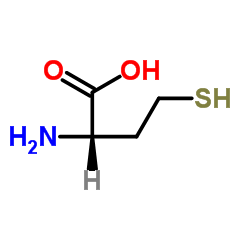
L-Homocystine

L-Homocystine structure
|
Common Name | L-Homocystine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 626-72-2 | Molecular Weight | 268.354 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 507.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16N2O4S2 | Melting Point | 281-284ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 260.8±30.1 °C | |
Use of L-HomocystineL-Homocystine is the oxidized member of the L-homocysteine. Homocysteine is a pro-thrombotic factor, vasodilation impairing agent, pro-inflammatory factor and endoplasmatic reticulum-stress inducer used to study cardiovascular disease mechanisms. |
| Name | L-Homocystine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Homocystine is the oxidized member of the L-homocysteine. Homocysteine is a pro-thrombotic factor, vasodilation impairing agent, pro-inflammatory factor and endoplasmatic reticulum-stress inducer used to study cardiovascular disease mechanisms. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | A single or multiple doses of L-Homocystine administered to mice during organogenesis can aggravate the developmental disturbances caused by a single dose of VPA administered on GD 8. Whereas, VPA lowers significantly plasma FA and vitamin B12 concentrations, it has no direct impact on the homocysteine concentrations. Therefore, it is proposed that high levels of homocysteine disturb the FA, vitamin B12, and possibly methionine metabolism thus providing a favorable situation for VPA to interfere with the development of susceptible embryos[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Groups of mice are first injected on GD 8 with a single dose of 75 mg/kg of L-Homocystine or an equal volume of saline. One half of the L-Homocystine-treated animals then receive a single dose of 600 mg/kg of VPA ((H-HoCys-OH)2+VPA group), while the other half are injected with a proportionate volume of saline (L-Homocystine+saline group). In the other experiment, mice are treated with a daily dose of 75 mg/kg of L-Homocystine or a proportionate volume of saline starting from GD 5 and continue through GD 10. One half of the L-Homocystine-treated animals also have a single exposure to 600 mg/kg of VPA (L-Homocystine+VPA group) or a proportionate volume of saline (L-Homocystine+saline group) on GD 8. The total volume of fluid injected corresponded to the body weight and does not exceed 0.45 mL[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 507.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 281-284ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16N2O4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 268.354 |
| Flash Point | 260.8±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 268.055145 |
| PSA | 177.24000 |
| LogP | 1.03 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.619 |
| InChIKey | ZTVZLYBCZNMWCF-WDSKDSINSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(CCSSCCC(N)C(=O)O)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~94% 
L-Homocystine CAS#:626-72-2 |
| Literature: Miyazaki, Hideya; Ohta, Atsushi; Kawakatsu, Nobuyuki; Waki, Yukitaka; Gogun, Yasuhiro; et al. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 1993 , vol. 66, # 2 p. 536 - 540 |
|
~% 
L-Homocystine CAS#:626-72-2 |
| Literature: Biochemical Preparations, , vol. 5, p. 96 Journal of Biological Chemistry, , vol. 109, p. 97,101 |
|
~% 
L-Homocystine CAS#:626-72-2 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 57, # 1 p. 123 - 127 |
|
~% 
L-Homocystine CAS#:626-72-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2: Physical Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), , # 4 p. 741 - 746 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Development of High-purity Certified Reference Materials for 17 Proteinogenic Amino Acids by Traceable Titration Methods.
Anal. Sci. 31 , 805-14, (2015) To ensure the reliability of amino acid analyses, the National Metrology Institute of Japan of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (NMIJ/AIST) has developed high-purit... |
|
|
Homocysteine Triggers Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages through Inhibiting CSE-H2S Signaling via DNA Hypermethylation of CSE Promoter.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 , 12560-77, (2015) Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) is an independent risk factor of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. Unfortunately, Hcy-lowering strategies were found to have limited effects in reducing ca... |
|
|
The species- and site-specific acid–base properties of biological thiols and their homodisulfides
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 95 , 184-92, (2014) Cysteamine, cysteine, homocysteine, their homodisulfides and 9 related compounds were studied by ¹H NMR-pH titrations and case-tailored evaluation methods. The resulting acid-base properties are quant... |
| L-Homocystine |
| Dl-Homocycine |
| (2S,2'S)-4,4'-Dithiobis(2-aminobutanoic acid) |
| dl-homocystine crystalline |
| HOMOCYSTINE,DL |
| Butanoic acid, 4,4'-dithiobis[2-amino-, (2S,2'S)- |
| QVYZ2SS2YZVQ &&L-L Form |
| (2S,2'S)-4,4'-Disulfanediylbis(2-aminobutanoic acid) |
| EINECS 210-962-5 |
| H-DL-Hcys-OH)2 |
| homocystine |
| (2S,2'S)-4,4'-Dithiobis(2-aminobutyric acid) |
| MFCD00020391 |
| DL-Homocystine |
| H-HoCys-OH |
| (H-HoCys-OH)2 |

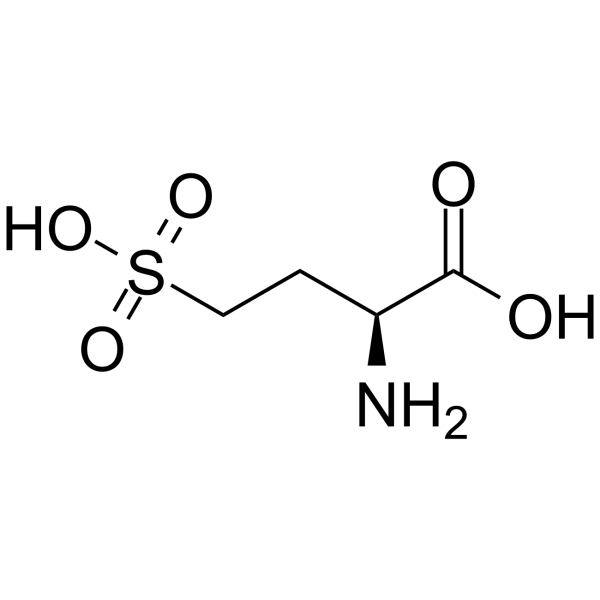 CAS#:14857-77-3
CAS#:14857-77-3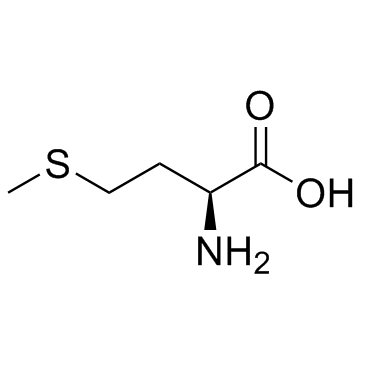 CAS#:63-68-3
CAS#:63-68-3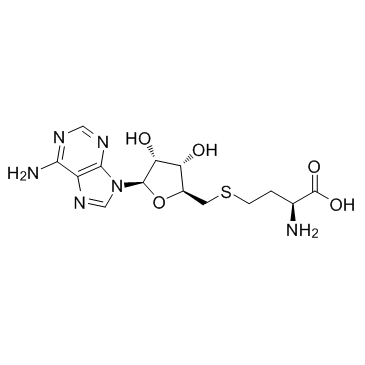 CAS#:979-92-0
CAS#:979-92-0 CAS#:13073-35-3
CAS#:13073-35-3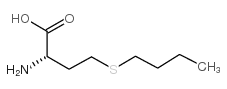 CAS#:13073-21-7
CAS#:13073-21-7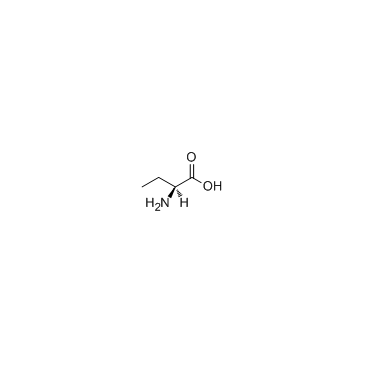 CAS#:1492-24-6
CAS#:1492-24-6 CAS#:73488-65-0
CAS#:73488-65-0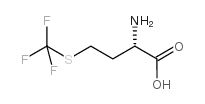 CAS#:764-52-3
CAS#:764-52-3
