Camostat Mesylate
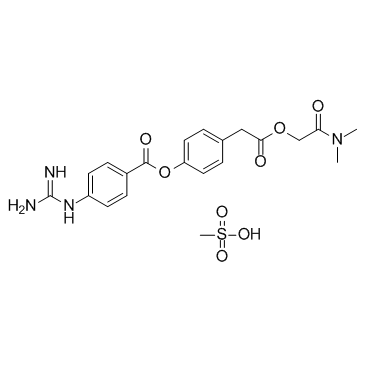
Camostat Mesylate structure
|
Common Name | Camostat Mesylate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59721-29-8 | Molecular Weight | 494.518 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 634.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N4O8S | Melting Point | 150-1550C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Camostat MesylateCamostat Mesylate(FOY305; FOY-S980) is a trypsin-like protease inhibitorTarget: Trypsin-like proteaseCamostat mesilate (500 mM) inhibits generation of TGF-beta by suppressing plasmin activity and reduces the activity of TGF-beta, which blocks in vitro activation of HSCs [1]. Camostat mesilate (20 mM) combined with insulin results a significant hypoglycemic effect following large intestinal administration. Camostat mesilate (20 mM) is effective in reducing insulin degradation in both small and large intestinal homogenates of rats [2]. Camostat mesilate (2 mM) inhibits MCP-1 and TNF- production in activated rat monocytes. Camostat mesilate (2 mM) inhibits proliferation and MCP-1 production of cultured rat PSCs. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) prevents pancreatic atrophy and improves pancreatic exocrine function of rat chronic pancreatitis induced by DBTC. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) inhibits chronic inflammation and pancreatic fibrosis induced by DBTC. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) inhibits the development of pancreatic fibrosis and PSCs activation in the pancreas induced by DBTC. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) suppresses monocytes infiltration and inhibits MCP-1 expression both in serum and in pancreatic tissue [3]. |
| Name | Camostat Mesylate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Camostat Mesylate(FOY305; FOY-S980) is a trypsin-like protease inhibitorTarget: Trypsin-like proteaseCamostat mesilate (500 mM) inhibits generation of TGF-beta by suppressing plasmin activity and reduces the activity of TGF-beta, which blocks in vitro activation of HSCs [1]. Camostat mesilate (20 mM) combined with insulin results a significant hypoglycemic effect following large intestinal administration. Camostat mesilate (20 mM) is effective in reducing insulin degradation in both small and large intestinal homogenates of rats [2]. Camostat mesilate (2 mM) inhibits MCP-1 and TNF- production in activated rat monocytes. Camostat mesilate (2 mM) inhibits proliferation and MCP-1 production of cultured rat PSCs. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) prevents pancreatic atrophy and improves pancreatic exocrine function of rat chronic pancreatitis induced by DBTC. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) inhibits chronic inflammation and pancreatic fibrosis induced by DBTC. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) inhibits the development of pancreatic fibrosis and PSCs activation in the pancreas induced by DBTC. Camostat mesilate (1 mg/g) suppresses monocytes infiltration and inhibits MCP-1 expression both in serum and in pancreatic tissue [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 634.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 150-1550C |
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N4O8S |
| Molecular Weight | 494.518 |
| Exact Mass | 494.147125 |
| PSA | 197.56000 |
| LogP | 2.84290 |
| InChIKey | FSEKIHNIDBATFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CN(C)C(=O)COC(=O)Cc1ccc(OC(=O)c2ccc(N=C(N)N)cc2)cc1.CS(=O)(=O)O |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,N |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| RTECS | UV7720000 |
|
~% 
Camostat Mesylate CAS#:59721-29-8 |
| Literature: US4021472 A1, ; |
|
ERK activation is required for CCK-mediated pancreatic adaptive growth in mice.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 307(7) , G700-10, (2014) High levels of cholecystokinin (CCK) can stimulate pancreatic adaptive growth in which mature acinar cells divide, leading to enhanced pancreatic mass with parallel increases in protein, DNA, RNA, and... |
|
|
Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry.
Antiviral Res. 116 , 76-84, (2015) In order to gain entry into cells, diverse viruses, including Ebola virus, SARS-coronavirus and the emerging MERS-coronavirus, depend on activation of their envelope glycoproteins by host cell proteas... |
|
|
Correction of defective CFTR/ENaC function and tightness of cystic fibrosis airway epithelium by amniotic mesenchymal stromal (stem) cells.
J. Cell. Mol. Med. 18(8) , 1631-43, (2014) Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, with most of the mortality given by the lung disease. Human amniotic mesenchymal stromal (stem) c... |
| Benzeneacetic acid, 4-[[4-[(aminoiminomethyl)amino]benzoyl]oxy]-, 2-(dimethylamino)-2-oxoethyl ester, methanesulfonate (1:1) |
| Camostat Mesylate |
| [4-[2-[2-(dimethylamino)-2-oxoethoxy]-2-oxoethyl]phenyl] 4-(diaminomethylideneamino)benzoate,methanesulfonic acid |
| 4-{2-[2-(Dimethylamino)-2-oxoethoxy]-2-oxoethyl}phenyl 4-carbamimidamidobenzoate methanesulfonate (1:1) |
| MFCD00941410 |
| Camostat mesilate |
| Camostat (mesylate) |
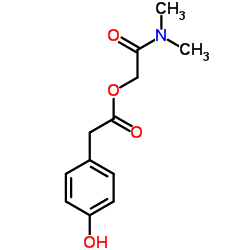
 CAS#:14658-93-6
CAS#:14658-93-6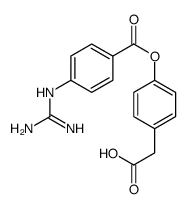 CAS#:71079-08-8
CAS#:71079-08-8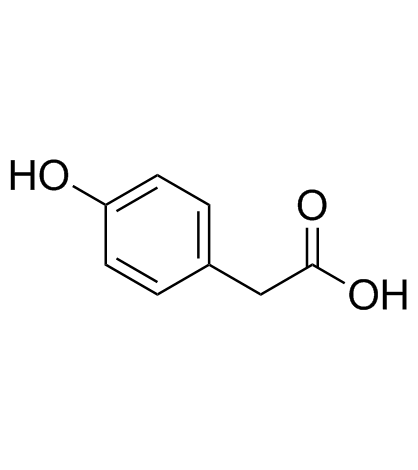 CAS#:156-38-7
CAS#:156-38-7 CAS#:16060-65-4
CAS#:16060-65-4