N-BOC-2,2′-(ethylenedioxy)bis(ethylamine)
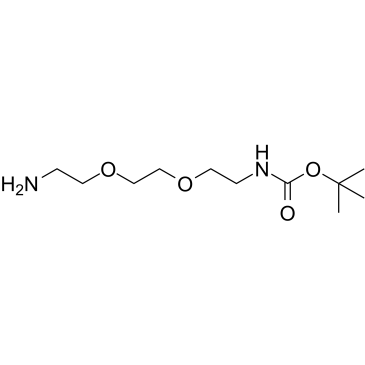
N-BOC-2,2′-(ethylenedioxy)bis(ethylamine) structure
|
Common Name | N-BOC-2,2′-(ethylenedioxy)bis(ethylamine) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 153086-78-3 | Molecular Weight | 248.319 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 365.2±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H24N2O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 174.6±23.7 °C | |
Use of N-BOC-2,2′-(ethylenedioxy)bis(ethylamine)PROTAC Linker 13 is a PROTAC linker, which refers to the alkyl/ether composition. PROTAC Linker 13 can be used in the synthesis of a series of PROTACs. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[1]. |
| Name | tert-butyl N-[2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethyl]carbamate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | PROTAC Linker 13 is a PROTAC linker, which refers to the alkyl/ether composition. PROTAC Linker 13 can be used in the synthesis of a series of PROTACs. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Alkyl/ether |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 365.2±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C11H24N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 248.319 |
| Flash Point | 174.6±23.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 248.173615 |
| PSA | 82.81000 |
| LogP | 0.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.460 |
| InChIKey | OCUICOFGFQENAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NCCOCCOCCN |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
|
A modular cross-linking approach for exploring protein interactions.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125 , 2416 - 2425, (2003) A method is described for the elucidation of protein-protein interactions using novel cross-linking reagents and mass spectrometry. The method incorporates (1) a modular solid-phase synthetic strategy... |
|
|
Spinke, J., et al.
J. Phys. Chem. 99(9) , 7012-7019, (1993)
|
|
|
Sigal, G. B., et al.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 , 3789-3800, (1996)
|
| CBZ-L-Asginine-OH Hydrochloride |
| AmbotzBNN1016 |
| 2-Methyl-2-propanyl {2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethyl}carbamate |
| N-BOC-2,2′-(ethylenedioxy)bis(ethylamine) |
| Carbamic acid, N-[2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethyl]-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester |
| N-Boc-3,6-dioxa-1,8-octanediamine |
| N-Boc-3,6-dioxaoctane-1,8-diamine |
| t-Boc-N-amido-PEG2-Amine |
 CAS#:929-59-9
CAS#:929-59-9 CAS#:24424-99-5
CAS#:24424-99-5 CAS#:950683-55-3
CAS#:950683-55-3![N-[2-[2-[2-[(2,2-dimethyl-1-phenylpropoxy)carbonylamino]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]carbamate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/440/796865-54-8.png) CAS#:796865-54-8
CAS#:796865-54-8 CAS#:58632-95-4
CAS#:58632-95-4![N-tert-butyl N-[2-(2-{2-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]ethoxy}ethoxy)ethyl]carbamate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/455/556065-62-4.png) CAS#:556065-62-4
CAS#:556065-62-4 CAS#:6627-89-0
CAS#:6627-89-0![N-{2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethyl}-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/493/556065-61-3.png) CAS#:556065-61-3
CAS#:556065-61-3 CAS#:1245727-44-9
CAS#:1245727-44-9 CAS#:59559-06-7
CAS#:59559-06-7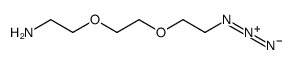 CAS#:166388-57-4
CAS#:166388-57-4 CAS#:660843-23-2
CAS#:660843-23-2![N-[2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethyl]-5-(dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/122/918827-51-7.png) CAS#:918827-51-7
CAS#:918827-51-7![N-[2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]ethyl]benzamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/325/923567-96-8.png) CAS#:923567-96-8
CAS#:923567-96-8![N-[2-[2-[2-[(3-tert-butyl-4-formyl-2,6-dimethylphenoxy)carbonylamino]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]carbamate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/299/627539-91-7.png) CAS#:627539-91-7
CAS#:627539-91-7
