苯酚
一般危化品
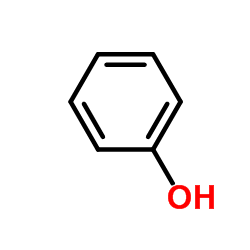
苯酚结构式
|
常用名 | 苯酚 | 英文名 | Phenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 108-95-2 | 分子量 | 94.111 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 181.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H6O | 熔点 | 40-42 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 79.4±0.0 °C | |
| 符号 |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Comparative in vitro study on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI tracking of adipose tissue-derived progenitor cells.
PLoS ONE 9(9) , e108055, (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using measurement of the transverse relaxation time (R2*) is to be considered as a promising approach for cell tracking experiments to evaluate the fate of transplanted progenitor cells and develop successful cell therapies fo... |
|
|
Influence of Fungal Strain, Temperature, and Wetness Duration on Infection of Grapevine Inflorescences and Young Berry Clusters by Botrytis cinerea.
Phytopathology 105(3) , 325-33, (2015) The effect of temperature and wetness duration on infection of Vitis vinifera inflorescences (from "inflorescence clearly visible" to "end of flowering" stages) and young berry clusters (at "fruit swelling" and "berries groat-sized" stages) by Botrytis cinere... |
|
|
Mechanisms of expression and translocation of major fission yeast glucose transporters regulated by CaMKK/phosphatases, nuclear shuttling, and TOR.
Mol. Biol. Cell 26(2) , 373-86, (2015) Hexose transporters are required for cellular glucose uptake; thus they play a pivotal role in glucose homeostasis in multicellular organisms. Using fission yeast, we explored hexose transporter regulation in response to extracellular glucose concentrations. ... |
|
|
Silencing urease: a key evolutionary step that facilitated the adaptation of Yersinia pestis to the flea-borne transmission route.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(52) , 18709-14, (2014) The arthropod-borne transmission route of Yersinia pestis, the bacterial agent of plague, is a recent evolutionary adaptation. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, the closely related food-and water-borne enteric species from which Y. pestis diverged less than 6,400 ... |
|
|
N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing.
Nature 519(7544) , 482-5, (2015) The first step in the biogenesis of microRNAs is the processing of primary microRNAs (pri-miRNAs) by the microprocessor complex, composed of the RNA-binding protein DGCR8 and the type III RNase DROSHA. This initial event requires recognition of the junction b... |
|
|
Microbial iron mats at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and evidence that Zetaproteobacteria may be restricted to iron-oxidizing marine systems.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0119284, (2015) Chemolithoautotrophic iron-oxidizing bacteria play an essential role in the global iron cycle. Thus far, the majority of marine iron-oxidizing bacteria have been identified as Zetaproteobacteria, a novel class within the phylum Proteobacteria. Marine iron-oxi... |
|
|
The ubiquitin-selective chaperone Cdc48/p97 associates with Ubx3 to modulate monoubiquitylation of histone H2B.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(17) , 10975-86, (2014) Cdc48/p97 is an evolutionary conserved ubiquitin-dependent chaperone involved in a broad array of cellular functions due to its ability to associate with multiple cofactors. Aside from its role in removing RNA polymerase II from chromatin after DNA damage, li... |
|
|
Dual growth factor-immobilized microspheres for tissue reinnervation: in vitro and preliminary in vivo studies.
J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 26(5) , 322-37, (2015) Growth factors (GFs) (basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and/or nerve growth factor (NGF))-immobilized polycaprolactone (PCL)/Pluronic F127 microspheres were prepared using an isolated particulate-melting method and the sequential binding of heparin and GF... |
|
|
CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE8 differentially regulates plant immunity to fungal pathogens through kinase-dependent and -independent functions in Arabidopsis.
Plant Cell 26(10) , 4149-70, (2014) CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE8 (CDK8) is a widely studied component of eukaryotic Mediator complexes. However, the biological and molecular functions of plant CDK8 are not well understood. Here, we provide evidence for regulatory functions of Arabidopsis thaliana C... |
|
|
Hydrophobic and charged residues in the C-terminal arm of hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase regulate initiation and elongation.
J. Virol. 89(4) , 2052-63, (2015) The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) is essential for viral genome replication. Crystal structures of the HCV RdRp reveal two C-terminal features, a β-loop and a C-terminal arm, suitably located for involvement in positioning com... |