D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate
Modify Date: 2025-08-22 21:16:25
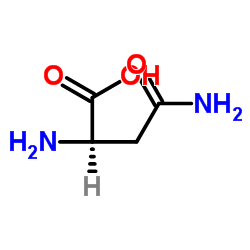
D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate structure
|
Common Name | D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2058-58-4 | Molecular Weight | 132.118 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 438.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 | Melting Point | 280ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 218.7±27.3 °C | |
Use of D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrateD-Asparagine (H-D-Asn-OH) is a competitive inhibitor of L-Asparagine hydrolysis with a Ki value of 0.24 mM. D-Asparagine is a source of nitrogen for yeast strains. D-Asparagine is a good substrate for the external yeast asparaginase but is a poor substrate for the internal enzyme[1]. |
| Name | D-asparagine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Asparagine (H-D-Asn-OH) is a competitive inhibitor of L-Asparagine hydrolysis with a Ki value of 0.24 mM. D-Asparagine is a source of nitrogen for yeast strains. D-Asparagine is a good substrate for the external yeast asparaginase but is a poor substrate for the internal enzyme[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 438.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 280ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 132.118 |
| Flash Point | 218.7±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 132.053497 |
| PSA | 106.41000 |
| LogP | -1.51 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| InChIKey | DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-UWTATZPHSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(=O)CC(N)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
In several cell types tumour suppressor p53 induces apoptosis largely via Puma but Noxa can contribute.
Cell Death Differ. 15(6) , 1019-29, (2008) The ability of p53 to induce apoptosis in cells with damaged DNA is thought to contribute greatly to its tumour suppressor function. P53 has been proposed to induce apoptosis via numerous transcriptio... |
| D-Asparagine |
| H-D-Asn-OH·H2O |
| D-b-Asparagine |
| EINECS 218-163-3 |
| Asparagine, DL- |
| H-D-Asn-OH.H2O |
| Aspartic Acid b-Amide |
| 2-Aminosuccinamic acid |
| H-D-Asn-OH |
| (R)-2,4-Diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid |
| a-Aminosuccinamic acid |
| (2R)-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid |
| Asparagine D-form |
| Asparagine |
| Asparamide |
| (R)-2-Aminosuccinamic acid |
| Asn |
| MFCD00008036 |
| D-Asparagin |
| D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate |
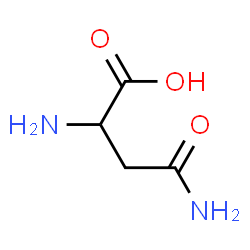 CAS#:3130-87-8
CAS#:3130-87-8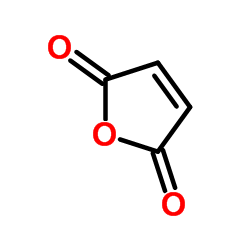 CAS#:108-31-6
CAS#:108-31-6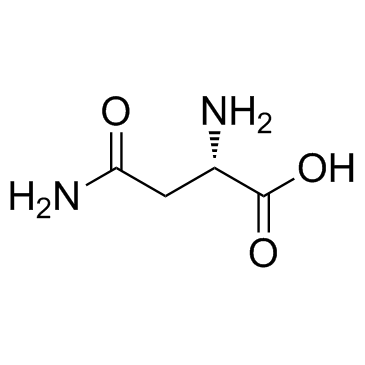 CAS#:70-47-3
CAS#:70-47-3 CAS#:101-41-7
CAS#:101-41-7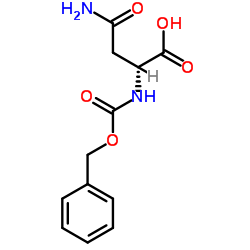 CAS#:4474-86-6
CAS#:4474-86-6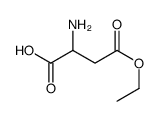 CAS#:21860-86-6
CAS#:21860-86-6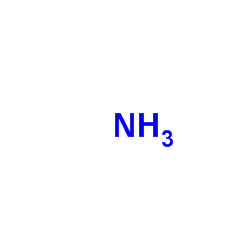 CAS#:7664-41-7
CAS#:7664-41-7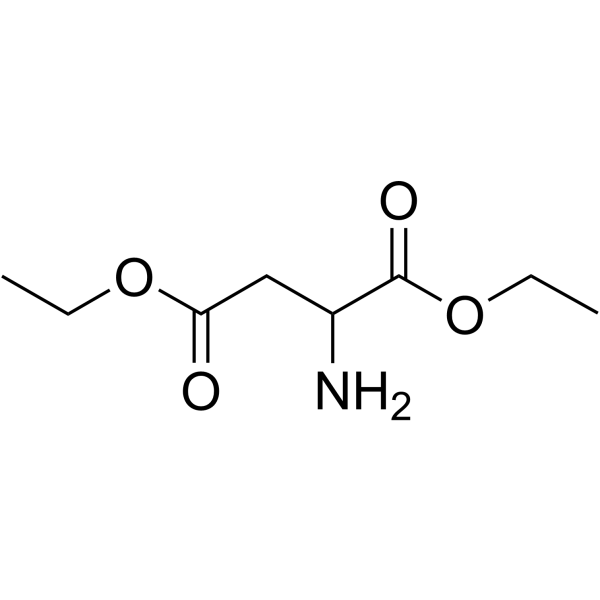 CAS#:43101-48-0
CAS#:43101-48-0 CAS#:7732-18-5
CAS#:7732-18-5 CAS#:636-61-3
CAS#:636-61-3 CAS#:33239-40-6
CAS#:33239-40-6 CAS#:617-45-8
CAS#:617-45-8 CAS#:1783-96-6
CAS#:1783-96-6![N2-[(4-Methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-L-asparagine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/335/92142-18-2.png) CAS#:92142-18-2
CAS#:92142-18-2
