4-Nitroquinoline 1-oxide
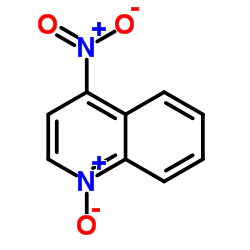
4-Nitroquinoline 1-oxide structure
|
Common Name | 4-Nitroquinoline 1-oxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-57-5 | Molecular Weight | 190.16 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 387.6±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6N2O3 | Melting Point | 154-156 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 188.2±25.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of 4-Nitroquinoline 1-oxideNitrochin (4-NQO) is a chemical carcinogen. Nitrochin induces oncostatin-M (OSM) in esophageal cells. Nitrochin induces DNA damage, and induces apoptosis via a p53-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway[1][2]. |
| Name | 4-nitroquinoline N-oxide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nitrochin (4-NQO) is a chemical carcinogen. Nitrochin induces oncostatin-M (OSM) in esophageal cells. Nitrochin induces DNA damage, and induces apoptosis via a p53-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 387.6±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 154-156 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 190.16 |
| Flash Point | 188.2±25.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 190.037842 |
| PSA | 71.28000 |
| LogP | 0.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.659 |
| InChIKey | YHQDZJICGQWFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=[N+]([O-])c1cc[n+]([O-])c2ccccc12 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Stable. Hygroscopic, light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | acetone: clear to hazy |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R33 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VC2100000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Rad23 interaction with the proteasome is regulated by phosphorylation of its ubiquitin-like (UbL) domain.
J. Mol. Biol. 426(24) , 4049-60, (2014) Rad23 was identified as a DNA repair protein, although a role in protein degradation has been described. The protein degradation function of Rad23 contributes to cell cycle progression, stress respons... |
|
|
DNA damage-specific deubiquitination regulates Rad18 functions to suppress mutagenesis.
J. Cell Biol. 206(2) , 183-97, (2014) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) lesions encountered during replication are often bypassed using DNA damage tolerance (DDT) pathways to avoid prolonged fork stalling and allow for completion of DNA replica... |
|
|
Genotoxicity testing of esterified propoxylated glycerol (EPG).
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 70 Suppl 2 , S131-42, (2014) Four versions of esterified propoxylated glycerols (EPGs) were evaluated for potential genotoxicity using a range of in vitro and in vivo assays. H-EPG-05 HR/SO 9:1, H-EPG-05 soyate, and H-EPG-14 soya... |
| EINECS 200-281-1 |
| MFCD00006738 |
| 4-nitro-1-oxidoquinolin-1-ium |
| 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide |
| Quinoline, 4-nitro-, 1-oxide |
| 4-Nitroquinoline 1-oxide |
| 4-nitroquinoline n-oxide |
 CAS#:1613-37-2
CAS#:1613-37-2 CAS#:3741-15-9
CAS#:3741-15-9 CAS#:120309-60-6
CAS#:120309-60-6 CAS#:7664-93-9
CAS#:7664-93-9 CAS#:39061-97-7
CAS#:39061-97-7 CAS#:607-31-8
CAS#:607-31-8 CAS#:4552-43-6
CAS#:4552-43-6 CAS#:36825-36-2
CAS#:36825-36-2 CAS#:486-74-8
CAS#:486-74-8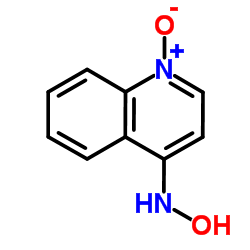 CAS#:4637-56-3
CAS#:4637-56-3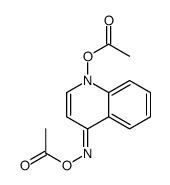 CAS#:18061-48-8
CAS#:18061-48-8 CAS#:20146-63-8
CAS#:20146-63-8 CAS#:20151-40-0
CAS#:20151-40-0
