Dichloroacetyl chloride
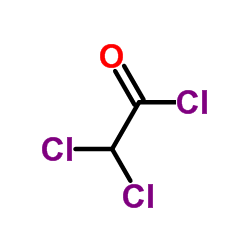
Dichloroacetyl chloride structure
|
Common Name | Dichloroacetyl chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79-36-7 | Molecular Weight | 147.388 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 107.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2HCl3O | Melting Point | < 25ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 31.8±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | dichloroacetyl chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 107.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | < 25ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C2HCl3O |
| Molecular Weight | 147.388 |
| Flash Point | 31.8±22.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 145.909302 |
| PSA | 17.07000 |
| LogP | 1.27 |
| Vapour Pressure | 27.0±0.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.467 |
| InChIKey | FBCCMZVIWNDFMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(Cl)C(Cl)Cl |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with water, alcohols and oxidizing agents. Fumes in air. |
| Water Solubility | MAY DECOMPOSE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H314-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R35;R50 |
| Safety Phrases | S9-S26-S45-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 1765 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | AO6650000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to predict haloacetic acids (HAA) mutagenicity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008) The risk of the presence of haloacetic acids in drinking water as chlorination by-products and the shortage of experimental mutagenicity data for most of them requires a research work. This paper desc... |
|
|
Autoimmune response in MRL+/+ mice following treatment with dichloroacetyl chloride or dichloroacetic anhydride.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 216(2) , 248-55, (2006) Dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) is formed from trichloroethene (TCE), which is implicated in inducing/accelerating autoimmune response. Due to its potent acylating activity, DCAC may convert proteins t... |
|
|
Photocatalysis of gaseous trichloroethylene (TCE) over TiO2: the effect of oxygen and relative humidity on the generation of dichloroacetyl chloride (DCAC) and phosgene.
J. Hazard. Mater. 146(1-2) , 302-8, (2007) Batch photocatalytic degradation of 80+/-2.5 ppm V trichloroethylene (TCE) was conducted to investigate the effect of the oxygen and relative humidity (RH) on the formation of the dichloroacetyl chlor... |
| Acetyl chloride, 2,2-dichloro- |
| Dichloroacetyl chloride |
| 2,2-Dichloroacetyl chloride |
| EINECS 201-199-9 |
| MFCD00000840 |
 CAS#:79-43-6
CAS#:79-43-6 CAS#:76-02-8
CAS#:76-02-8 CAS#:79-34-5
CAS#:79-34-5 CAS#:156-60-5
CAS#:156-60-5 CAS#:67-66-3
CAS#:67-66-3 CAS#:463-51-4
CAS#:463-51-4 CAS#:79-01-6
CAS#:79-01-6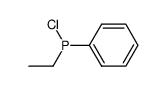 CAS#:15849-83-9
CAS#:15849-83-9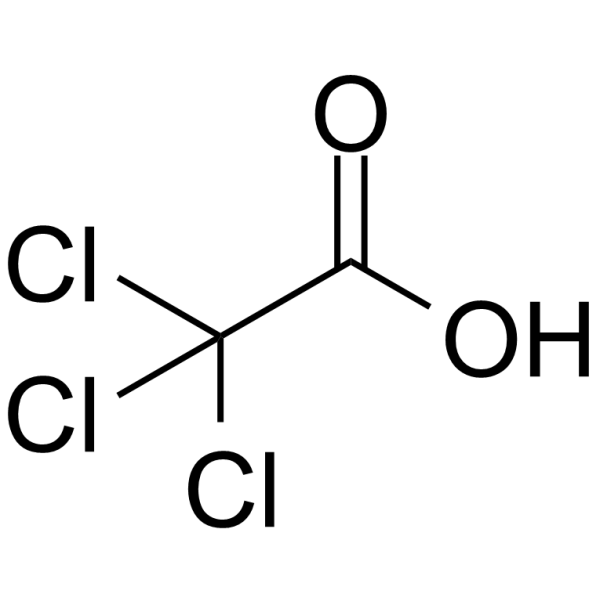 CAS#:76-03-9
CAS#:76-03-9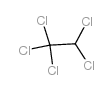 CAS#:76-01-7
CAS#:76-01-7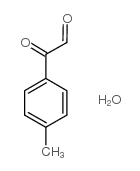 CAS#:1075-47-4
CAS#:1075-47-4 CAS#:4974-59-8
CAS#:4974-59-8 CAS#:10565-20-5
CAS#:10565-20-5 CAS#:104767-34-2
CAS#:104767-34-2 CAS#:10579-62-1
CAS#:10579-62-1![[[chloro(phenyl)methylidene]amino] 2,2-dichloroacetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/454/105755-38-2.png) CAS#:105755-38-2
CAS#:105755-38-2 CAS#:59867-68-4
CAS#:59867-68-4 CAS#:52836-31-4
CAS#:52836-31-4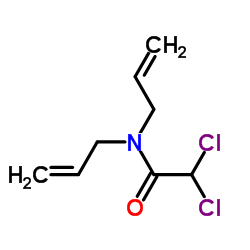 CAS#:37764-25-3
CAS#:37764-25-3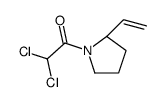 CAS#:146405-63-2
CAS#:146405-63-2
