Hemin
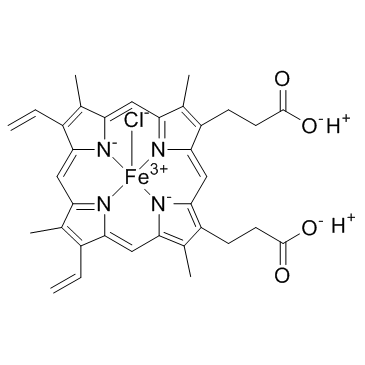
Hemin structure
|
Common Name | Hemin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16009-13-5 | Molecular Weight | 651.940 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C34H32ClFeN4O4 | Melting Point | 300 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Enhancing the anti-inflammatory activity of chalcones by tuning the Michael acceptor site.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 13(10) , 3040-7, (2015) Inflammatory signaling pathways orchestrate the cellular response to infection and injury. These pathways are known to be modulated by compounds that alkylate cysteinyl thiols. One class of phytochemicals with strong thiol alkylating activity is the chalcones... |
|
|
Kinetics of serotonin oxidation by heme-Aβ relevant to Alzheimer's disease.
J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 19(8) , 1355-65, (2014) Serotonin (5-HT) is an essential neurotransmitter for cognitive functions and formation of new memories. A deficit in 5-HT dependent neuronal activity is somewhat specific for Alzheimer's disease. Metal-mediated oxidative degradation of neurotransmitters by A... |
|
|
Trypanocidal Activity of Long Chain Diamines and Aminoalcohols.
Molecules 20 , 11554-68, (2015) Thirteen aminoalcohols and eight diamines were obtained and tested against Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes strains MG, JEM and CL-B5 clone. Some of them were equal or more potent (1.0-6.6 times) than the reference compound nifurtimox. From them, three aminoal... |
|
|
PKC/ROS-Mediated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Is Attenuated by Leishmania Zinc-Metalloprotease during Infection.
PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9 , e0003868, (2015) Parasites of the Leishmania genus infect and survive within macrophages by inhibiting several microbicidal molecules, such as nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines. In this context, various species of Leishmania have been reported to inhibit or reduce t... |
|
|
A role for catalase-peroxidase large loop 2 revealed by deletion mutagenesis: control of active site water and ferric enzyme reactivity.
Biochemistry 54(8) , 1648-62, (2015) Catalase-peroxidases (KatGs), the only catalase-active members of their superfamily, all possess a 35-residue interhelical loop called large loop 2 (LL2). It is essential for catalase activity, but little is known about its contribution to KatG function. LL2 ... |
|
|
High-yield reactivation of anionic tobacco peroxidase overexpressed in Escherichia coli.
Protein Expr. Purif. 113 , 85-93, (2015) Anionic tobacco peroxidase (TOP) is extremely active in chemiluminescence reaction of luminol oxidation without addition of enhancers and more stable than horseradish peroxidase under antibody conjugation conditions. In addition, recombinant TOP (rTOP) produc... |
|
|
Ancestral amino acid substitution improves the thermal stability of recombinant lignin-peroxidase from white-rot fungi, Phanerochaete chrysosporium strain UAMH 3641.
Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 28 , 221-30, (2015) Stabilizing enzymes from mesophiles of industrial interest is one of the greatest challenges of protein engineering. The ancestral mutation method, which introduces inferred ancestral residues into a target enzyme, has previously been developed and used to im... |
|
|
Preparation and testing of a Haemophilus influenzae Type b/Hepatitis B surface antigen conjugate vaccine.
Vaccine 33(13) , 1614-9, (2015) The majority of conjugate vaccines focus on inducing an antibody response to the polysaccharide antigen and the carrier protein is present primarily to induce a T-cell dependent response. In this study conjugates consisting of poly(ribosylribitolphosphate) (P... |
|
|
Site-directed mutagenesis of tobacco anionic peroxidase: Effect of additional aromatic amino acids on stability and activity.
Biochimie 115 , 71-7, (2015) Tobacco anionic peroxidase (TOP) is known to effectively catalyze luminol oxidation without enhancers, in contrast to horseradish peroxidase (HRP). To pursue structure-activity relationship studies for TOP, two amino acids have been chosen for mutation, namel... |
|
|
Interprotein Coupling Enhances the Electrocatalytic Efficiency of Tobacco Peroxidase Immobilized at a Graphite Electrode.
Anal. Chem. 87 , 10807-14, (2015) Covalent immobilization of enzymes at electrodes via amide bond formation is usually carried out by a two-step protocol, in which surface carboxylic groups are first activated with the corresponding cross-coupling reagents and then reacted with protein amine ... |