Oxipurinol
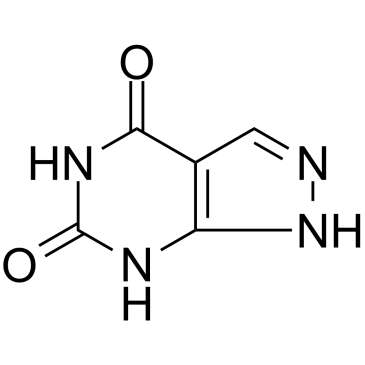
Oxipurinol structure
|
Common Name | Oxipurinol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2465-59-0 | Molecular Weight | 152.11 | |
| Density | 2.19g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 662.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O2 | Melting Point | 300 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 354.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of OxipurinolOxipurinol (Oxipurinol), the major active metabolite of Allopurinol, is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Oxipurinol can be used to regulate blood urate levels and treat gout[1]. |
| Name | alloxanthine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Oxipurinol (Oxipurinol), the major active metabolite of Allopurinol, is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Oxipurinol can be used to regulate blood urate levels and treat gout[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Allopurinol is rapidly metabolized (half-life approximately 1 h) to its active metabolite oxypurinol. Oxypurinol is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidoreductase and has a considerably longer elimination half-life (approximately 23 h)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 2.19g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 662.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.11 |
| Flash Point | 354.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 152.03300 |
| PSA | 94.92000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 3.5E-18mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.989 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Evaluation of neuronal protective effects of xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitors on severe whole-brain ischemia in mouse model and analysis of xanthine oxidoreductase activity in the mouse brain.
Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 55(1) , 77-85, (2015) Global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) often result in high mortality. Free radicals play an important role in global cerebral I/R. Xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) inhibitors, such as allopurino... |
|
|
Systematic and Molecular Basis of the Antibacterial Action of Quinoxaline 1,4-Di-N-Oxides against Escherichia coli.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0136450, (2015) Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides (QdNOs) are widely known as potent antibacterial agents, but their antibacterial mechanisms are incompletely understood. In this study, the transcriptomic and proteomic pro... |
| OXYPURINOL |
| BW-55-5 |
| Alloxanthine |
| OXIPURINOL |
| 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6-diol |
| 4,6-Dihydropyrazolo Pyrimidine |
| MFCD00056934 |
| 1,7-Dihydro |
| 4,6-DIHYDROXYPYRAZOLO[3,4-D]PYRIMIDINE |
| 4,6-Dihydroxy-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine |
| EINECS 219-570-9 |
| Oxyprim |
| Oxoallopurinol |
![6H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-6-one,4-amino-1,7-dihydro- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/242/5472-41-3.png) CAS#:5472-41-3
CAS#:5472-41-3![4,6-Dichloro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/370/42754-96-1.png) CAS#:42754-96-1
CAS#:42754-96-1![4-Hydroxy-6-aminopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/217/2537-04-4.png) CAS#:2537-04-4
CAS#:2537-04-4![4-amino-6-mercaptopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/317/23771-52-0.png) CAS#:23771-52-0
CAS#:23771-52-0![1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine,6-chloro- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/107/5417-78-7.png) CAS#:5417-78-7
CAS#:5417-78-7 CAS#:16220-08-9
CAS#:16220-08-9![3-dimethylamino-2,4,8,9-tetrazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,6-triene-5-thione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/184/7152-45-6.png) CAS#:7152-45-6
CAS#:7152-45-6![3-chloro-N-methyl-2,4,8,9-tetrazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-2,4,7,10-tetraen-5-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/439/7251-92-5.png) CAS#:7251-92-5
CAS#:7251-92-5![3-chloro-2,4,8,9-tetrazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-1,3,6-triene-5-thione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/358/7508-59-0.png) CAS#:7508-59-0
CAS#:7508-59-0![4,6-dimethoxy-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/384/98277-30-6.png) CAS#:98277-30-6
CAS#:98277-30-6
