Sodium Dichloroacetate
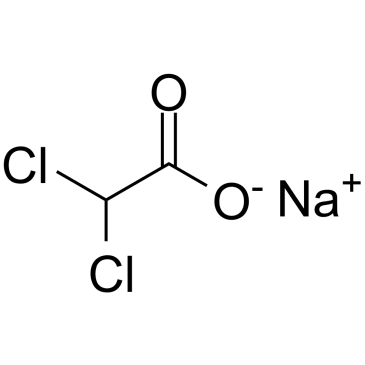
Sodium Dichloroacetate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium Dichloroacetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2156-56-1 | Molecular Weight | 150.924 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 194ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2HCl2NaO2 | Melting Point | 198 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Sodium DichloroacetateSodium dichloroacetate is a metabolic regulator in cancer cells' mitochondria with anticancer activity. Sodium dichloroacetate inhibits PDHK, resulting in decreased lactic acid in the tumor microenvironment. Sodium dichloroacetate increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and promotes cancer cell apoptosis. Sodium dichloroacetate also works as NKCC inhibitor[1]. |
| Name | sodium,2,2-dichloroacetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Sodium dichloroacetate is a metabolic regulator in cancer cells' mitochondria with anticancer activity. Sodium dichloroacetate inhibits PDHK, resulting in decreased lactic acid in the tumor microenvironment. Sodium dichloroacetate increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and promotes cancer cell apoptosis. Sodium dichloroacetate also works as NKCC inhibitor[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PDHK; Reactive oxygen species (ROS); Apoptosis; NKCC[1] |
| In Vitro | Sodium dichloroacetate increases ROS generation in mitochondria. Sodium dichloroacetate affects cell growth and viability through the ROS production increase derived from the promotion of oxidative metabolism. The effects of Sodium dichloroacetate on multiple myeloma cell viability, cell cycle arrest, and apoptotic cell death were associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDK) inhibition, restored pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity, and the promotion of oxidative metabolism in association with increased intracellular ROS production which depends on the Sodium dichloroacetate dose. The Sodium dichloroacetate effects cooperated with C I inhibition promoting the oxidative stress in rat VM-M3 glioblastoma cells. Increased ROS levels in Sodium dichloroacetate-treated cancer cells are related to the induction of apoptosis associated with the increased cytochrome c expression. Sodium dichloroacetate causes ROS-dependent T-cell differentiation[1]. |
| In Vivo | The NKCC1 RNA expression levels in Sodium dichloroacetate-treated gonad-intact and castrated males are significantly decreased, and no such effect is determined in the gonad-intact and castrated female Sodium dichloroacetate-treated rats[1]. A single Sodium dichloroacetate dose causes a significantly higher 24 h diuresis in Wistar male rats, and the increased diuresis is related to NKCC2 inhibition. The NKCC2 is more abundant in kidneys of intact females compared to intact males, with a greater transporter density in Sprague-Dawley female rats[1]. The oral Sodium dichloroacetate bioavailability in naïve male rats dosed 5, 20 and 100 mg/kg is significantly lower than in GSTζ-depleted ones (10%, 13%, 81% and 31%, 75%, 100%, respectively). The liver extraction of Sodium dichloroacetate in the GSTζ-depleted rats has linear kinetics, but it decreases with the metabolism saturation at higher doses[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 194ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 198 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C2HCl2NaO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 150.924 |
| Exact Mass | 149.925125 |
| PSA | 40.13000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.196mmHg at 25°C |
| InChIKey | LUPNKHXLFSSUGS-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | O=C([O-])C(Cl)Cl.[Na+] |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
| Water Solubility | soluble in cold water |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P281-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | AG9275000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
Dual-targeting of aberrant glucose metabolism in glioblastoma.
J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res 34 , 14, (2015) Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and malignant primary brain tumor. In contrast to some other tumor types, aberrant glucose metabolism is an important component of GBM growth and chemoresistance.... |
|
|
A Korean female patient with thiamine-responsive pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency due to a novel point mutation (Y161C)in the PDHA1 gene.
J. Korean Med. Sci. 21 , 800-4, (2006) Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC) deficiency is mostly due to mutations in the X-linked E1alpha subunit gene (PDHA1). Some of the patients with PDHC deficiency showed clinical improvements with th... |
|
|
Sensitization of Glioblastoma Cells to Irradiation by Modulating the Glucose Metabolism.
Mol. Cancer Ther. 14 , 1794-804, (2015) Because radiotherapy significantly increases median survival in patients with glioblastoma, the modulation of radiation resistance is of significant interest. High glycolytic states of tumor cells are... |
| Acetic acid, 2,2-dichloro-, sodium salt (1:1) |
| EINECS 218-461-3 |
| MFCD00070489 |
| Cpc 211 |
| sodium salt of dichloroacetate |
| Sodium dichloroacetate [USAN] |
| Natriumdichloracetat |
| dichloroacetate de sodium |
| ACETIC ACID,DICHLORO-,SODIUM SALT |
| Sodium dichloroacetate |
| Dichloroctan sodny [Czech] |
| dichloroacetic acid sodium salt |
| sodium dichlroacetate |
| dichloroacetate sodium salt |
| Sodium 2,2-dichloroacetate |
 CAS#:4124-30-5
CAS#:4124-30-5 CAS#:74304-83-9
CAS#:74304-83-9
