2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid

2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 303-07-1 | Molecular Weight | 154.120 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 343.7±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 | Melting Point | 165 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 175.8±21.6 °C | |
Use of 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a secondary metabolite of salicylic acid which has been hydrolyzed by liver enzymes during phase I metabolism. |
| Name | 2,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a secondary metabolite of salicylic acid which has been hydrolyzed by liver enzymes during phase I metabolism. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 343.7±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 165 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 154.120 |
| Flash Point | 175.8±21.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 154.026611 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| LogP | 2.24 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.671 |
| InChIKey | AKEUNCKRJATALU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)c1c(O)cccc1O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DG8578000 |
| HS Code | 29182990 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918290000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2918290000 other carboxylic acids with phenol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) VAT:17.0% MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only ... |
|
|
Molecularly imprinted polymers with synthetic dummy template for simultaneously selective removal and enrichment of ginkgolic acids from Ginkgo biloba L. leaves extracts.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1368 , 44-51, (2014) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers (DMIPs) for simultaneously selective removal and enrichment of ginkgolic acids (GAs) during the processing of Ginkgo biloba leaves have been prepared. Two dummy te... |
|
|
Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a fragment-based approach.
J. Med. Chem. 54 , 591-602, (2011) Fragment-based lead design (FBLD) has been used to identify new metal-binding groups for metalloenzyme inhibitors. When screened at 1 mM, a chelator fragment library (CFL-1.1) of 96 compounds produced... |
| EINECS 206-134-8 |
| Gamma-Resorcylic Acid |
| 2-Carboxyresorcinol |
| γ-Resorcylic acid |
| Benzoic acid,2,6-dihydroxy |
| 2,6-dihydroxy-benzoic acid |
| 2,5-DIFLUOROBENZYLSULFONAMIDE |
| 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
| g-Resorcylic Acid |
| 2,6-Resorcylic acid |
| 6-Hydroxysalicylic acid |
| MFCD00002462 |
| Benzoic acid, 2,6-dihydroxy- |
 CAS#:108-46-3
CAS#:108-46-3 CAS#:69-72-7
CAS#:69-72-7 CAS#:298-14-6
CAS#:298-14-6 CAS#:1466-76-8
CAS#:1466-76-8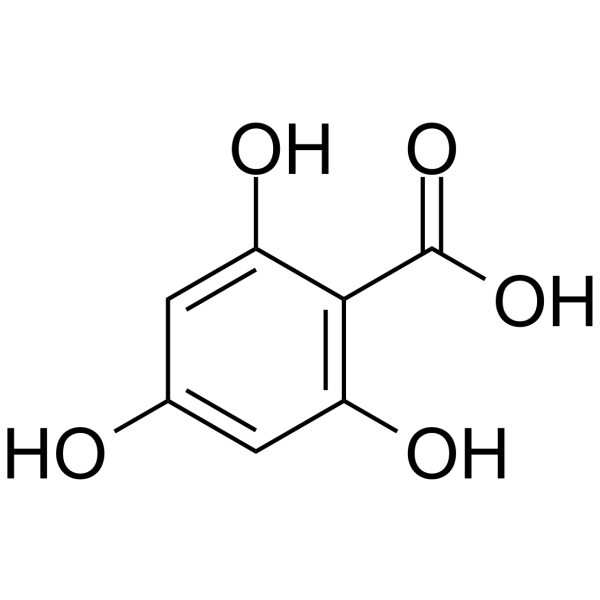 CAS#:83-30-7
CAS#:83-30-7 CAS#:699-83-2
CAS#:699-83-2 CAS#:109-72-8
CAS#:109-72-8 CAS#:60-29-7
CAS#:60-29-7 CAS#:124-41-4
CAS#:124-41-4 CAS#:108124-75-0
CAS#:108124-75-0 CAS#:54640-04-9
CAS#:54640-04-9 CAS#:387-46-2
CAS#:387-46-2 CAS#:204846-40-2
CAS#:204846-40-2 CAS#:22833-69-8
CAS#:22833-69-8 CAS#:75-27-4
CAS#:75-27-4 CAS#:67-66-3
CAS#:67-66-3 CAS#:124-48-1
CAS#:124-48-1 CAS#:75-25-2
CAS#:75-25-2 CAS#:25983-51-1
CAS#:25983-51-1
