Paeonol
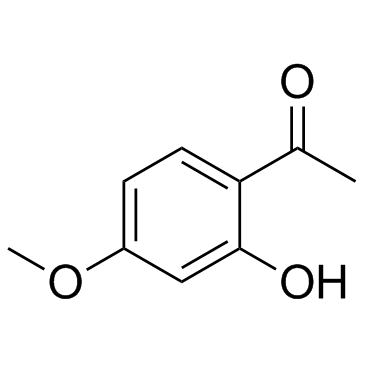
Paeonol structure
|
Common Name | Paeonol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 552-41-0 | Molecular Weight | 166.174 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 301.9±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 | Melting Point | 48-50 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 122.3±15.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of PaeonolPaeonol is an active extraction from the root of Paeonia suffruticosa, Paeonol inhibits MAO-A and MAO-B with IC50 of 54.6 μM and 42.5 μM, respectively. |
| Name | Paeonol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Paeonol is an active extraction from the root of Paeonia suffruticosa, Paeonol inhibits MAO-A and MAO-B with IC50 of 54.6 μM and 42.5 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 42.5 μM (MAO-B), 54.6 μM (MAO-A)[1] |
| In Vitro | Paeonol is found to be inhibitory against MAO A in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 value of 54.6 μM. Paeonol is shown to inhibit MAO-B in a dose-dependent manner with the IC50 of 42.5 μM. For Paeonol, the Ki is estimated to be 51.1 μM. The inhibition of Paeonol on MAO B is of competitive type with Ki value of 38.2 μM[1]. |
| In Vivo | The 200 mg/kg Paeonol+I/R group [AN/V (%): 7.6±2.2, p<0.01] and 100 mg/kg Paeonol+I/R group [AN/V (%): 9.4±2.8, p<0.05] both show lesser extents of no-reflow area in the ventricles compared with the I/R group [AN/V (%): 18.2±2.9]. In particular, the 200 mg/kg Paeonol + I/R group experienced markedly alleviated no-reflow in the whole heart [AN/WH (%): 4.6±1, p<0.05] compared with the I/R group [AN/WH (%): 10.0±1.9][2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Male Wistar rats (180-220 g, average age of 8 week) are randomly divided into four groups: (1) sham group, thoracotomy without left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) occlusion or Paeonol pretreatment; (2) I/R group, LAD occlusion (ischemia) for 4 h followed by reperfusion for 8 h; (3) Paeonol (100 mg/kg)+I/R group, oral administration of 100 mg/kg Paeonol (1 mL/kg) for 7 days using a intragastric tube prior to I/R procedure; (4) Paeonol (200 mg/kg) + I/R group, oral administration of 200 mg/kg Paeonol (1 mL/kg) for 7 days using a intragastric tube prior to I/R procedure. In addition, rats in the sham and I/R groups received a dosage of DMSO equal to that with which the Paeonol was dissolved in for the other two groups. DMSO was also administered intragastrically for 7 consecutive days. A minimum of eight rats were assigned to each group. An ischemia group without reperfusion is not included since our present study mainly focuses on the effect of Paeonol on the cardiac injuries after reperfusion, which is closely related to the real-world situation of no-reflow after coronary revascularization. However, future studies may include a group subjected only to 4 h of ischemia to differentiate, in terms of damage to the cardiac function, which was due to the ischemia and which was due to the no-reflow. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 301.9±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 48-50 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 166.174 |
| Flash Point | 122.3±15.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 166.062988 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 2.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| InChIKey | UILPJVPSNHJFIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1ccc(C(C)=O)c(O)c1 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S28-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RT1215000 |
| HS Code | 2914509090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2914509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2914509090 other ketones with other oxygen function VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Competitive molecular interaction among paeonol-loaded liposomes: differential scanning calorimetry and synchrotron X-ray diffraction studies.
Int. J. Pharm. 438(1-2) , 91-7, (2012) Thermotropic phase behavior of 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) liposomes containing 5 mol% cholesterol, or 5 mol% stigmasterol, or 5 mol% paeonol have been investigated by different... |
|
|
Paeonol inhibits oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced monocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cells by inhibiting the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35(5) , 767-72, (2012) Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by increased expression of adhesion molecules, which contribute to monocytes adhesion to vascular endothelial cells (VECs). Paeonol, an ... |
|
|
Influence of co-administered danshensu on pharmacokinetic fate and tissue distribution of paeonol in rats.
Planta Med. 78(2) , 135-40, (2012) Cortex Moutan (root bark of Paeonia suffruticosa Andrew) and Radix Salviae miltiorrhizae (root and rhizome of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) are two herbs widely used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)... |
| 1-(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone |
| 2-Acetyl-5-methoxy-phenol |
| 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxyacetophenone |
| EINECS 209-012-2 |
| 2'-hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone |
| 4-Methoxy-2-hydroxyacetophenone |
| Paeonol |
| MFCD00008730 |
| 1-(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)ethan-1-one |
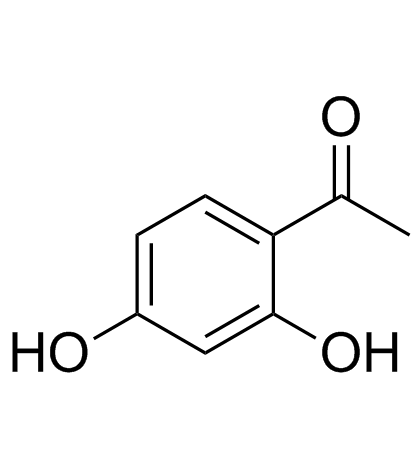 CAS#:89-84-9
CAS#:89-84-9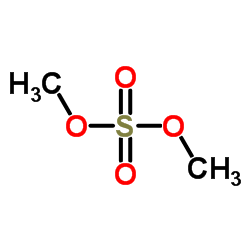 CAS#:77-78-1
CAS#:77-78-1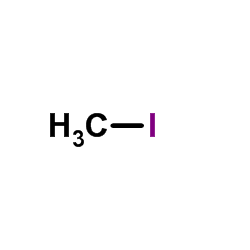 CAS#:74-88-4
CAS#:74-88-4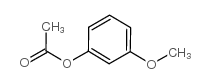 CAS#:5451-83-2
CAS#:5451-83-2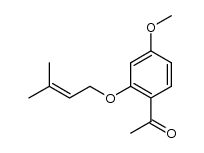 CAS#:128961-25-1
CAS#:128961-25-1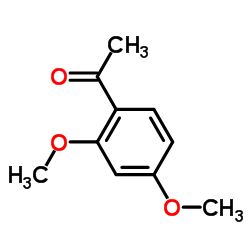 CAS#:829-20-9
CAS#:829-20-9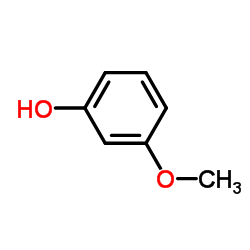 CAS#:150-19-6
CAS#:150-19-6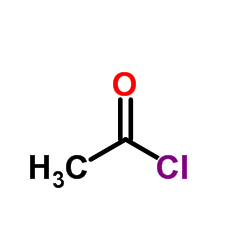 CAS#:75-36-5
CAS#:75-36-5 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7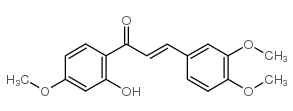 CAS#:10493-06-8
CAS#:10493-06-8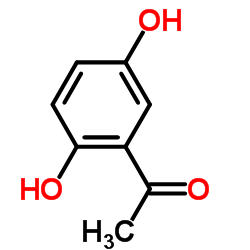 CAS#:490-78-8
CAS#:490-78-8 CAS#:491-37-2
CAS#:491-37-2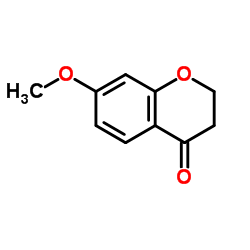 CAS#:42327-52-6
CAS#:42327-52-6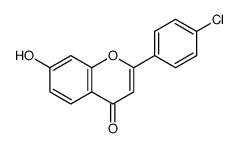 CAS#:22609-52-5
CAS#:22609-52-5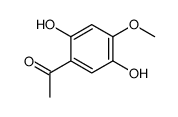 CAS#:22089-12-9
CAS#:22089-12-9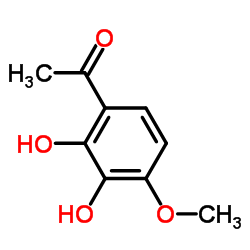 CAS#:708-53-2
CAS#:708-53-2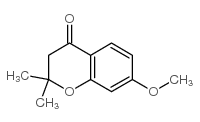 CAS#:20321-73-7
CAS#:20321-73-7 CAS#:20784-60-5
CAS#:20784-60-5
