DL-Homocysteine
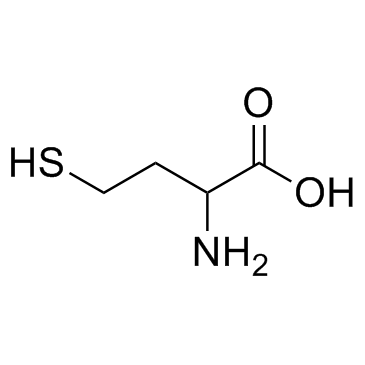
DL-Homocysteine structure
|
Common Name | DL-Homocysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 454-29-5 | Molecular Weight | 135.185 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 299.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2S | Melting Point | 232-233 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 135.0±25.9 °C | |
Use of DL-HomocysteineDL-Homocysteine is a weak neurotoxin, and can affect the production of kynurenic acid in the brain. |
| Name | DL-Homocysteine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Homocysteine is a weak neurotoxin, and can affect the production of kynurenic acid in the brain. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | DL-Homocysteine (0.1-0.5 mM) significantly enhances kynurenic acid (KYNA) production in rat cortical slices, and diministes the production of at 3.0, 5.0, and 10.0 mM, with the estimated IC50 of 6.4 (5.5-7.5) mM. DL-Homocysteine dose-dependently inhibits kynurenine aminotransferases I (KATI) activity at concentrations ≥0.2 mM, with an IC50 of 0.566 (0.442-0.724) mM, and the activity of KAT II with IC50 value of 8.046 (5.804-11.154) mM[1]. |
| In Vivo | DL-Homocysteine (1.3 mmol/kg, i.p.) increases KYNA content (pmol/g tissue) from 8.47 ± 1.57 to 13.04 ± 2.86 and 11.4 ± 1.72 in cortex, and from 4.11 ± 1.54 to 10.02 ± 3.08 in rat hippocampus[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 299.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 232-233 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 135.185 |
| Flash Point | 135.0±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 135.035400 |
| PSA | 102.12000 |
| LogP | 0.22 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | C |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MT0175000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~36% 
DL-Homocysteine CAS#:454-29-5 |
| Literature: ADISSEO FRANCE S.A.S.; Huet, Robert; Joerger, Jean-Michel; Henryon, Vivien Patent: US2013/184474 A1, 2013 ; Location in patent: Paragraph 0031; 0032; 0033; 0034; 0035; 0036 ; |
|
~% 
DL-Homocysteine CAS#:454-29-5 |
| Literature: Allen; Steinman Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1952 , vol. 74, p. 3932 |
|
~% 
DL-Homocysteine CAS#:454-29-5 |
| Literature: Riegel; du Vigneaud Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1935 , vol. 112, p. 149,153 Full Text Show Details duVigneaud; Brown Biochemical Preparations, 1957 , vol. 5, p. 96 |
|
~% 
DL-Homocysteine CAS#:454-29-5 |
| Literature: Bregant, Sarah; Burlina, Fabienne; Chassaing, Gerard Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2002 , vol. 12, # 7 p. 1047 - 1050 Title/Abstract Full Text View citing articles Show Details Guerard, Christine; Breard, Maud; Courtois, Fabienne; Drujon, Thierry; Ploux, Olivier Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2004 , vol. 14, # 7 p. 1661 - 1664 |
|
~% 
DL-Homocysteine CAS#:454-29-5 |
| Literature: Bommarius, Andreas S.; Drauz, Karlheinz; Guenther, Kurt; Knaup, Guenter; Schwarm, Michael Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 1997 , vol. 8, # 19 p. 3197 - 3200 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase protects against homocysteine-induced apoptosis of osteocytic MLO-Y4 cells by regulating the expressions of NADPH oxidase 1 (Nox1) and Nox2.
Bone 77 , 135-41, (2015) Elevated plasma homocysteine (Hcy) level is associated with the risk of osteoporotic fracture. While Hcy increases oxidative stress, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation ameliorates it. This... |
|
|
Protective effect of sulfurous water in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of Alzheimer's disease patients.
Life Sci. 132 , 61-7, (2015) One of the main features of sulfurous water (SW) is the presence of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which confers its antioxidant activity. Since oxidative stress plays an important role in Alzheimer's diseas... |
|
|
Sulfur amino acid metabolism in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 96 , 256-66, (2015) The present study was aimed to investigate the metabolomics of sulfur amino acids in Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats, an obese type 2 diabetic animal model. Plasma levels of total cysteine, homocyste... |
| DL-HoMocysteine |
| DL-2-amino-4-mercapto-Butyric acid |
| D-L-homocysteine |
| usafb-12 |
| Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto- |
| DL-2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid |
| Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-, DL- |
| 2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid |
| D,L-Homocysteine |
| 2-Amino-4-mercaptobutanoic acid |
| HOMOCYSTEINE,DL |
| 2-AMINO-4-MERCAPTOBUYRIC ACID |
| 1-carboxy-3-mercaptopropylamine |
| Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto- |
| 2-amino-4-mercapto-DL-Butyric acid |
| 2-amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid |
| Homocysteine (VAN) |
| TOTALHOMOCYSTEINE |
| H-DL-Hcys-OH |
| 2-Amino-4-Mercapto-Butyric Acid |
| EINECS 207-222-9 |
| homocystine |
| (±)-Homocysteine |
| 2-amino-4-mercapto-Butanoic acid |
| UNII:S7IJP4A89K |
| MFCD00004898 |
| Homocysteine |
| 2-thioethylglycine |
| Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-, DL- (9CI) |
![4,4'-Dithiobis[2-aminobutyric Acid] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/253/462-10-2.png)

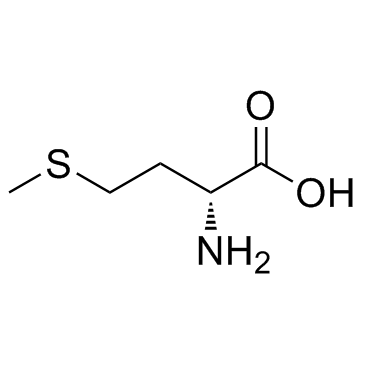 CAS#:348-67-4
CAS#:348-67-4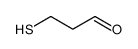 CAS#:20291-59-2
CAS#:20291-59-2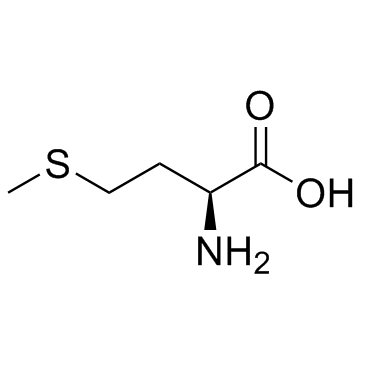 CAS#:63-68-3
CAS#:63-68-3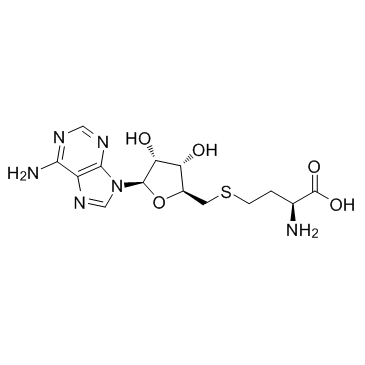 CAS#:979-92-0
CAS#:979-92-0 CAS#:2906-60-7
CAS#:2906-60-7 CAS#:65061-27-0
CAS#:65061-27-0 CAS#:88096-02-0
CAS#:88096-02-0 CAS#:88096-03-1
CAS#:88096-03-1