Amlodipine
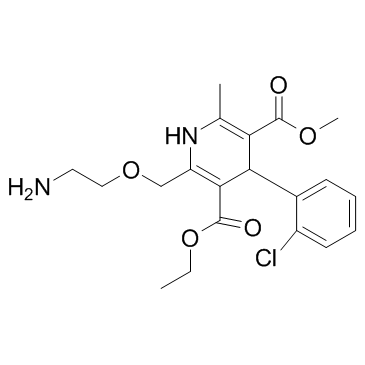
Amlodipine structure
|
Common Name | Amlodipine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 88150-42-9 | Molecular Weight | 408.876 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H25ClN2O5 | Melting Point | 178-179ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 272.6±30.1 °C | |
Use of AmlodipineAmlodipine is a long-acting calcium channel blocker.Target: Calcium ChannelAmlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (calcium ion antagonist or slow-channel blocker) that inhibits the movement of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells. Experimental data suggest amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects, or decreased heart muscle contractility, can be detected in vitro, but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine. Within the physiologic pH range, amlodipine is an ionized compound (pKa = 8.6), and its interaction with the calcium channel receptor is characterized by a gradual rate of association and dissociation with the receptor binding site, resulting in a gradual onset of effect. Amlodipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator that acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure. From Wikipedia. |
| Name | amlodipine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Amlodipine is a long-acting calcium channel blocker.Target: Calcium ChannelAmlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (calcium ion antagonist or slow-channel blocker) that inhibits the movement of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells. Experimental data suggest amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects, or decreased heart muscle contractility, can be detected in vitro, but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine. Within the physiologic pH range, amlodipine is an ionized compound (pKa = 8.6), and its interaction with the calcium channel receptor is characterized by a gradual rate of association and dissociation with the receptor binding site, resulting in a gradual onset of effect. Amlodipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator that acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure. From Wikipedia. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 527.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 178-179ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H25ClN2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 408.876 |
| Flash Point | 272.6±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 408.145203 |
| PSA | 99.88000 |
| LogP | 4.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.546 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | 75.3 mg/L |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|
~90% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: SELAMINE LTD Patent: WO2008/65424 A1, 2008 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 33 ; |
|
~90% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: MATRIX LABORATORIES LTD Patent: WO2006/3672 A1, 2006 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 7 ; |
|
~% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 29, # 9 p. 1696 - 1702 |
|
~% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 29, # 9 p. 1696 - 1702 |
|
~% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 29, # 9 p. 1696 - 1702 |
|
~% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 29, # 9 p. 1696 - 1702 |
|
~% 
Amlodipine CAS#:88150-42-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 29, # 9 p. 1696 - 1702 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 5 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
| Norvasc |
| Lipinox |
| Amlodis |
| 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 2-((2-aminoethoxy)methyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-, 3-ethyl 5-methyl ester |
| T6M DHJ B1O2Z CVO2 DR BG& EVO1 F1 |
| 2-[(2-Aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid 3-ethyl 5-methyl Ester |
| UNII:1J444QC288 |
| 2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine |
| 3-Ethyl 5-methyl 2-{[(2-aminoethyl)oxy]methyl}-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
| Amlodipino |
| 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-, 3-ethyl 5-methyl ester |
| 3-ethyl 5-methyl ()-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridine dicarboxylate |
| Istin |
| (R,S)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-ethoxycarbonyl-5-methoxycarbonyl-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine |
| Amlodipinum [Latin] |
| Amlodipinum |
| Amlocard |
| Amlodipine |
| 3-ethyl-5-methyl-(4RS)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)-methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-carboxylate benzene sulphonate |
| MFCD00864687 |
| 3-ethyl 5-methyl 2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
| 3-Ethyl 5-methyl 2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate |
| Coroval |

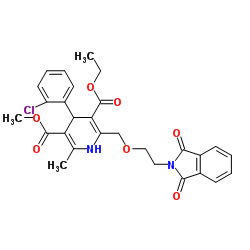

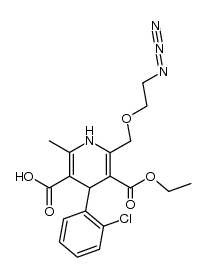
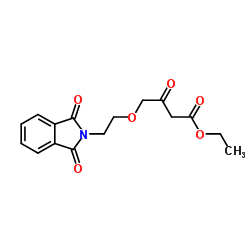
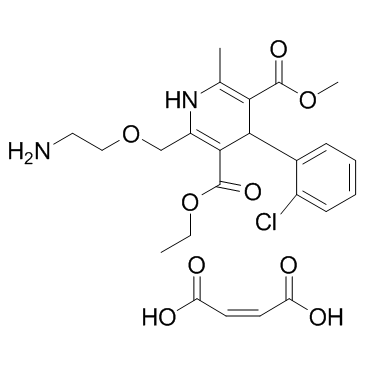 CAS#:88150-47-4
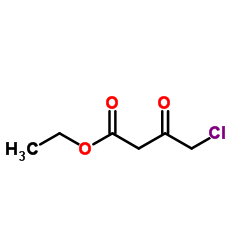
CAS#:88150-47-4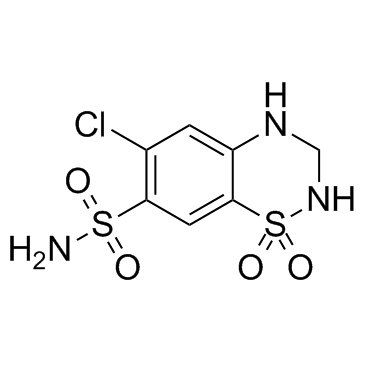 CAS#:58-93-5
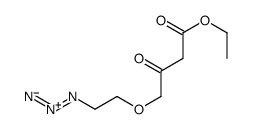
CAS#:58-93-5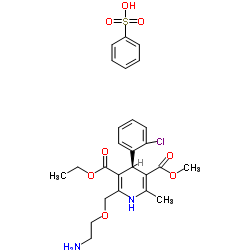 CAS#:103129-82-4
CAS#:103129-82-4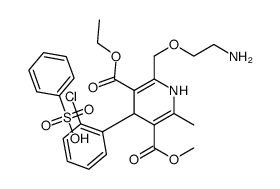 CAS#:103129-81-3
CAS#:103129-81-3
