4α-佛波醇-12,13-二癸酸酯
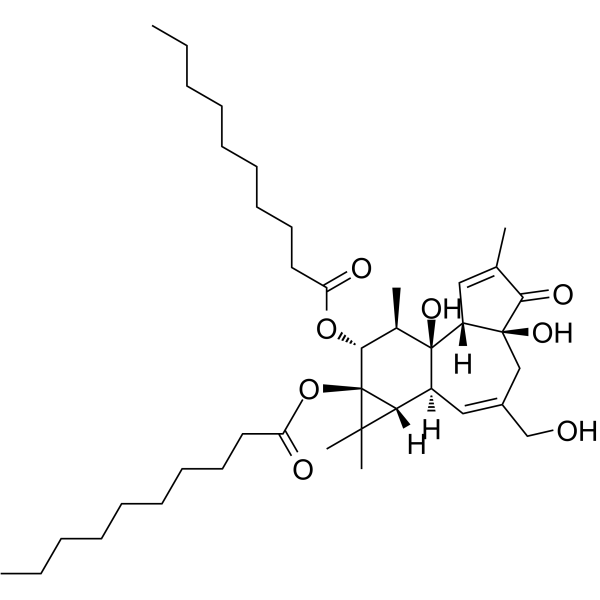
4α-佛波醇-12,13-二癸酸酯结构式

|
常用名 | 4α-佛波醇-12,13-二癸酸酯 | 英文名 | 4alpha-PDD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 27536-56-7 | 分子量 | 672.93100 | |
| 密度 | 1.14g/cm3 | 沸点 | 734.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C40H64O8 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 212.4ºC | |
| 符号 |


GHS06, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
|
Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPV4 channels in migration of rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.
Pflugers Arch. 464(3) , 261-72, (2012) Pulmonary hypertension, the main disease of the pulmonary circulation, is characterized by an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance, involving proliferation and migration of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMC). However, cellular and molecular m... |
|
|
Ca2+ entry via alpha1G and TRPV4 channels differentially regulates surface expression of P-selectin and barrier integrity in pulmonary capillary endothelium.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 297(4) , L650-7, (2009) Pulmonary vascular endothelial cells express a variety of ion channels that mediate Ca(2+) influx in response to diverse environmental stimuli. However, it is not clear whether Ca(2+) influx from discrete ion channels is functionally coupled to specific outco... |
|
|
Salt intake augments hypotensive effects of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4: functional significance and implication.
Hypertension 53(2) , 228-35, (2009) To test the hypothesis that activation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channel conveys a hypotensive effect that is enhanced during salt load, male Wistar rats fed a normal-sodium (0.5%) or high-sodium (HS; 4%) diet for 3 weeks were gi... |
|
|
Axonal neuropathy-associated TRPV4 regulates neurotrophic factor-derived axonal growth.
J. Biol. Chem. 287(8) , 6014-24, (2012) Spinal muscular atrophy and hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies are characterized by muscle weakness and atrophy caused by the degenerations of peripheral motor and sensory nerves. Recent advances in genetics have resulted in the identification of misse... |
|
|
Characterization of the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of doxycycline and minocycline in different experimental models.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 576(1-3) , 171-9, (2007) Tetracyclines induce anti-inflammatory effects unrelated to their antimicrobial activities. We investigated the effect induced by minocycline and doxycycline in models of nociceptive and inflammatory pain, edema, fever, cell migration and formation of fibrova... |
|
|
Phosphorylation on the Ser 824 residue of TRPV4 prefers to bind with F-actin than with microtubules to expand the cell surface area.
Cell. Signal. 24(3) , 641-51, (2012) Previously, we demonstrated that the transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) cation channel, a member of the TRP vanilloid subfamily, is one of the serum glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase1 (SGK1) authentic substrate proteins, and that the Ser 824... |
|
|
Phenotypic heterogeneity in lung capillary and extra-alveolar endothelial cells. Increased extra-alveolar endothelial permeability is sufficient to decrease compliance.
J. Surg. Res. 143(1) , 70-7, (2007) In acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary vascular permeability increases, causing intravascular fluid and protein to move into the lung's interstitium. The classic model describing the formation of pulmonary edema suggests that fluid crossing the cap... |
|
|
4α-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate activates cultured mouse dorsal root ganglia neurons independently of TRPV4.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 168(3) , 761-72, (2013) The Ca(2+) -permeable cation channel TRPV4 is activated by mechanical disturbance of the cell membrane and is implicated in mechanical hyperalgesia. Nerve growth factor (NGF) is increased during inflammation and causes mechanical hyperalgesia. 4α-phorbol 12,1... |
|
|
Forward genetic analysis reveals multiple gating mechanisms of TRPV4.
J. Biol. Chem. 285(26) , 19884-90, (2010) TRPV4 is a polymodal cation channel gain-of-function (GOF) allele which causes skeletal dysplasia in humans. To better understand its gating, we screened for additional GOF alleles based on their ability to block yeast proliferation. Repeatedly, only a limite... |
|
|
Functional TRPV4 channels are expressed in mouse skeletal muscle and can modulate resting Ca2+ influx and muscle fatigue.
Pflugers Arch. 461(1) , 115-22, (2011) Skeletal muscle contraction is basically controlled by Ca(2+) release and its reuptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. However, the long-term maintenance of muscle function requires an additional Ca(2+) influx from extracellular. Several mechanisms seem to c... |