CHIR-98014
Modify Date: 2024-01-15 19:17:55
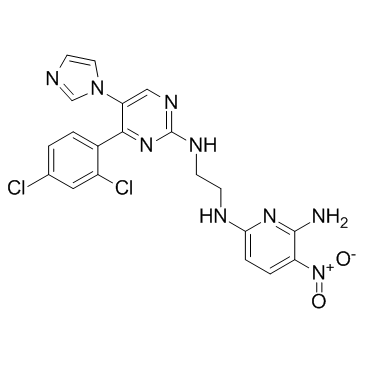
CHIR-98014 structure
|
Common Name | CHIR-98014 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 252935-94-7 | Molecular Weight | 486.314 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 839.0±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H17Cl2N9O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 461.2±37.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CHIR-98014CHIR-98014 is a potent, cell-permeable GSK-3 inhibitor with IC50s of 0.65 and 0.58 nM for GSK-3α and GSK-3β, respectively; it shows less potent activities against cdc2 and erk2. |
| Name | 6-N-[2-[[4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-imidazol-1-ylpyrimidin-2-yl]amino]ethyl]-3-nitropyridine-2,6-diamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | CHIR-98014 is a potent, cell-permeable GSK-3 inhibitor with IC50s of 0.65 and 0.58 nM for GSK-3α and GSK-3β, respectively; it shows less potent activities against cdc2 and erk2. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
GSK-3β:0.58 nM (IC50) GSK-3α:0.65 nM (IC50) cdc2:3700 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | CHIR 98014 inhibits human GSK-3β with Ki value of 0.87 nM. CHIR 98014 causes GS stimulation in CHO-IR cells and rat hepatocytes, with EC50s of 106 nM and 107 nM, respectively[1]. CHIR-98014 (1 μM) reduces the viability of ES-CCE cells by 52%, with IC50 of 1.1 μM. Moreover, CHIR-98014 in combination with CHIR-99021 results in a significant activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in ES-D3 cells. In CHIR-98014 treated cells, the T gene expression is induced up to 2,500-fold. CHIR-98014 (1 μM) also yields around 50% Brachyury-positive cells, with EC50 of 0.32 μM[2]. CHIR98014 (10 μM) prevents loss of neurites caused by 20 μM PrP1-30 in cortical and hippocampal neurons, and substantially decreases the amount of dead cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | CHIR 98014 (30 mg/kg, i.p.) exhibits a significant reduction in fasting hyperglycemia within 4 h of treatment and shows improved glucose disposal during an ipGTT in markedly diabetic and insulin-resistant db/db mice[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Polypropylene 96-well plates are filled with 300 μL/well buffer (50 mM tris HCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 25 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM NaF, 0.01% BSA, pH 7.5) containing kinase, peptide substrate, and any activators. Information on the kinase concentration, peptide substrate, and activator for these assays is as follows: GSK-3α (27 nM, and 0.5 μM biotin-CREB peptide); GSK-3β (29 nM, and 0.5 μM biotin-CREB peptide); cdc2 (0.8 nM, and 0.5 μM biotin histone H1 peptide); erk2 (400 units/mL, and myelin basic protein-coated Flash Plate); PKC-α (1.6 nM, 0.5 μM biotin-histone H1 peptide, and 0.1 mg/mL phosphatidylserine + 0.01 mg/mL diglycerides); PKC-ζ (0.1 nM, 0.5 μM biotin-PKC-86 peptide, and 50 μg/mL phosphatidylserine + 5 μg/mL diacylglycerol); akt1 (5.55 nM, and 0.5 μM biotin phospho-AKT peptide); p70 S6 kinase (1.5 nM, and 0.5 μM biotin-GGGKRRRLASLRA); p90 RSK2 (0.049 units/mL, and 0.5 μM biotin-GGGKRRRLASLRA); c-src (4.1 units/mL, and 0.5 μM biotin-KVEKIGEGTYGVVYK); Tie2 (1 μg/mL, and 200 nM biotin-GGGGAPEDLYKDFLT); flt1 (1.8 nM, and 0.25 μM KDRY1175 [B91616] biotin-GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI-NH2); KDR (0.95 nM, and 0.25 μM KDRY1175 [B91616] biotin-GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI-NH2); bFGF receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK; 2 nM, and 0.25 μM KDRY1175 [B91616] biotin-GGGGQDGKDYIVLPI-NH2); IGF1 RTK (1.91 nM, and 1 μM biotin-GGGGKKKSPGEYVNIEFG-amide); insulin RTK (using DG44 IR cells); AMP kinase (470 units/mL, 50 μM SAMS peptide, and 300 μM AMP); pdk1 (0.25 nM, 2.9 nM unactivated Akt, and 20 μM each of DOPC and DOPS + 2 μM PIP3); CHK1 (1.4 nM, and 0.5 μM biotin-cdc25 peptide); CK1-ε (3 nM, and 0.2 μM biotin-peptide); DNA PK (see 31); and phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase (5 nM, and 2 μg/mL PI). Test compounds or controls are added in 3.5 μL of DMSO, followed by 50 μL of ATP stock to yield a final concentration of 1 μM ATP in all cell-free assays. After incubation, triplicate 100-μL aliquots are transferred to Combiplate eight plates containing 100 μL/well 50 μM ATP and 20 mM EDTA. After 1 h, the wells are rinsed five times with PBS, filled with 200 μL of scintillation fluid, sealed, left 30 min, and counted in a scintillation counter. All steps are performed at room temperature. Inhibition is calculated as 100% × (inhibited − no enzyme control)/(DMSO control − no enzyme control)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The viability of the mouse ES cells is determined after exposure to different concentrations of GSK3 inhibitors for three days using the MTT assay. The decrease of MTT activity is a reliable metabolism-based test for quantifying cell viability; this decrease correlates with the loss of cell viability. 2,000 cells are seeded overnight on gelatine-coated 96-well plates in LIF-containing ES cell medium. On the next day the medium is changed to medium devoid of LIF and with reduced serum and supplemented with 0.1-1 μM BIO, or 1-10 μM SB-216763, CHIR-99021 or CHIR-98014. Basal medium without GSK3 inhibitors or DMSO is used as control. All tested conditions are analyzed in triplicates[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Blood is obtained by shallow tail snipping at lidocaine-anesthetized tips. Blood glucose is measured directly or heparinized plasma is collected for measurement of glucose or insulin. Animals are prebled and randomized to vehicle control or GSK-3 inhibitor treatment groups. For glucose tolerance tests (GTTs), animals are fasted throughout the procedure with food removal early in the morning, 3 h before first prebleed (db/db mice), or the previous night, 16 h before the bleed (ZDF rats). When the time course of plasma glucose and insulin changes in fasting ZDF rats is measured, food is removed ∼16 h before test agent administration. The glucose challenges in the GTT are 1.35 g/kg i.p. (ipGTT) or 2 g/kg via oral gavage (oGTT). Test inhibitors are formulated as solutions in 20 mM citrate-buffered 15% Captisol or as fine suspensions in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 839.0±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H17Cl2N9O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 486.314 |
| Flash Point | 461.2±37.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 485.088226 |
| PSA | 158.85000 |
| LogP | 3.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.753 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
| 2,5-dimethyl-3-furohydrazide |
| 2,6-Pyridinediamine, N-[2-[[4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(1H-imidazol-2-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]ethyl]-3-nitro- |
| N-(2-{[4-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-5-(1H-imidazol-2-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino}ethyl)-3-nitro-2,6-pyridinediamine |
| CHIR-98014 |