Glutaric acid

Glutaric acid structure
|
Common Name | Glutaric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 110-94-1 | Molecular Weight | 132.115 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 302.9±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O4 | Melting Point | 95-98 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 151.2±16.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Glutaric acidGlutaric acid induces oxidative stress in brain of young rats. |
| Name | glutaric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Glutaric acid induces oxidative stress in brain of young rats. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Glutaric acid (GA) at concentrations of 1 and 2 mM is able to reduce TRAP measurement by up to 28% in a dose-dependent manner (β=0.77; P<0.001). Furthermore, a significantly inverse correlation is also verified between chemiluminescence and TRAP (β=0.81; P<0.001). Glutaric acid does not alter the activities of Cat and SOD, but strongly inhibits (up to 46%) the activity of GPx even at the lower concentration used (0.5 mM). It is observed that the metabolite inhibits this activity in a dose-dependent manner at concentrations as low as 0.05 mM[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 302.9±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-98 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 132.115 |
| Flash Point | 151.2±16.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 132.042252 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | -1.04 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.477 |
| InChIKey | JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCC(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with bases, oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 430 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | MA3740000 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2917190090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2917190090 acyclic polycarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Novel Dammarane-Type Triterpene Saponins from Panax ginseng Root.
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 63 , 927-34, (2015) Four phytochemical constituents were isolated from Panax ginseng root by repeated column chromatography (CC), medium pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC), high-speed counter current chromatography (H... |
|
|
Physiology and pathophysiology of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 16(4) , 648-69, (1993) Concentrations of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) appear to be directly dependent upon their rate of production in the brain. There is evidence that the net release of short-chain monocarbo... |
|
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population.
Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994) Organic acid concentrations were quantified by gas chromatography and the individual acids identified by mass spectrometry in urine specimens from a healthy Turkish pediatric population of ages 2 days... |
| Iressa |
| Pentanedioic acid |
| Irressat |
| 1,5-Pentanedioate |
| Propane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid |
| n-Pyrotartaric acid |
| 1,5-Pentanedioic acid |
| 1,3-propanedicarboxylic acid |
| EINECS 203-817-2 |
| hydrogen glutarate |
| Glutaric acid |
| ZD 1839 |
| Gefitinib |
| 1,3-Propanedicarboxylate |
| MFCD00004410 |
 CAS#:13246-39-4
CAS#:13246-39-4 CAS#:53715-97-2
CAS#:53715-97-2 CAS#:111-29-5
CAS#:111-29-5 CAS#:96-41-3
CAS#:96-41-3 CAS#:120-92-3
CAS#:120-92-3 CAS#:142-29-0
CAS#:142-29-0 CAS#:675-20-7
CAS#:675-20-7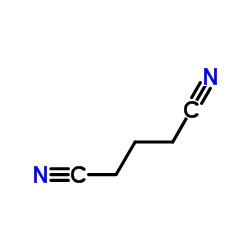 CAS#:544-13-8
CAS#:544-13-8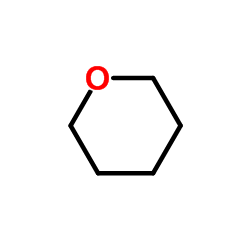 CAS#:142-68-7
CAS#:142-68-7 CAS#:5057-98-7
CAS#:5057-98-7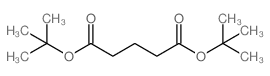 CAS#:43052-39-7
CAS#:43052-39-7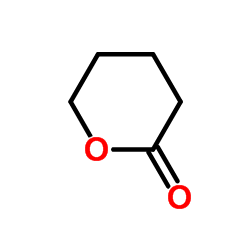 CAS#:542-28-9
CAS#:542-28-9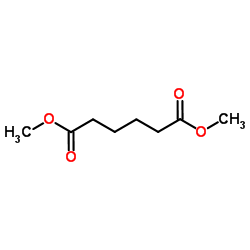 CAS#:627-93-0
CAS#:627-93-0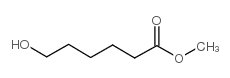 CAS#:4547-43-7
CAS#:4547-43-7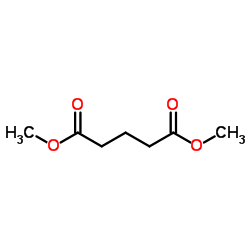 CAS#:1119-40-0
CAS#:1119-40-0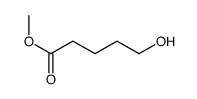 CAS#:14273-92-8
CAS#:14273-92-8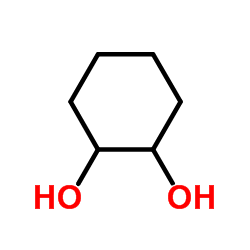 CAS#:931-17-9
CAS#:931-17-9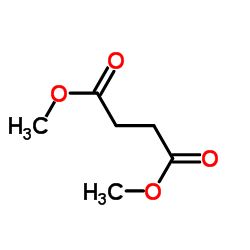 CAS#:106-65-0
CAS#:106-65-0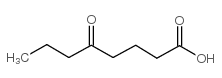 CAS#:3637-14-7
CAS#:3637-14-7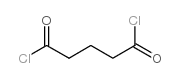 CAS#:2873-74-7
CAS#:2873-74-7
