维生素D3
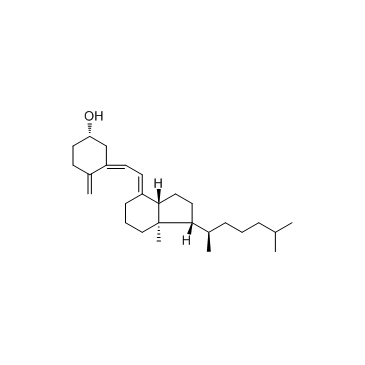
维生素D3结构式

|
常用名 | 维生素D3 | 英文名 | Vitamin D3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 67-97-0 | 分子量 | 384.638 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 496.4±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C27H44O | 熔点 | 83-86 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 214.2±15.1 °C | |
| 符号 |


GHS06, GHS08 |
信号词 | Danger |
维生素D3用途Cholecalciferol(Vitamin D3)是维生素D的天然存在形式,代谢激活后能诱导细胞分化和癌细胞增殖。 |
| 中文名 | 维生素 D3 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | calciol |
| 中文别名 | 胆钙化醇 | 9,10-开环胆甾-5,7,10(19)-三烯-3beta-醇 | 活化7-去氢胆固醇 | 维生素D3 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Cholecalciferol(Vitamin D3)是维生素D的天然存在形式,代谢激活后能诱导细胞分化和癌细胞增殖。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点实验 |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 496.4±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 83-86 °C(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C27H44O |
| 分子量 | 384.638 |
| 闪点 | 214.2±15.1 °C |
| 精确质量 | 384.339203 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 9.72 |
| 外观性状 | 结晶 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.523 |
| 储存条件 | 3本品应密封于阴凉干燥处避光保存。 |
| 稳定性 | 无色结晶。在潮湿空气中几天就氧化失活,纯结晶在棕色真空安瓿中冰箱相存放一年后仅有极微量变质。通常维生素D3比维生素D2稳定。D3存在于人和大多数动物组织中,在鱼肝油、肝、鱼子、乳汁、奶油和蛋黄等食物中含D3量丰富。人体皮肤内含有维生素D3的前体7-脱氢胆固醇,经日光或紫外线照射,可转变为D3,故多晒太阳可防止维生素D缺乏。 |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:80.73 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):186.5 3、 等张比容(90.2K):594.5 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):103.2 5、 极化率(10-24cm3):32 |
| 计算化学 | 1、 疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):7.5 2、 氢键供体数量:1 3、 氢键受体数量:1 4、 可旋转化学键数量:6 5、 拓扑分子极性表面积(TPSA):20.2 6、 重原子数量:28 7、 表面电荷:0 8、 复杂度:610 9、 同位素原子数量:0 10、 确定原子立构中心数量:5 11、 不确定原子立构中心数量:0 12、 确定化学键立构中心数量:0 13、 不确定化学键立构中心数量:2 14、 共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:白色柱状结晶或结晶性粉末,无臭无味,耐热性好,但对光不稳定,在空气中易氧化 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃):不确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):不确定 4. 熔点(ºC):84-85 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):不确定 6. 沸点(ºC, 5.2kPa):不确定 7. 折射率:不确定 8. 闪点(ºC):不确定 9. 比旋光度(º):105 º (c=0.8, EtOH 25 ºC) 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):不确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):不确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):不确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):不确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):不确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):不确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:不确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):不确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):不确定 19. 溶解性:溶于醇、醚、丙酮、氯仿及植物油,不溶于水(<0.1 g/L,20 ºC) |
|
维生素D3毒理学数据: 急性毒性:婴儿口经LDLo:39 mg/kg/34W-I;大鼠口经LD50:42 mg/kg; 小鼠口经LD50:42500 ug/kg;小鼠腹腔LD50:136 mg/kg;狗口经LD50:80 mg/kg; 繁殖:大鼠皮下注射TDLo:90 mg/kgSEX/DURATION : female 12-20 day(s) after conception; |
| 符号 |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H301 + H311-H330-H372 |
| 警示性声明 | P260-P280-P284-P301 + P310-P310 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | T+:Verytoxic; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R24/25;R26;R48/25 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S28-S36/37-S45-S28A |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK德国 | 2 |
| RTECS号 | VS2900000 |
| 包装等级 | II |
| 危险类别 | 6.1 |
| 海关编码 | 2936240000 |
1.将7-脱氢胆固醇溶于乙醇,用紫外光照射开环,反应液浓缩、冷冻、过滤,滤液通氮减压浓缩至干,得粗维生素D3液。再经精制而得维生素D3。
2.从植物油或酵母中提取人体不能吸收的7-脱氢胆固醇,溶于氯仿或环己烷,用紫外线照射转化成维生素
D3
3.将7-脱氢胆固醇溶于乙醇,用紫外光照射开环,反应液浓缩、冷冻、过滤,滤液通氮减压浓缩至干,得粗维生素D3,再经精制即可。
| 海关编码 | 2936240000 |
|---|
|
Effect of concentrate feeder design on performance, eating and animal behavior, welfare, ruminal health, and carcass quality in Holstein bulls fed high-concentrate diets.
J. Anim. Sci. 93 , 3018-33, (2015) A total of 240 Holstein bulls (121 ± 2.0 kg initial BW; 99 ± 1.0 d of age), from 2 consecutive fattening cycles, were randomly allocated in 1 of 6 pens and assigned to 1 of the 3 treatments consisting... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
| Oxarol |
| Vitamin D3 |
| Ebivit |
| Cholecalciferolum |
| (3S,5Z,7E)-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10-trien-3-ol |
| (1S,3Z)-3-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R)-1,5-Dimethylhexyl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-yliden}ethyliden]-4-methylidencyclohexanol |
| Micro-Dee |
| (5Z,7E)-(3S)-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol |
| Deparal |
| FeraCol |
| MFCD00078131 |
| Prezios |
| cholecalciferol |
| (1S,3Z)-3-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R)-1,5-dimethylhexyl]octahydro-7a-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-4-methylenecyclohexanol |
| UNII-1C6V77QF41 |
| Vi-De3 |
| MC 1275 |
| Granuvit D3 |
| Devaron |
| (3b,5Z,7E)-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol |
| rampage |
| vitamin D3 powder |
| D3-Vicotrat |
| NEO Dohyfral D3 |
| (1S,3Z)-3-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R)-1,5-dimethylhexyl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]-4-methylidenecyclohexanol |
| Vigantol |
| EINECS 200-673-2 |
| (1S,3Z)-4-Methylene-3-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-7a-methyl-1-[(2R)-6-methyl-2-heptanyl]octahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]cyclohexanol |
| colecalciferol |
| Videkhol |
| (3β,Z,7E)-9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol |
| [3H]-Vitamin D3 |
| 9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3b-ol |
| calciol |
| Provitina |
| VITAMIN D |

 CAS号98854-76-3
CAS号98854-76-3 CAS号105764-33-8
CAS号105764-33-8 CAS号75-91-2
CAS号75-91-2 CAS号13403-10-6
CAS号13403-10-6![叔丁基[3-[2-(二苯基膦酰)亚乙基]-4-亚甲基环己基氧基]二甲基硅烷结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/214/100858-27-3.png) CAS号100858-27-3
CAS号100858-27-3![{[(3Z)-3-(2-Chloroethylidene)-4-methylenecyclohexyl]oxy}(dimethyl )(2-methyl-2-propanyl)silane结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/289/138313-18-5.png) CAS号138313-18-5
CAS号138313-18-5 CAS号19356-17-3
CAS号19356-17-3





