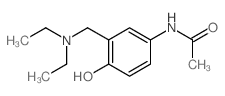
86-42-0
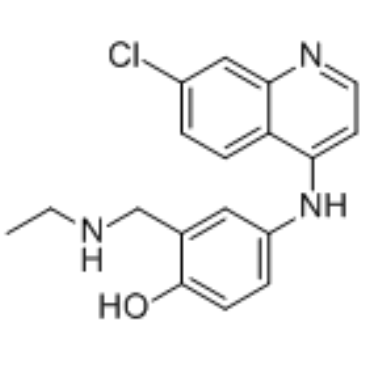
| Name | amodiaquine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
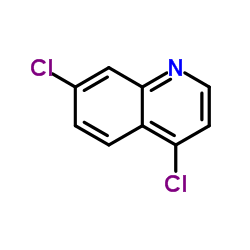
4-[(7-Chloro-4-quinolinyl)amino]-2-[(diethylamino)methyl]phenol
SN 10,751 CAM-AQI Camoquinal 4-[(7-Chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]-2-[(diethylamino)methyl]phenol Camoquine EINECS 201-669-3 4-[(7-chloro-4-quinolinyl)amino]-2-[(diethylamino) methyl]phenol MFCD00552927 Camoquin Flavoquine Miaquin aminodiaquine Amodiaquine CAM-AQ1 Camochin |
| Description | Amodiaquine (Amodiaquin), a 4-aminoquinoline class of antimalarial agent, is a potent and orally active histamine N-methyltransferase inhibitor. Amodiaquine is also a Nurr1 agonist and specifically binds to Nurr1-LBD (ligand binding domain) with an EC50 of ~20 μM. Anti-inflammatory effect[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: ~20 μM (Nurr1-LBD (ligand binding domain))[1] Histamine N-methyltransferase[3] |
| In Vitro | Amodiaquine (10-20 μM; 4 hours) treatment suppresses LPS-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, interleukin-6, TNF-α and iNOS) in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Amodiaquine (5 μM; 24 hours) significantly inhibits neurotoxin (6-OHDA-induced cell death in primary dopamine cells as examined by the number of TH+ neurons and dopamine uptake. The neuroprotective effect of Amodiaquine is also observed in rat PC12 cells[1]. RT-PCR[1] Cell Line: Primary microglia Concentration: 10 µM, 15 µM, 20 µM Incubation Time: 4 hours Result: Suppressed LPS-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, interleukin-6, TNF-α and iNOS) in a dose-dependent manner. |
| In Vivo | Amodiaquine (40 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 3 days; male ICR mice) treatment diminishes perihematomal activation of microglia/macrophages and astrocytes. Amodiaquine also suppresses ICH-induced mRNA expression of IL-1β, CCL2 and CXCL2, and ameliorated motor dysfunction of mice[2]. Animal Model: Male ICR mice (8-10 weeks of age) induced ntracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)[2] Dosage: 40 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 3 days Result: Diminished perihematomal activation of microglia/macrophages and astrocytes. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 478.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208°C |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22ClN3O |
| Molecular Weight | 355.861 |
| Flash Point | 242.9±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 355.145142 |
| PSA | 48.39000 |
| LogP | 4.77 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.669 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25-S8 |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|
~% 
86-42-0 |
| Literature: WO2013/138200 A1, ; Paragraph 0073; 0074 ; |
|
~% 
86-42-0 |
| Literature: Zhurnal Obshchei Khimii, , vol. 25, p. 331,335; engl. Ausg. S. 313, 316 Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 70, p. 1363,1372 Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 72, p. 1024 |
|
~% 
86-42-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 37, # 9 p. 1362 - 1370 |
|
~% 
86-42-0 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 70, p. 1363,1372 Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 72, p. 1024 |
|
~% 
86-42-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 37, # 9 p. 1362 - 1370 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933499090. other compounds containing in the structure a quinoline or isoquinoline ring-system (whether or not hydrogenated), not further fused. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |