| Description |
Rosuvastatin is a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase with IC50 of 11 nM. IC50 Value: 11 nM [1]Target: HMG-CoA reductasein vitro: Rosuvastatin is relatively hydrophilic and is highly selective for hepatic cells; its uptake is mediated by the liver-specific organic anion transporter OATP-C. Rosuvastatin is a high-affinity substrate for OATP-C with apparent association constant of 8.5 μM [2]. Rosuvastatin inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis in rat liver isolated hepatocytes with IC50 of 1.12 nM. Rosuvastatin causes approximately 10 times greater increase of mRNA of LDL receptors than pravastatin [1]. Rosuvastatin (100 μM) decreases the extent of U937 adhesion to TNF-α-stimulated HUVEC. Rosuvastatin inhibits the expressions of ICAM-1, MCP-1, IL-8, IL-6, and COX-2 mRNA and protein levels through inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and nuclear factor-kB in endothelial cells [3].in vivo: Rosuvastatin (3 mg/kg) daily administration for 14 days decreases plasma cholesterol levels by 26% in male beagle dogs with normal cholesterol levels. In cynomolgus monkeys, Rosuvastatin decreases plasma cholesterol levels by 22% [1]. Rosuvastatin (20 mg/kg/day) administration for 2 weeks, significantly reduces very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) in diabetes mellitus rats induced by Streptozocin [4]. Rosuvastatin shows antiatherothromhotic effects in vivo. Rosuvastatin (1.25 mg/kg) significantly inhibits thrombin-induced transmigration of monocvtes across mesenteric venules via inhibition of the endothelial cell surface expression of P-selectin, and increases the basal rate of nitric oxide in aortic segments by 2-fold times [5].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| References |
[1]. Watanabe, M., et al., Synthesis and biological activity of methanesulfonamide pyrimidine- and N-methanesulfonyl pyrrole-substituted 3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoates, a novel series of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem, 1997. 5(2): p. 437-44. [2]. Schneck, D.W., et al., The effect of gemfibrozil on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2004. 75(5): p. 455-63. [3]. Kim, Y.S., et al., Rosuvastatin suppresses the inflammatory responses through inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Nuclear Factor-kappaB in endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2007. 49(6): p. 376-83. [4]. Carswell, C.I., G.L. Plosker, and B. Jarvis, Rosuvastatin. Drugs, 2002. 62(14): p. 2075-85; discussion 2086-7. [5]. Stalker, T.J., A.M. Lefer, and R. Scalia, A new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, rosuvastatin, exerts anti-inflammatory effects on the microvascular endothelium: the role of mevalonic acid. Br J Pharmacol, 2001. 133(3): p. 406-12.
|
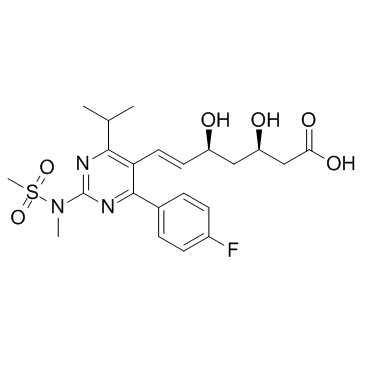
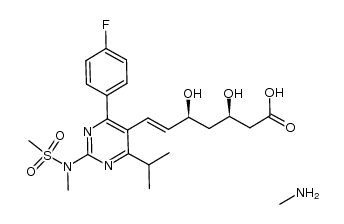 CAS#:355805-96-8
CAS#:355805-96-8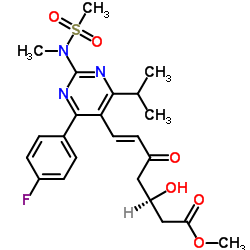 CAS#:147118-39-6
CAS#:147118-39-6![tert-butyl 2-[6-[(E)-2-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-6-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-5-yl]ethenyl]-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/488/1007871-85-3.png) CAS#:1007871-85-3
CAS#:1007871-85-3![(+)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(N-methyl-N-methylsulfonylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]-(3R,5S)-dihydroxy-(E)-heptenoic acid iso-propylammonium salt Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/017/852820-97-4.png) CAS#:852820-97-4
CAS#:852820-97-4![tert-Butyl 6-[(1E)-2-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-5-pyrimidinyl]ethenyl]-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/152/289042-12-2.png) CAS#:289042-12-2
CAS#:289042-12-2 CAS#:147118-40-9
CAS#:147118-40-9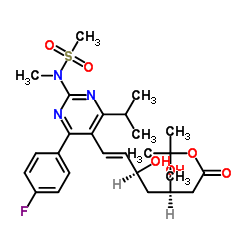 CAS#:355806-00-7
CAS#:355806-00-7 CAS#:851443-04-4
CAS#:851443-04-4![N-[4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-formyl-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]-N-methyl-methanesulfonamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/248/147118-37-4.png) CAS#:147118-37-4
CAS#:147118-37-4 CAS#:503610-43-3
CAS#:503610-43-3
