Uric Acid

Uric Acid structure
|
Common Name | Uric Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69-93-2 | Molecular Weight | 168.110 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 863ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O3 | Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 475.7ºC | |
Use of Uric AcidUric acid is an endogenous antioxidant that scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS) including singlet oxygen, oxygen radicals, and peroxynitrite. |
| Name | 7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Uric acid is an endogenous antioxidant that scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS) including singlet oxygen, oxygen radicals, and peroxynitrite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Uric acid is an endogenous antioxidant that scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS) including singlet oxygen, oxygen radicals, and peroxynitrite. Incubation with indomethacin significantly increases malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in Caco-2 cells compare to those not treated indomethacin. Incubation with both indomethacin and Uric acid significantly decreases MDA levels compare to those grown in the presence of indomethacin alone. Co-treatment of cells with indomethacin and Uric acid significantly decreases ROS levels compare to those in cells incubated with indomethacin alone. Cell viability in Caco-2 cells treated with both indomethacin and Uric acid is higher than that in cells treated with indomethacin alone. Uric acid has a protective effect on indomethacin-induced intestinal cell changes through its antioxidant activity[1]. |
| In Vivo | When mice treated with indomethacin are concurrently administered Uric acid orally, ulcer areas are significantly reduced, in a Uric acid dose-dependent manner. Indomethacin increases the ratio of crypt depth to villous height in the ileum, while the ratio is significantly lower when mice are concurrently administered Uric acid orally. Administration of indomethacin also increases the histopathological score of tissue damage in the small intestine, while mice concurrently administered Uric acid orally has a significantly lower histopathological score. The ileal levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) in indomethacin-induced enteropathy model mice orally administered Uric acid are also significantly lower than the levels in mice administered indomethacin alone[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Human colon carcinoma cells (Caco-2) are used and grown in Eagle’s minimum essential medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% non-essential amino acid mixture, and 1% Pen-Strep at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Caco-2 cells are incubated with indomethacin in the presence or absence of Uric acid for 24 or 48 hours[1]. |
| Animal Admin | To evaluate the effect of oral administration of Uric acid on NSAID-induced enteropathy, mice are given Uric acid (2.5, 10, 25, 100, or 250 mg/kg body weight) suspended in 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose orally at 30 minutes before, and 12 hours after indomethacin or vehicle treatment. To evaluate the effect of intraperitoneal administration of inosinic acid plus potassium oxonate on NSAID-induced enteropathy, mice are given inosinic acid (500 mg/kg body weight) plus potassium oxonate (250 mg/kg body weight) 24 intraperitoneally at 30 minutes before, and 12 hours after indomethacin or vehicle treatment[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 863ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H4N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 168.110 |
| Flash Point | 475.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 168.028336 |
| PSA | 114.37000 |
| LogP | -1.08 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.721 |
| InChIKey | LEHOTFFKMJEONL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1[nH]c(=O)c2[nH]c(=O)[nH]c2[nH]1 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with acids, bases, oxidising agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Graphene modified glassy carbon sensor for the determination of aspirin metabolites in human biological samples.
Talanta 143 , 328-34, (2015) A graphene modified glassy carbon (GR/GCE) sensor has been developed for the determination of aspirin metabolites 2,3- and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acids (2,3- and 2,5-DHB). The modified sensor was charac... |
|
|
Hepatorenal protective effect of Antistax(®) against chemically-induced toxicity.
Pharmacogn. Mag. 11 , S173-81, (2015) Antioxidant natural products and chemoprevention are considered nowadays as an effective approach against health various disorders and diseases induced by oxidative stress or free radicals.The aim of ... |
|
|
Facile and controllable one-step fabrication of molecularly imprinted polymer membrane by magnetic field directed self-assembly for electrochemical sensing of glutathione.
Anal. Chim. Acta 886 , 37-47, (2015) Based on magnetic field directed self-assembly (MDSA) of the ternary Fe3O4@PANI/rGO nanocomposites, a facile and controllable molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor (MIES) was fabricated through... |
| 2,6,8-trioxypurine |
| [14C]-Uric acid |
| 2,6,8-trioxopurine |
| EINECS 200-720-7 |
| 7,9-Dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione |
| 1H-Purine-2,6,8-triol |
| urate |
| [3H]-Uric acid |
| 2,6,8-trihydroxypurine |
| Uric Acid |
| Uric acid (8CI) |
| MFCD00005712 |
| 1H-Purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione, 7,9-dihydro- (9CI) |
| 1H-Purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione,7,9-dihydro |
| Lithic acid |
| 7,9-dihydro-3H-purine-2,6,8-trione |
 CAS#:68-94-0
CAS#:68-94-0 CAS#:69-89-6
CAS#:69-89-6 CAS#:57-13-6
CAS#:57-13-6 CAS#:72553-23-2
CAS#:72553-23-2 CAS#:3240-72-0
CAS#:3240-72-0 CAS#:73-24-5
CAS#:73-24-5 CAS#:73-40-5
CAS#:73-40-5 CAS#:80156-61-2
CAS#:80156-61-2 CAS#:58-61-7
CAS#:58-61-7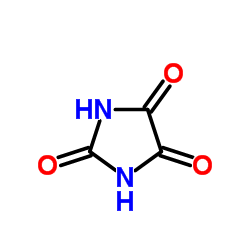 CAS#:120-89-8
CAS#:120-89-8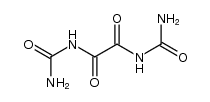 CAS#:5676-27-7
CAS#:5676-27-7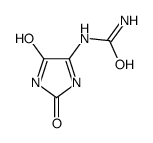 CAS#:105245-87-2
CAS#:105245-87-2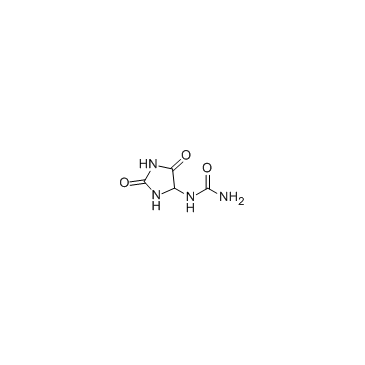 CAS#:97-59-6
CAS#:97-59-6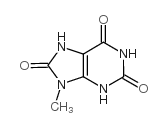 CAS#:55441-71-9
CAS#:55441-71-9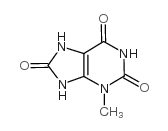 CAS#:605-99-2
CAS#:605-99-2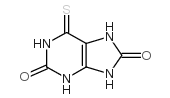 CAS#:2002-60-0
CAS#:2002-60-0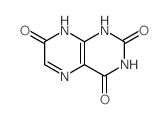 CAS#:2577-38-0
CAS#:2577-38-0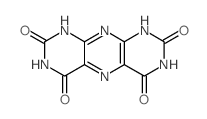 CAS#:5807-13-6
CAS#:5807-13-6 CAS#:27038-96-6
CAS#:27038-96-6
