Mefenamic acid
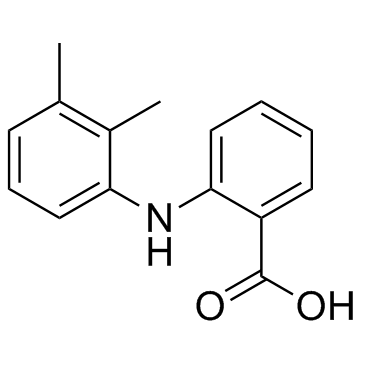
Mefenamic acid structure
|
Common Name | Mefenamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 61-68-7 | Molecular Weight | 241.285 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 398.8±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H15NO2 | Melting Point | 230 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 195.0±24.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Mefenamic acidMefenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, acting as a competitive inhibitor of hCOX-1 and hCOX-2, with IC50s of 40 nM and 3 μM for hCOX-1 and hCOX-2, respectively. |
| Name | mefenamic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Mefenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, acting as a competitive inhibitor of hCOX-1 and hCOX-2, with IC50s of 40 nM and 3 μM for hCOX-1 and hCOX-2, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
hCOX-1:40 nM (IC50) hCOX-2:3 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Mefenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, acting as a competitive inhibitor of hCOX-1, with IC50s of 40 nM and 3 μM for hCOX-1 and hCOX-2, respectively[1]. Mefenamic acid (0-100 μM) has cytotoxic effects on KB, Saos-2, and 1321N cells, however, U-87MG cells are resistant to Mefenamic acid[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Powder forms of Mefenamic acid, indometacin, aspirin, and celecoxib are dissolved in 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to achieve a concentration of 100 μM of stock solution, which is sterilized by filtration through a 0.22-µm filter and then stored at 4°C. Different concentrations (100, 50, 25, 10, and 5 μM) of the drugs (Mefenamic acid, etc.) are prepared by serial dilutions with the FCS-free medium or the medium containing 10% FCS in sterile plastic centrifuge tubes[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 398.8±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 230 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H15NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 241.285 |
| Flash Point | 195.0±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 241.110275 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | 5.33 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| InChIKey | HYYBABOKPJLUIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1cccc(Nc2ccccc2C(=O)O)c1C |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CB4550000 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Characterization of a highly sensitive and selective novel trapping reagent, stable isotope labeled glutathione ethyl ester, for the detection of reactive metabolites.
J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 76 , 83-95, (2015) Glutathione (GSH) trapping assays are widely used to predict the post-marketing risk for idiosyncratic drug reactions (IDRs) in the pharmaceutical industry. Although several GSH derivatives have been ... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
| Benzoic acid, 2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]- |
| Ponstyl |
| Pontal |
| Parkemed |
| Mefenacid |
| Mefenamate |
| EINECS 200-513-1 |
| Lysalgo |
| MFCD00051721 |
| Ponalar |
| Mefenamic acid |
| 2-[(2,3-Dimethylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid |
| Ponstel |
| N-(2,3-Xylyl)anthranilic acid |
| Ponstan |
![2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]benzonitrile Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/399/13481-67-9.png) CAS#:13481-67-9
CAS#:13481-67-9 CAS#:87-59-2
CAS#:87-59-2 CAS#:118-91-2
CAS#:118-91-2 CAS#:1488-42-2
CAS#:1488-42-2 CAS#:88-67-5
CAS#:88-67-5 CAS#:55591-34-9
CAS#:55591-34-9 CAS#:873-32-5
CAS#:873-32-5 CAS#:1804-54-2
CAS#:1804-54-2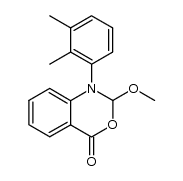 CAS#:137488-33-6
CAS#:137488-33-6 CAS#:10457-97-3
CAS#:10457-97-3 CAS#:106724-32-7
CAS#:106724-32-7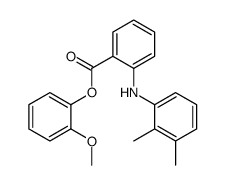 CAS#:20723-85-7
CAS#:20723-85-7![Benzoic acid, 2-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]-, monosodium salt structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/439/1804-47-3.png) CAS#:1804-47-3
CAS#:1804-47-3 CAS#:29098-16-6
CAS#:29098-16-6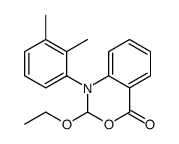 CAS#:137488-42-7
CAS#:137488-42-7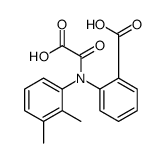 CAS#:1618-52-6
CAS#:1618-52-6![2-[(2,3-Dimethylphenyl)amino]benzoic acid methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/273/1222-42-0.png) CAS#:1222-42-0
CAS#:1222-42-0 CAS#:59338-12-4
CAS#:59338-12-4
