DL-Homocysteine
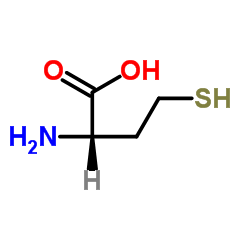
DL-Homocysteine structure
|
Common Name | DL-Homocysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6027-13-0 | Molecular Weight | 135.185 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 299.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2S | Melting Point | 231 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 135.0±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of DL-HomocysteineL-Homocysteine, a homocysteine metabolite, is a homocysteine that has L configuration. L-Homocysteine induces upregulation of cathepsin V that mediates vascular endothelial inflammation in hyperhomocysteinaemia[1][2]. |
| Name | L-homocysteine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Homocysteine, a homocysteine metabolite, is a homocysteine that has L configuration. L-Homocysteine induces upregulation of cathepsin V that mediates vascular endothelial inflammation in hyperhomocysteinaemia[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[1]. Finkelstein JD, et al. Homocysteine. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2000 Apr;32(4):385-9. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 299.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 231 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C4H9NO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 135.185 |
| Flash Point | 135.0±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 135.035400 |
| PSA | 102.12000 |
| LogP | 0.22 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| InChIKey | FFFHZYDWPBMWHY-VKHMYHEASA-N |
| SMILES | NC(CCS)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Biomarkers of one-carbon metabolism are associated with biomarkers of inflammation in women.
J. Nutr. 144(5) , 714-21, (2014) Folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism is essential for DNA synthesis, repair, and methylation. Perturbations in one-carbon metabolism have been implicated in increased risk of some cancers and may als... |
|
|
Abstracts of the 9th International Conference On Homocysteine and One-Carbon Metabolism - HCY2013. Dublin, Ireland. September 8-12, 2013.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 36 Suppl 1 , S1-54, (2013)
|
|
|
Derivation and validation of homocysteine score in u.s. Men and women.
J. Nutr. 145(1) , 96-104, (2015) One-carbon metabolism, which is crucial in DNA synthesis and genomic stability, is an interrelated network of biochemical reactions involved in several dietary and lifestyle factors. The development o... |
| (2S)-2-amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid |
| Homocysteine, L- |
| L-2-Amino-4-Mercapto-butyric acid |
| (S)-2-amino-4-mercapto-Butanoic acid |
| DL-2-amino-4-mercapto-Butyric acid |
| HOMO-CYS |
| H-Hcys-OH |
| Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto- |
| DL-2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid |
| Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-, DL- |
| (S)-2-Amino-4-mercaptobutanoic acid |
| 2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid |
| D,L-Homocysteine |
| Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-, (S)- |
| (S)-homocysteine |
| MFCD00151320 |
| Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto- |
| 2-amino-4-mercapto-DL-Butyric acid |
| 2-amino-4-sulfanylbutanoic acid |
| EINECS 227-891-0 |
| D,L-homocystine |
| Homocysteine (VAN) |
| 2-Amino-4-Mercapto-Butyric Acid |
| (S)-2-Amino-4-mercaptobutyric acid |
| (±)-Homocysteine |
| 2-amino-4-mercapto-Butanoic acid |
| UNII:S7IJP4A89K |
| Homocysteine |
| Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-mercapto-, DL- (9CI) |
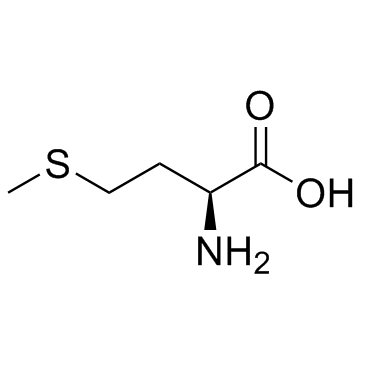 CAS#:63-68-3
CAS#:63-68-3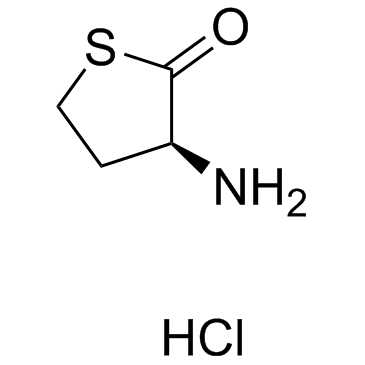 CAS#:31828-68-9
CAS#:31828-68-9 CAS#:626-72-2
CAS#:626-72-2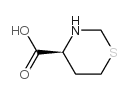 CAS#:147331-83-7
CAS#:147331-83-7 CAS#:2338-04-7
CAS#:2338-04-7 CAS#:69955-57-3
CAS#:69955-57-3 CAS#:7689-60-3
CAS#:7689-60-3 CAS#:7540-67-2
CAS#:7540-67-2 CAS#:70-18-8
CAS#:70-18-8 CAS#:75027-08-6
CAS#:75027-08-6 CAS#:56-88-2
CAS#:56-88-2 CAS#:7732-18-5
CAS#:7732-18-5 CAS#:7783-06-4
CAS#:7783-06-4 CAS#:52-90-4
CAS#:52-90-4 CAS#:1118-68-9
CAS#:1118-68-9 CAS#:979-92-0
CAS#:979-92-0
