylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)acetonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/279/79707-49-6.png)

![2-methyl-8-(phenylmethoxy)-3-[(trimethylammonio)methyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine iodide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/072/79707-59-8.png)
