(Rs)-4-溴高鹅膏蕈氨酸
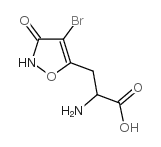
(Rs)-4-溴高鹅膏蕈氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | (Rs)-4-溴高鹅膏蕈氨酸 | 英文名 | (RS)-1-(3-FLUOROPHENYL)ETHYLAMINE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 71366-32-0 | 分子量 | 251.03500 | |
| 密度 | 1.95g/cm3 | 沸点 | 443.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H7BrN2O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 221.9ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Turning behaviour and catalepsy after injection of excitatory amino acids into rat substantia nigra.
Neurosci. Lett. 23 , 337, (1981) Unilateral injection of AMPA ((R,S)-alpha-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid), 4-bromohomoibotenic acid, kainic acid and N-methylaspartic acid into the caudal part of substantia nigra induced ipsilateral turning behaviour. AMPA and kainic acid were... |
|
|
Excitatory amino acid agonists. Enzymic resolution, X-ray structure, and enantioselective activities of (R)- and (S)-bromohomoibotenic acid.
J. Med. Chem. 32(10) , 2254-60, (1989) The enantiomers of alpha-amino-4-bromo-3-hydroxy-5-isoxazolepropionic acid (4-bromohomoibotenic acid, Br-HIBO, 1) a selective and potent agonist at one class of the central (S)-glutamic acid receptors, were prepared with an enantiomeric excess higher than 98.... |
|
|
Structural determinants of agonist-specific kinetics at the ionotropic glutamate receptor 2.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102(34) , 12053-8, (2005) Glutamate receptors (GluRs) are the most abundant mediators of the fast excitatory neurotransmission in the human brain. Agonists will, after activation of the receptors, induce different degrees of desensitization. The efficacy of agonists strongly correlate... |
|
|
Identification of amino acid residues in GluR1 responsible for ligand binding and desensitization.
J. Neurosci. 21(9) , 3052-62, (2001) Although GluR1(o) and GluR3(o) are homologous at the amino acid level, GluR3(o) desensitizes approximately threefold faster than GluR1(o). By creating chimeras of GluR1(o) and GluR3(o) and point amino acid exchanges in their S2 regions, two residues were iden... |
|
|
4-Methylhomoibotenic acid activates a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor coupled to phosphoinositide hydrolysis.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283(2) , 742-9, (1997) Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are a family of glutamate receptors that are coupled to a variety of second messenger systems through GTP-binding proteins. Of the eight subtypes cloned to date, mGluR1 and mGluR5 are coupled to phosphoinositide hydro... |
|
|
4-Bromohomoibotenic acid selectively activates a 1-aminocyclopentane-1S,3R-dicarboxylic acid-insensitive metabotropic glutamate receptor coupled to phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat cortical slices.
J. Neurochem. 63(1) , 133-9, (1994) Glutamate activates a family of receptors, known as metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), that are coupled to various second messenger systems through G proteins. All mGluR subtypes characterized to date in rat brain slices are activated by the glutamate... |
|
|
The non-depolarizing D-form of bromohomoibotenic acid enhances depolarizations evoked by the L-form or quisqualate.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 230(3) , 383-6, (1993) The D-enantiomer of bromohomoibotenic acid (Br-HIBO) was inactive in electrophysiological experiments when administered alone, but enhanced depolarizations evoked by L-Br-HIBO or quisqualate when co-administered with these agonists. In addition, quisqualate i... |
|
|
Agonist discrimination between AMPA receptor subtypes.
Neuroreport 11(12) , 2643-8, (2000) The lack of subtype-selective compounds for AMPA receptors (AMPA-R) led us to search for compounds with such selectivity. Homoibotenic acid analogues were investigated at recombinant GluR1o, GluR2o(R), GluR3o and GluR1o + 3o receptors expressed in Sf9 insect ... |
|
|
Effects of bromohomoibotenate on metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Neuroreport 5(18) , 2417-20, (1994) (S)-Bromohomoibotenic acid [(S)-BrHIbo] stereoselectively antagonized glutamate-stimulated phosphoinositide (PI) hydrolysis in baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells expressing mGluR1a in a competitive manner with an IC50 of 250 microM. However, (S)-BrHIbo did not i... |
|
|
Stereoselectivity of AMPA receptors. Hansen, J
Mol. Neuropharmacol. 2 , 51-55, (1992)
|