Acid-C2-PEG4-C2-NHS ester
Modify Date: 2025-11-03 11:12:20
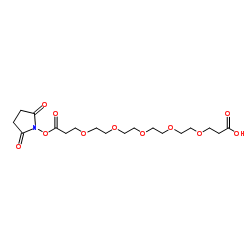
Acid-C2-PEG4-C2-NHS ester structure
|
Common Name | Acid-C2-PEG4-C2-NHS ester | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1343476-41-4 | Molecular Weight | 435.423 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 574.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H29NO11 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 301.5±32.9 °C | |
Use of Acid-C2-PEG4-C2-NHS esterAcid-C2-PEG4-C2-NHS ester is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
| Name | 19-[(2,5-Dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)oxy]-19-oxo-4,7,10,13,16-pentaoxanonadecan-1-oic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acid-C2-PEG4-C2-NHS ester is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PEGs Alkyl/ether |
| In Vitro | PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 574.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H29NO11 |
| Molecular Weight | 435.423 |
| Flash Point | 301.5±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 435.174072 |
| LogP | -3.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.509 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| 19-[(2,5-Dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)oxy]-19-oxo-4,7,10,13,16-pentaoxanonadecan-1-oic acid |
| 4,7,10,13,16-Pentaoxanonadecan-1-oic acid, 19-[(2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)oxy]-19-oxo- |