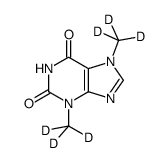
Pentoxifylline-d6

Pentoxifylline-d6 structure
|
Common Name | Pentoxifylline-d6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1185878-98-1 | Molecular Weight | 284.34400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12D6N4O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Pentoxifylline-d6Pentoxifylline-d6 (BL-191-d6) is the deuterium labeled Pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline (BL-191), a haemorheological agent, is an orally active non-selective phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor, with immune modulation, anti-inflammatory, hemorheological, anti-fibrinolytic and anti-proliferation effects. Pentoxifylline can be used for the research of peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease and a number of other conditions involving a defective regional microcirculation[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-bis(trideuteriomethyl)purine-2,6-dione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pentoxifylline-d6 (BL-191-d6) is the deuterium labeled Pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline (BL-191), a haemorheological agent, is an orally active non-selective phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor, with immune modulation, anti-inflammatory, hemorheological, anti-fibrinolytic and anti-proliferation effects. Pentoxifylline can be used for the research of peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease and a number of other conditions involving a defective regional microcirculation[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12D6N4O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 284.34400 |
| Exact Mass | 284.17600 |
| PSA | 78.89000 |
| LogP | 0.19300 |
| InChIKey | BYPFEZZEUUWMEJ-XERRXZQWSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)CCCCn1c(=O)c2c(ncn2C)n(C)c1=O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
|
~15% 
Pentoxifylline-d6 CAS#:1185878-98-1 |
| Literature: US2009/239886 A1, ; Page/Page column 27-28 ; US 20090239886 A1 |
|
~% 
Pentoxifylline-d6 CAS#:1185878-98-1 |
| Literature: WO2011/28835 A1, ; |
|
~% 
Pentoxifylline-d6 CAS#:1185878-98-1 |
| Literature: WO2011/28835 A1, ; |
| Oxpentifylline-d6 |
| Vazofirin-d6 |
| Pentoxifylline-d6 |
| 3,7-di(methyl-d3)-1-(5-oxohexyl)-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione |
| 1-(5-Oxohexyl)-3,7-(dimethyl-d6)xanthine-d6 |
| 3,7-Dihydro-3,7-(dimethyl-d6)-1-(5-oxohexyl)-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| Trental-d6 |
| 1-(5-Oxohexyl)theobromine-d6 |